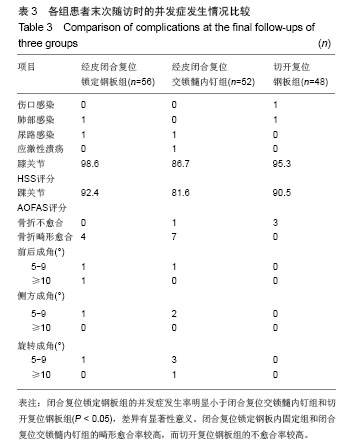
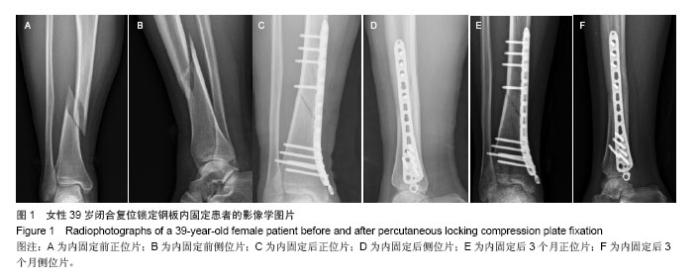
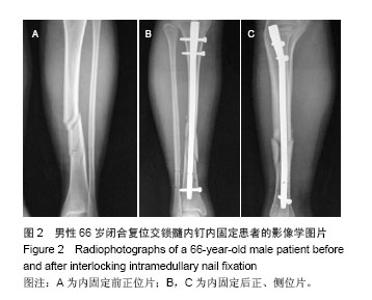
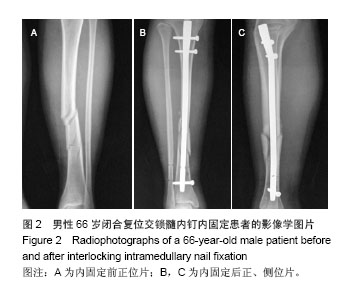
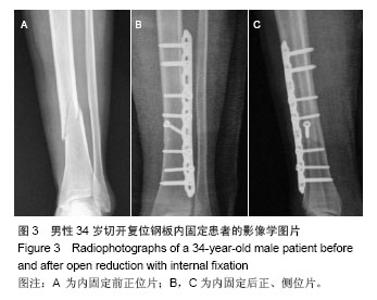
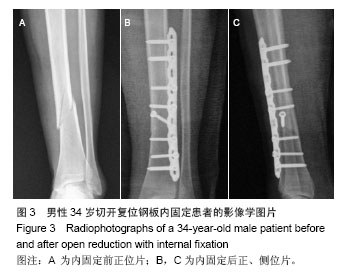
| [1]Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, et al. Treatment of distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(1):76-79.
[2]Adam P, Bonnomet F, Ehlinger M. Advantage and limitations of a minimally-invasive approach and early weight bearing in the treatment of tibial shaft fractures with locking plates. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(5):564-569.
[3]Gupta RK, Rohilla RK, Sangwan K, et al. Locking plate fixation in distal metaphyseal tibial fractures: series of 79 patients. Int Orthop. 2010;34(8):1285-1290.
[4]Nawaf CB, Kelly DM, Warner WC Jr, et al. Fat embolism syndrome in an adolescent before surgical treatment of an isolated closed tibial shaft fracture. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2012;41(12):565-568.
[5]Yaligod V, Rudrappa GH, Nagendra S, et al. Minimizing the complications of intramedullary nailing for distal third tibial shaft and metaphyseal fractures. J Orthop. 2013;11(1):10-18.
[6]Li Y, Jiang X, Guo Q, et al. Treatment of distal tibial shaft fractures by three different surgical methods: a randomized, prospective study. Int Orthop. 2014;38(6):1261-1267.
[7]Ghafil D, Ackerman P, Baillon R, et al. Expandable intramedullary nails for fixation of tibial shaft fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2012;78(6):779-785.
[8]Ghazavi MT, Pritzker KP, Davis AM, et al. Fresh osteochondral allografts for post-traumatic osteochondral defects of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(6):1008-1013.
[9]Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, et al. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 1994;15(7):349-353.
[10]Gupta RK, Rohilla RK, Sangwan K, et al. Locking plate fixation in distal metaphyseal tibial fractures: series of 79 patients. Int Orthop. 2010;34(8):1285-1290.
[11]Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. et al. Randomized, prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25(12):736-741.
[12]Weresh MJ, Hakanson R, Stover MD, et al. Failure of exchange reamed intramedullary nails for ununited femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14(5):335-338.
[13]Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. et al. Factors influencing functional outcomes after distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(3):178-183.
[14]Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, et al. Treatment of distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(1):76-79.
[15]Hoegel FW, Hoffmann S, Weninger P, et al. Biomechanical comparison of locked plate osteosynthesis, reamed and unreamed nailing in conventional interlocking technique, and unreamed angle stable nailing in distal tibia fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(4):933-938.
[16]Horn J, Linke B, Höntzsch D, et al. Angle stable interlocking screws improve construct stability of intramedullary nailing of distal tibia fractures: a biomechanical study. Injury. 2009;40(7): 767-771.
[17]Kuhn S, Appelmann P, Pairon P, et al. The Retrograde Tibial Nail: presentation and biomechanical evaluation of a new concept in the treatment of distal tibia fractures. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 1:S81-86
[18]杨宗宇,刘非,刘国强,等.阻挡钉加强交锁髓内钉与锁定钢板在治疗胫骨远端骨折中的对比研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 20(6): 566-567.
[19]田文,王富明,黄俭,等.髓内钉、锁定加压钢板内固定术治疗胫骨下段骨折疗效比较[J].山东医药,2013,53(31):53-56.
[20]Bagheri F, Sharifi SR, Mirzadeh NR, et al. Clinical outcome of ream versus unream intramedullary nailing for femoral shaft fractures. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013;15(5):432-435.
[21]Ozdemir B, Akesen B, Demira? B, et al. Long-term outcome of unreamed intramedullary nails in femur diaphyseal fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2012;18(2):147-152.
[22]Duan X, Li T, Mohammed AQ, et al. Reamed intramedullary nailing versus unreamed intramedullary nailing for shaft fracture of femur: a systematic literature review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(10):1445-1452.
[23]王磊,陈根元,王凤凤,等.扩髓与非扩髓髓内钉置入固定治疗成人闭合性胫骨干骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(17): 3130-3133.
[24]朱龙章,薛锋,韩本松,等.髓内针置入内固定胫骨骨折后膝关节功能比较及组织学评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(43):8079-8082.
[25]王亦璁. BO与AO的不同之处[J].骨与关节损伤杂志, 2002,17(1): 3-5. |