Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (32): 5120-5125.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.32.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interferon-gamma enhances immunosuppression mediated by adipose-derived stem cells
Yiliyaer Yilihamu1, Wang Yun-hai1, Wang Li1, Xu Xin-cai1, Aimulaguli Abula2, Zhang Wen-bin1
- 1Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2School of Life Science, Xinjiang Normal University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2014-07-09Online:2014-08-06Published:2014-09-18 -
Contact:Zhang Wen-bin, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yiliyaer Yilihamu, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Tissue Engineering Special Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, No. 201022GC02; the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2014211C036; the National Key Clinical Specialty: the Project of General Surgery
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yiliyaer Yilihamu, Wang Yun-hai, Wang Li, Xu Xin-cai, Aimulaguli Abula, Zhang Wen-bin. Interferon-gamma enhances immunosuppression mediated by adipose-derived stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(32): 5120-5125.
share this article

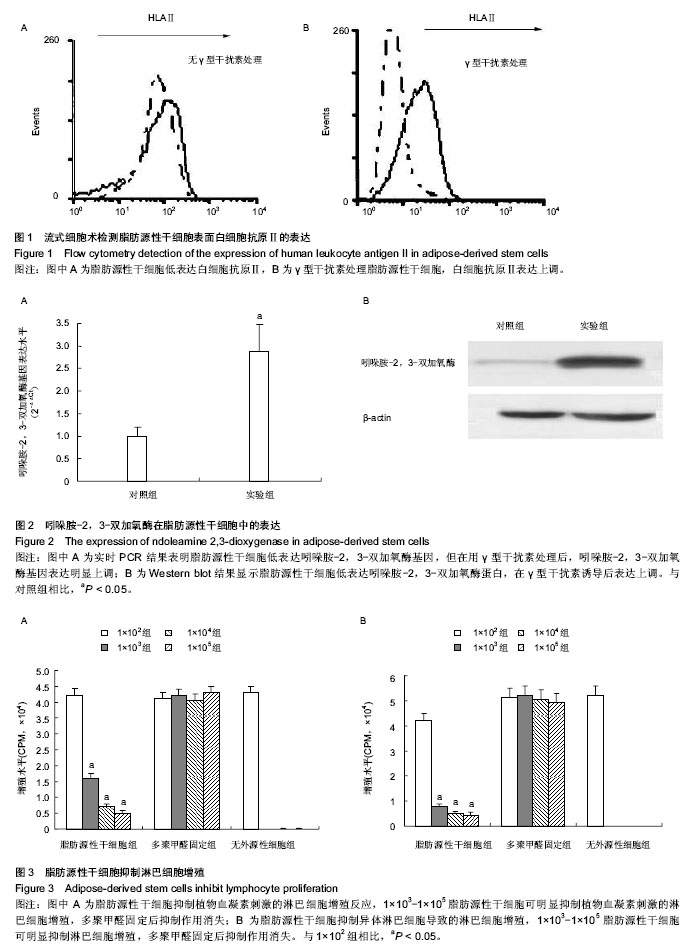
2.1 脂肪源性干细胞表面白细胞抗原Ⅱ的表达 流式细胞仪检测结果显示白细胞抗原Ⅱ在脂肪源性干细胞表面阳性表达较弱,但在γ型干扰素刺激48 h后,白细胞抗原Ⅱ类分子表达明显上调(图1),说明脂肪干细胞免疫原性低,经γ型干扰素诱导后,白细胞抗原Ⅱ表达增强,免疫抑制能力可能增强。 2.2 经γ型干扰素诱导后脂肪源性干细胞中吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶表达 研究表明人间充质干细胞的免疫抑制作用是通过吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶介导的[4],因此,为观察脂肪源性干细胞是否也通过吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶介导免疫抑制作用,将脂肪源性干细胞用γ型干扰素处理后,实时PCR及Western blot法分别检测其吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶基因和蛋白的表达。 实时PCR结果显示,脂肪源性干细胞低表达吲哚 胺-2,3-双加氧酶基因,但在用γ型干扰素处理后,吲哚 胺-2,3-双加氧酶基因表达明显上调,是未处理时的(2.86±0.32)倍(图2 A)。 Western blot结果显示脂肪源性干细胞低表达吲哚 胺-2,3-双加氧酶蛋白,同时在γ型干扰素诱导后吲哚 胺-2,3-双加氧酶蛋白表达增加(图2 B)。 2.3 脂肪源性干细胞单向刺激淋巴细胞增殖反应 根据测量的CPM值,可见未经处理的脂肪源性干细胞并不能刺激淋巴细胞增殖(1 652±189) CPM;同样,当脂肪源性干细胞经γ型干扰素处理后,淋巴细胞也未见明显增殖(1 735±201) CPM,两者差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),说明无论脂肪源性干细胞是否高表达白细胞抗原Ⅱ,脂肪源性干细胞均不会刺激异体淋巴细胞增殖,间接证明脂肪源性干细胞具有低免疫原性。 但在对照组中,加入异体淋巴细胞,淋巴细胞有明显增殖(52 886±3 862)CPM,与经干扰素处理的细胞的差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.4 脂肪源性干细胞对非特异性淋巴细胞反应的作用 当淋巴细胞用植物血凝素刺激后,会出现明显增殖,加入脂肪源性干细胞后,除1×102组脂肪源性干细胞外,其余浓度的细胞均可以明显抑制淋巴细胞的增殖(P < 0.05);但当脂肪干细胞用多聚甲醛固定失活后,所有浓度的抑制作用均消失(图3A)。 2.5 脂肪源性干细胞对混合淋巴细胞反应的作用 为了观察脂肪源性干细胞能否抑制异体淋巴细胞刺激导致的淋巴细胞增殖,在双向混合淋巴细胞培养中加入脂肪源性干细胞,作为第三者细胞。 共培养7 d后可见,除1×102组外,1×103-1×105数量级的脂肪源性干细胞均使淋巴细胞的增殖得到明显抑制。脂肪源性干细胞以多聚甲醛作用失活后,所有浓度的抑制作用均消失(图3B)。 流式细胞术检测到具有活性脂肪源性干细胞组的上清液中有大量γ型干扰素(21.354±1.78) μg/L,而失活脂肪源性干细胞组的上清液中γ型干扰素含量较少,几乎检测不到,证明脂肪源性干细胞在抑制淋巴细胞增殖过程中,会释放大量的γ型干扰素,从而促使吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶表达,发挥免疫抑制作用。"
