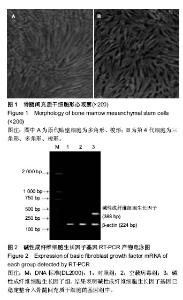
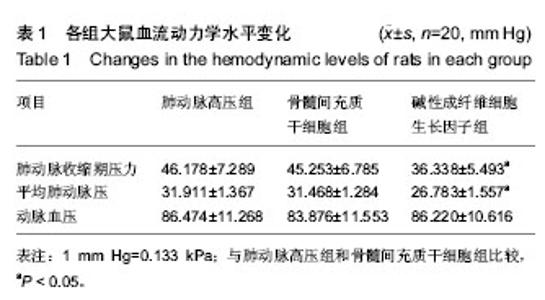
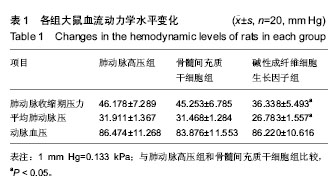
| [1] 何志旭,汪浩文,尚峰,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗实验性肺动脉高压后肺组织结构的变化[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(10): 1907-1911.
[2] 曲素萍,牛丽丽.经气管注射骨髓间充质干细胞治疗早期血管炎性作用所致肺动脉高压的实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2012, 47(10):1169-1173.
[3] 赵科研,王辉山,侯明晓,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植肺动脉高压大鼠内皮素-1的变化[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(8):1460- 1462.
[4] 赵科研,王辉山,侯明晓,等.不同数目骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肺动脉高压的作用及内皮素-1表达的影响[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2012,19(3):298-303.
[5] 卢艳,孔令彩,张兆华,等.移植骨髓间充质干细胞预防野百合碱诱导的肺动脉高压[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(36):6468- 6473.
[6] 赵科研,王辉山,侯明晓,等.不同数目骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肺损伤的抑制作用[J].中国比较医学杂志,2012,22(1):34-38.
[7] 胡建明,高占成.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗肺动脉高压的研究进展[J].国际呼吸杂志,2013,33(5):385-388.
[8] 张春曦,黄达德,陈敏东,等.间充质干细胞联合辛伐他汀对动力性肺动脉高压的影响[J].广州医药,2012,43(6):1-3.
[9] 张洪连,吴晓牧.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死及存在问题[J].中华脑血管病杂志:电子版,2010,4(4):300-307.
[10] 郭亮,麦晓燕,申晶,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植后在脑梗死大鼠脑内的存活与分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(34):6661-6664.
[11] 孙晓娟,杨乃龙.成人与胎儿骨髓间充质干细胞生物学性状的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(14):2701-2704.
[12] 夏文杰,许茹,叶欣,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外扩增的生物评估[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2008,16(3):639-644.
[13] 谢茂松,徐国兴,李琼,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养方法的比较[J].国际眼科杂志,2007,7(5):1285-1287.
[14] 郑健樑,杨玉霞,张平,等.成年大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外培养及生物学特性[J].国际眼科杂志,2006,6(3):562-564.
[15] Lisignoli G, Remiddi G, Cattini L,et al.An elevated number of differentiated osteoblast colonies can be obtained from rat bone marrow stromal cells using a gradient isolation procedure. Connect Tissue Res. 2001;42(1):49-58.
[16] Colter DC, Class R, DiGirolamo CM,et al.Rapid expansion of recycling stem cells in cultures of plastic-adherent cells from human bone marrow.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(7): 3213-3218.
[17] Dexter TM, Allen TD, Lajtha LG.Conditions controlling the proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro.J Cell Physiol. 1977;91(3):335-344.
[18] Zohar R, Sodek J, McCulloch CA.Characterization of stromal progenitor cells enriched by flow cytometry.Blood. 1997;90(9): 3471-3481.
[19] Encina NR, Billotte WG, Hofmann MC.Immunomagnetic isolation of osteoprogenitors from human bone marrow stroma. Lab Invest. 1999;79(4):449-457.
[20] Prockop DJ.Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues.Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74.
[21] Barry F, Boynton R, Murphy M,et al.The SH-3 and SH-4 antibodies recognize distinct epitopes on CD73 from human mesenchymal stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289(2):519-524.
[22] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[23] Dvorakova J, Hruba A, Velebny V,et al.Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cell population entrapped in bone marrow collection sets.Cell Biol Int. 2008; 32(9):1116-1125.
[24] Bruder SP, Ricalton NS, Boynton RE,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell surface antigen SB-10 corresponds to activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule and is involved in osteogenic differentiation.J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(4):655-663.
[25] Conget PA, Minguell JJ.Phenotypical and functional properties of human bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells.J Cell Physiol. 1999;181(1):67-73.
[26] Peister A, Mellad JA, Larson BL,et al.Adult stem cells from bone marrow (MSCs) isolated from different strains of inbred mice vary in surface epitopes, rates of proliferation, and differentiation potential.Blood. 2004;103(5):1662-1668.
[27] Gronthos S, Simmons PJ, Graves SE,et al.Integrin-mediated interactions between human bone marrow stromal precursor cells and the extracellular matrix.Bone. 2001;28(2):174-181.
[28] Glennie S, Soeiro I, Dyson PJ,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells.Blood. 2005;105(7):2821-2827.
[29] Barbash IM, Chouraqui P, Baron J,et al.Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration, and body distribution.Circulation. 2003;108(7):863-868.
[30] Terai S, Sakaida I, Yamamoto N,et al.An in vivo model for monitoring trans-differentiation of bone marrow cells into functional hepatocytes.J Biochem. 2003;134(4):551-558.
[31] Wu GD, Nolta JA, Jin YS,et al.Migration of mesenchymal stem cells to heart allografts during chronic rejection. Transplantation. 2003;75(5):679-685.
[32] Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729.
[33] Wang XX, Zhang FR, Shang YP,et al.Transplantation of autologous endothelial progenitor cells may be beneficial in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: a pilot randomized controlled trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 49(14):1566-1571.
[34] Baber SR, Deng W, Master RG,et al.Intratracheal mesenchymal stem cell administration attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension and endothelial dysfunction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(2):H1120-1128.
[35] Raoul W, Wagner-Ballon O, Saber G,et al.Effects of bone marrow-derived cells on monocrotaline- and hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice.Respir Res. 2007;8:8.
[36] Wang JL,Sun JF,Tang YX,et al.Basic fibroblast growth factor attenuates the degeneration of injured spinal cord motor endplates.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(24): 2213-2224.
[37] Breitbach M, Bostani T, Roell W,et al.Potential risks of bone marrow cell transplantation into infarcted hearts.Blood. 2007; 110(4):1362-1369.
[38] Collino F, Deregibus MC, Bruno S,et al.Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11803.
[39] He J, Wang Y, Sun S,et al.Bone marrow stem cells-derived microvesicles protect against renal injury in the mouse remnant kidney model.Nephrology (Carlton). 2012;17(5): 493-500.
[40] 陈建英,徐军发,杨宇,等.辛伐他汀对野百合碱诱导的肺动脉高压大鼠IL-6和IL-8表达的影响[J].中南药学,2009,7(7):506-510.
[41] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M,et al.Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli.Blood. 2002;99(10):3838-3843. |