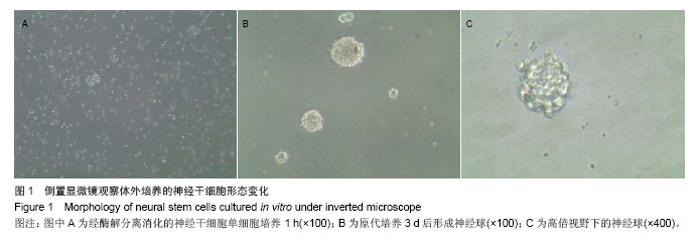
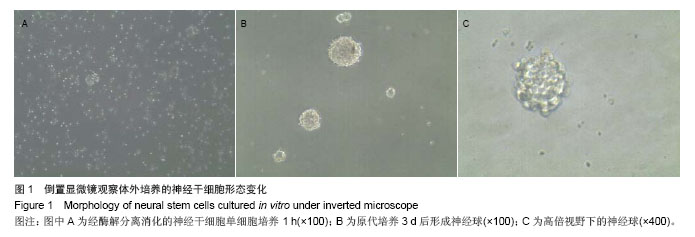
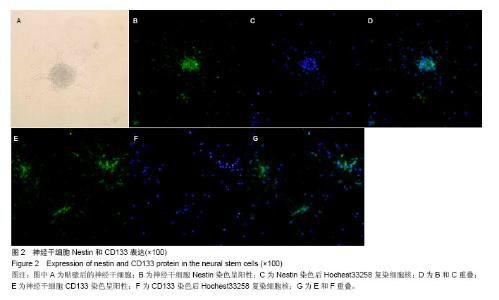
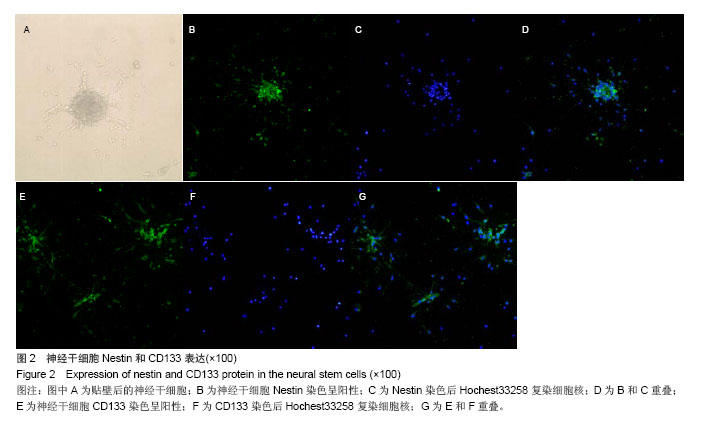
| [1]Walker MR, Patel KK, Stappenbeck TS.The stem cell niche.J Pathol. 2009;217(2):169-180.
[2]Martino G, Pluchino S, Bonfanti L,et al.Brain regeneration in physiology and pathology: the immune signature driving therapeutic plasticity of neural stem cells.Physiol Rev. 2011; 91(4):1281-1304.
[3]Kanno H.Regenerative therapy for neuronal diseases with transplantation of somatic stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2013;5(4):163-171.
[4]Ahmed S.The culture of neural stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(1):1-6.
[5]Sun D.The potential of endogenous neurogenesis for brain repair and regeneration following traumatic brain injury.Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(7):688-692.
[6]Mine Y, Tatarishvili J, Oki K,et al.Grafted human neural stem cells enhance several steps of endogenous neurogenesis and improve behavioral recovery after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.Neurobiol Dis. 2013;52:191-203.
[7]Luo Y, Zou Y, Yang L,et al.Transplantation of NSCs with OECs alleviates neuropathic pain associated with NGF downregulation in rats following spinal cord injury.Neurosci Lett. 2013;549:103-108.
[8]Sakata H, Narasimhan P, Niizuma K,et al.Interleukin 6-preconditioned neural stem cells reduce ischaemic injury in stroke mice.Brain. 2012;135(Pt 11):3298-3310.
[9]Jensen MB, Yan H, Krishnaney-Davison R,et al.Survival and differentiation of transplanted neural stem cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells in a rat stroke model.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(4):304-308.
[10]Karussis D, Petrou P, Kassis I.Clinical experience with stem cells and other cell therapies in neurological diseases.J Neurol Sci. 2013;324(1-2):1-9.
[11]Hao L, Zou Z, Tian H,et al.Stem cell-based therapies for ischemic stroke.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:468748.
[12]van Strien ME, Sluijs JA, Reynolds BA,et al.Isolation of neural progenitor cells from the human adult subventricular zone based on expression of the cell surface marker CD271.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(4):470-480.
[13]Brüstle O, Spiro AC, Karram K,et al.In vitro-generated neural precursors participate in mammalian brain development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(26):14809-14814.
[14]Reynolds BA, Weiss S.Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system.Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710.
[15]Estrada-Mondaca S, Carreón-Rodríguez A, Belkind-Gerson J.Biology of the adult enteric neural stem cell.Dev Dyn. 2007; 236(1):20-32.
[16]Sabo PJ, Kuehn MS, Thurman R,et al.Genome-scale mapping of DNase I sensitivity in vivo using tiling DNA microarrays.Nat Methods. 2006;3(7):511-518.
[17]Ramasamy S, Narayanan G, Sankaran S,et al.Neural stem cell survival factors.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013;534(1-2): 71-87.
[18]Drago D, Cossetti C, Iraci N,et al. The stem cell secretome and its role in brain repair.Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2271-2285.
[19]Pluchino S, Cossetti C.How stem cells speak with host immune cells in inflammatory brain diseases.Glia. 2013;61(9): 1379-1401.
[20]Baraniak PR, McDevitt TC.Stem cell paracrine actions and tissue regeneration.Regen Med. 2010;5(1):121-143.
[21]Ihrie RA, Alvarez-Buylla A.Lake-front property: a unique germinal niche by the lateral ventricles of the adult brain. Neuron. 2011;70(4):674-686.
[22]Huang F,Shen Q,Zhao JT Growth and differentiation of neural stem cells in a three-dimensional collagen gel scaffold. Neural Regen Rese. 2013; 8(4): 313-319.
[23]Zhou JH, Sui FG, Yao M, et al. Novel nanometer scaffolds regulate the biological behaviors of neural stem cells. Neural Regen Res.2013;8(16): 1455-1464.
[24]Hulspas R, Tiarks C, Reilly J,et al.In vitro cell density-dependent clonal growth of EGF-responsive murine neural progenitor cells under serum-free conditions.Exp Neurol. 1997;148(1):147-156.
[25]Marzesco AM, Janich P, Wilsch-Bräuninger M,et al.Release of extracellular membrane particles carrying the stem cell marker prominin-1 (CD133) from neural progenitors and other epithelial cells.J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 13):2849-2858.
[26]Florek M, Haase M, Marzesco AM,et al.Prominin-1/CD133, a neural and hematopoietic stem cell marker, is expressed in adult human differentiated cells and certain types of kidney cancer.Cell Tissue Res. 2005;319(1):15-26. |