| [1] Nauta AJ, Fibbe WE. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood. 2007;110(10):3499-3506. [2] Ong WK, Sugii S. Adipose-derived stem cells: fatty potentials for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(6):1083-1086. [3] Zhou Z, Zhang M, Lu MJ. Application of adipose-derived stem cells in lower urinary tract reconstruction. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2013;19(4):365-369. [4] Yagi H, Kitagawa Y. The role of mesenchymal stem cells in cancer development. Front Genet. 2013;4:261. [5] Zhao S, Wehner R, Bornhäuser M, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells and their therapeutic consequences for immune-mediated disorders. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(5):607-614. [6] García-Castro J, Trigueros C, Madrenas J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and their use as cell replacement therapy and disease modelling tool. J Cell Mol Med. 2008; 12(6B):2552-2565. [7] Reiser J, Zhang XY, Hemenway CS, et al. Potential of mesenchymal stem cells in gene therapy approaches for inherited and acquired diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005; 5(12):1571-1584. [8] Mishra PK. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of heart failure: is it all paracrine actions and immunomodulation? J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2008; 9(2):122-128. [9] Wei YJ, Lin YJ. Recent research advance in immunomodulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells on immune cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2010;18(4):1079-1083. [10] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295. [11] Sun S, Chen G, Xu M, et al. Differentiation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplanted through the spleen in rats with portal hypertension. PLoS One. 2013; 8(12):e83523. [12] Yang YM, Li H, Zhang L, et al. A new method for isolating and culturing mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013;21(6):1563-1567 [13] Yang P, Yin S, Cui L, et al. Experiment of adipose derived stem cells induced into smooth muscle cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008;22(4):481-486. [14] Choi YS, Matsuda K, Dusting GJ, et al. Engineering cardiac tissue in vivo from human adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(8):2236-2242. [15] Fujimura J, Ogawa R, Mizuno H, et al. Neural differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells isolated from GFP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;333(1):116-121. [16] Yagi K, Kojima M, Oyagi S, et al. Application of mesenchymal stem cells to liver regenerative medicine. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008;128(1):3-9. [17] Hellstrand P, Albinsson S. Stretch-dependent growth and differentiation in vascular smooth muscle: role of the actin cytoskeleton. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2005;83(10): 869-875. [18] Yang G, Zhang MZ, Jiang W. Progress of study on inhibitory effects of traditional Chinese herbs on growth factor induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2005;25(10):951-954. [19] Petschnik AE, Fell B, Kruse C, et al. The role of alpha-smooth muscle actin in myogenic differentiation of human glandular stem cells and their potential for smooth muscle cell replacement therapies. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(6): 853-861. [20] Kokai LE, Rubin JP, Marra KG. The potential of adipose-derived adult stem cells as a source of neuronal progenitor cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116(5): 1453-1460. [21] Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(2):141-150. [22] Ren G, Su J, Zhang L, et al. Species variation in the mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression. Stem Cells. 2009;27(8):1954-1962. [23] 戴向晨,刘彤,张树建,等.