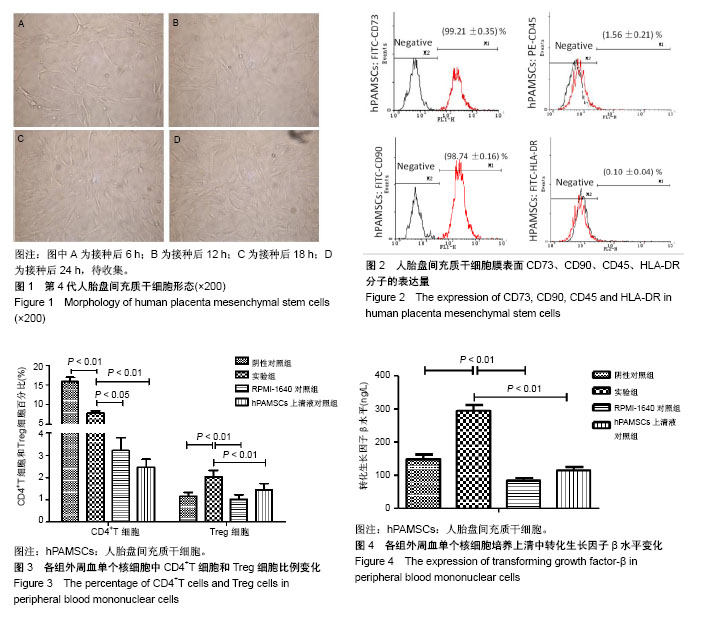
| [1] Fukuchi Y, Nakajima H, Sugiyama D, et al. Human placenta-derived cells have mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell potential. Stem Cells. 2004;22(5):649-658.[2] 陆琰,陈丽,张洹.人足月胎盘间充质干细胞的分离纯化及其特征[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2008,29(4):370-374.[3] 杨乃龙,张红艳,孙晓娟,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞的体外分离纯化及成骨能力的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(11):824-828.[4] 费倩怡,刘春丽,朱振威,等.人胎盘来源间充质干细胞和大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特征比较[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2013,39(3):467-471.[5] 邹旭凤,于润红,刘玉峰.胎盘间充质干细胞对骨髓、脐血、胎盘不同来源造血干细胞的体外扩增支持作用比较[J].中国实用医刊, 2009,36(19):32-33.[6] Prather WR, Toren A, Meiron M. Placental-derived and expanded mesenchymal stromal cells (PLX-I) to enhance the engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008;8(8): 1241-1250. [7] Zhang Y, Li C, Jiang X, et al. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells support culture expansion of long-term culture-initiating cells from cord blood CD34+ cells. Exp Hematol. 2004;32(7):657-664.[8] Chao YH, Wu HP, Wu KH, et al. An increase in CD3+CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells after administration of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells during sepsis. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e110338.[9] Johnson JL, Jones MB, Cobb BA. Polysaccharide- experienced effector T cells induce IL-10 in FoxP3+ regulatory T cells to prevent pulmonary inflammation. Glycobiology. 2018; 28(1):50-58.[10] Fehervari Z. Treg cell wiring. Nature Immunology. 2015;17(1): 47.[11] Shipman L. Tumour immunology: Interrogating intratumoral Treg cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(1):4-5.[12] Wang M, Liu C, Bond A, et al. Dysfunction of regulatory T cells in patients with ankylosing spondylitis is associated with a loss of Tim-3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;59:53-60.[13] Miao J, Zhu P. Functional Defects of Treg Cells: New Targets in Rheumatic Diseases, Including Ankylosing Spondylitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018;20(5):30. [14] Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(8): 569-579. [15] 赖平,陈懿建,罗耀玲,等.人胎盘源间充质干细胞的分离、培养及生物学鉴定[J].赣南医学院学报,2016,36(2):183-186.[16] 牛婷,李爱斌,曹景云,等.胎盘间充质干细胞的应用研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32):5236-5242.[17] Ventura Ferreira MS, Bienert M, Müller K, et al. Comprehensive characterization of chorionic villi-derived mesenchymal stromal cells from human placenta. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):28.[18] 朱少芳,何援利,卢国辉,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞生物学特性和抗凋亡细胞因子的分泌[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(6):1005-1008.[19] Fajardo-Orduña GR, Mayani H, Flores-Guzmán P, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood and Placenta Exhibit Similar Capacities to Promote Expansion of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:6061729.[20] Yuan YH, Wang Y, Ding Y, et al. The effect of cotransplantation of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in combination with human cord blood mononuclear cells on early hematopoietic reconstitution in SCID mice. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010; 26(11):1097-1100.[21] 邹旭凤,于润红,刘玉峰.胎盘间充质干细胞对骨髓、脐血、胎盘不同来源造血干细胞的体外扩增支持作用比较[J].中国实用医刊, 2009,36(19):32-33.[22] Zhao H, Yenari MA, Cheng D, et al. Biphasic cytochrome c release after transient global ischemia and its inhibition by hypothermia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25(9): 1119-1129.[23] Horbelt D, Denkis A, Knaus P. A portrait of Transforming Growth Factor β superfamily signalling: Background matters. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(3):469-474.[24] Gu AD, Wang Y, Lin L, et al. Requirements of transcription factor Smad-dependent and -independent TGF-β signaling to control discrete T-cell functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(3):905-910.[25] Iizuka-Koga M, Nakatsukasa H, Ito M, et al. Induction and maintenance of regulatory T cells by transcription factors and epigenetic modifications. J Autoimmun. 2017;83:113-121.[26] Harikrishnan LS, Warrier J, Tebben AJ, et al. Heterobicyclic inhibitors of transforming growth factor beta receptor I (TGFβRI). Bioorg Med Chem. 2018;26(5):1026-1034.[27] Ikushima H, Miyazono K. TGFbeta signalling: a complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(6):415-424.[28] 麦明杰,陈星权,叶秀娟,等.西罗莫司促进TGF-β分泌对小鼠调节性T细胞体外增殖的影响[J].岭南心血管病杂志, 2013,19(2): 219-225.[29] Pang N, Zhang F, Ma X, et al. TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway regulates Th17/Treg balance during Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;20(1): 248-257.[30] Maywald M, Meurer SK, Weiskirchen R, et al. Zinc supplementation augments TGF-β1-dependent regulatory T cell induction. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017;61(3).[31] Li S, Fan Q, He S, et al. MicroRNA-21 negatively regulates Treg cells through a TGF-β1/Smad-independent pathway in patients with coronary heart disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(3):866-878.[32] Ruan Q, Kameswaran V, Tone Y, et al. Development of Foxp3(+) regulatory t cells is driven by the c-Rel enhanceosome. Immunity. 2009;31(6):932-940.[33] Powell J, Mota F, Steadman D, et al. Small Molecule Neuropilin-1 Antagonists Combine Antiangiogenic and Antitumor Activity with Immune Modulation through Reduction of Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGFβ) Production in Regulatory T-Cells. J Med Chem. 2018;61(9):4135-4154. |