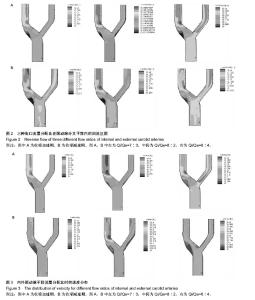
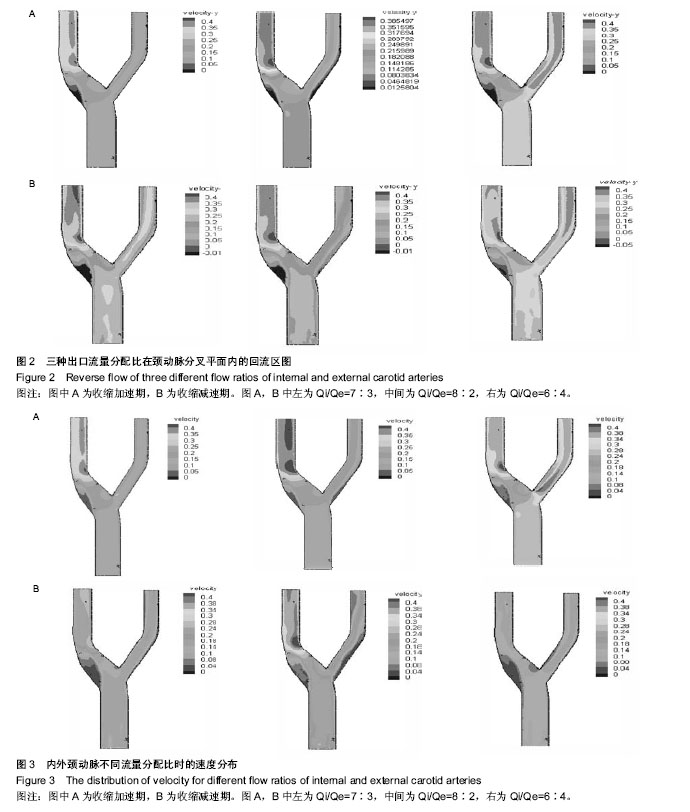
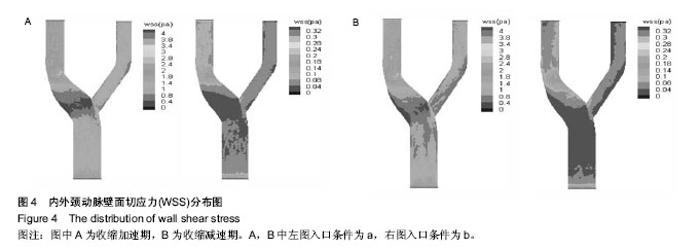
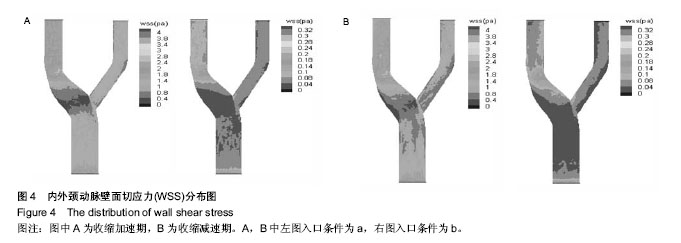
| [1] Razavi A, Shirani E, Sadeghi MR.Numerical simulation of blood pulsatile flow in a stenosed carotid artery using different rheological models.J Biomech. 2011;44(11):2021-2030.
[2] Pasternak RC, Criqui MH, Benjamin EJ, et al.Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Conference: Writing Group I: epidemiology.Circulation. 2004;109(21):2605-2612.
[3] Taxon M. Hemodynamic Basis of Atherosclerosis with Critique of the Cholesterol-Heart Disease Hypothesis.Begell House, Wallingford, U.K., 1995.
[4] Ku DN, Giddens DP, Zarins CK,et al.Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress.Arteriosclerosis. 1985;5(3):293-302.
[5] Davies PF.Hemodynamic shear stress and the endothelium in cardiovascular pathophysiology.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2009;6(1):16-26.
[6] Malek AM, Alper SL, Izumo S.Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis.JAMA. 1999;282(21):2035-2042.
[7] Morbiducci U, Gallo D, Massai D,et al.Outflow conditions for image-based hemodynamic models of the carotid bifurcation: implications for indicators of abnormal flow.J Biomech Eng. 2010;132(9):091005.
[8] Lee SW, Antiga L, Steinman DA.Correlations among indicators of disturbed flow at the normal carotid bifurcation.J Biomech Eng. 2009;131(6):061013.
[9] Fry DL.Certain histological and chemical responses of the vascular interface to acutely induced mechanical stress in the aorta of the dog.Circ Res. 1969;24(1):93-108.
[10] 丁祖荣,王克强.人颈动脉分叉的TF-AHCB模型[J].上海交通大学学报,2002,36(1):87-90.
[11] Piskin S, Serdar Celebi M.Analysis of the effects of different pulsatile inlet profiles on the hemodynamical properties of blood flow in patient specific carotid artery with stenosis. Comput Biol Med. 2013;43(6):717-728.
[12] 王青,王炜哲,万大伟,等.三例人体颈动脉分叉管血液动力学的数值对比分析[J].水动力学研究与进展, 2009,24(3):313-319
[13] Bharadvaj BK, Mabon RF, Giddens DP.Steady flow in a model of the human carotid bifurcation. Part I--flow visualization.J Biomech. 1982;15(5):349-362.
[14] Caro CG.The mechanics of the circulation. Oxford:Oxford University Press,1978.
[15] 王鸿儒,文宗耀.血液循环力学[M].北京:北京医科大学、中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1990.
[16] Papaharilaou Y, Aristokleous N, Seimenis I,et al.Effect of head posture on the healthy human carotid bifurcation hemodynamics.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2013;51(1-2):207-218.
[17] Fry DL.Acute vascular endothelial changes associated with increased blood velocity gradients.Circ Res. 1968;22(2): 165-197.
[18] 邓小燕.动脉狭窄内低密度脂蛋白传输的数值研究:LDL的浓度极化现象[J].计算力学学报,2002,19(3):253. |