吲哚胺2,3双加氧酶对小鼠CD4+T细胞增殖的抑制作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(9):1434-1437. [24] 王建军,樊艳,马爱群,等.人脂肪间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,(45):8430-8434. [25] Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol. 2002; 30(1):42-48. [26] Bingaman AW, Waitze SY, Alexander DZ, et al. Transplantation of the bone marrow microenvironment leads to hematopoietic chimerism without cytoreductive conditioning. Transplantation. 2000;69(12):2491-2496. [27] Leatherman J. Stem cells supporting other stem cells. Front Genet. 2013;4:257. [28] Kraushaar DC, Zhao K. The epigenomics of embryonic stem cell differentiation. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(10):1134-1144. [29] Biteau B, Hochmuth CE, Jasper H. Maintaining tissue homeostasis: dynamic control of somatic stem cell activity. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(5):402-411. [30] Mayani H. A glance into somatic stem cell biology: basic principles, new concepts, and clinical relevance. Arch Med Res. 2003;34(1):3-15. [31] Zanetti AS, Sabliov C, Gimble JM, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells and three-dimensional scaffold constructs: a review of the biomaterials and models currently used for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(1):187-199. [32] Kaewsuwan S, Song SY, Kim JH, et al. Mimicking the functional niche of adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(12): 1575-1588. [33] Mizuno H, Tobita M, Uysal AC. Concise review: Adipose-derived stem cells as a novel tool for future regenerative medicine. Stem Cells. 2012;30(5):804-810. [34] Markarian CF, Frey GZ, Silveira MD, et al. Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: a comparison among different methods. Biotechnol Lett. 2014;36(4):693-702. [35] Araña M, Mazo M, Aranda P, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, expansion, and characterization. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1036:47-61. [36] Navarro-Betancourt JR, Baldassarri-Ortego LF, Urquiza-Y-Conde F, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells expressing cardiac progenitor markers: the best source of mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular repair? Int J Cardiol. 2014;174(2):451-452. [37] 郭娟,范华骅,钱燕翔,等.干扰素-γ增强人脐带间充质干细胞免疫抑制作用的研究[J].诊断学理论与实践,2010,9(2):181-185. [38] 王建军,樊艳,马爱群,等.人脂肪间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(45):8430-8434. [39] Umemoto Y, Tsuji K, Yang FC, et al. Leptin stimulates the proliferation of murine myelocytic and primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1997 ;90(9):3438-3443. [40] Shimozato T, Kincade PW. Prostaglandin E(2) and stem cell factor can deliver opposing signals to B lymphocyte precursors. Cell Immunol. 1999;198(1):21-29. [41] Yokota T, Meka CS, Kouro T, et al. Adiponectin, a fat cell product, influences the earliest lymphocyte precursors in bone marrow cultures by activation of the cyclooxygenase- prostaglandin pathway in stromal cells. J Immunol. 2003;171 (10):5091-5099. |
| [1] | Xuan Juanjuan, Bai Hongtai, Zhang Jixiang, Wang Yaoquan, Chen Guoyong, Wei Sidong. Role of regulatory T cell subsets in liver transplantation and progress in clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1143-1148. |
| [2] | Yang Wei, Yuan Puwei, Du Longlong, Li Xuefeng, Gao Qimeng, Han Qingmin. Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profile of peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3706-3713. |
| [3] | Hu Mingzhi, Zhang Jingying, Yang Guoan, Pang Chunyan, Zhang Wei, Wang Yongfu, Sun Xiaolin. Immunomodulatory effects of umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-1-5p on T lymphocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4928-4938. |
| [4] | He Yixiang, Zhao Yuhao, Gao Zhao, Zhao Haiyan, Wang Wenji. Effect of B lymphocytes and related cytokines on osteoclast differentiation in the osteoimmunology system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4709-4714. |
| [5] | Mao Xin, Yu Limei, Wang Feng. Important role of mesenchymal stem cells in immune tolerance induction in heart transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2070-2078. |
| [6] | Feng Yang, Yan Xu, Wang Yongkui, Yang Tengyue, Shang Lijie, Zhang Chunlin. Relationship between degenerative lumbar disc disease and peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2630-2635. |
| [7] | Zhao Xiao1, Zhang Fengbo2, Wang Hongying1, Yan Fang3, An Mengting1, Li Yujiao1, Pang Nannan4, Ding Jianbing1. Dominant T cell and B cell epitopes in EgA31 protein of Echinococcus granulosus by bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1078-1083. |
| [8] | Xu Xiaoling, Pan Wangping, Lü Xiaojun, Zhang Ju, Hu Yuanhua, He Kaiyong. Immunotoxicity of absorbable silk fibroin biofilm on rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2190-2195. |
| [9] | Li Weiwei, Li Xiaofeng, Hou Ping, Li Jianping. CD4+T and Treg immunomodulatory functions after culture with the supernatant of human placenta mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 85-89. |
| [10] | Jiang Shanshan, Wang Feng, Yu Limei. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their application in organ transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 103-109. |
| [11] | Wang Jin, Niu Ben, Ma Xiao-rong, Zhang Wang-gang. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on CXC chemokine receptor 4 expression and chemotaxis in bone marrow microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5268-5273. |
| [12] | Li Yu-long, Huang Zhou-feng, Zhang Lei, Wu Cheng-ye, Cheng Wei, Dong Xiao-yan, Zhu Zun-min, Sun Kai. The characteristics and significance of non-clonal chromosome aberrations in the in vitro expanded NK cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5362-5367. |
| [13] | Niu Zi-han1, Ran Xin-jian2, Mawlan•Mamut1, Pan Chuan-peng1, He Dong-hang3, Ren Cong-gai3, Xu Qi4. Changes of microenvironment in a rat model of arthritis treated by the combination of methotrexate and diclofenac sodium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(32): 5163-5168. |
| [14] | Gong Yu-bo1, Liu Yong2, Zhao Hong-wei1, Xu Qian-qian1, Guo Hui-ling1 . Expression levels of Foxp3 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in mouse corneal allograft rejection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4513-4517. |
| [15] | Qu Yuan-qian, Zhou Qing, Zhang Jin, Xu San-rong. Inhibiting colorectal cancer liver metastasis by combined injection of allogeneic bone marrow cells and lymphocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(25): 4053-4058. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||