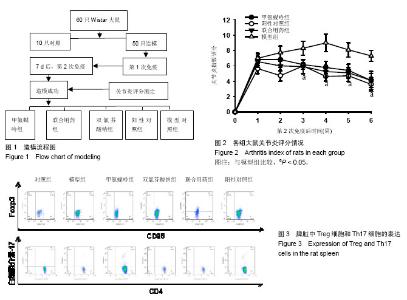
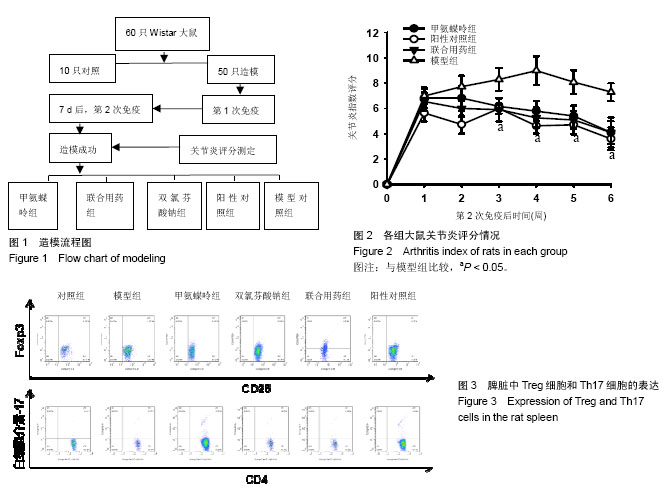
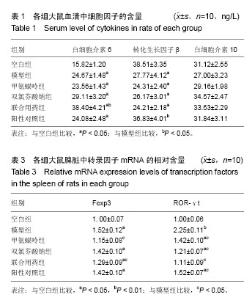
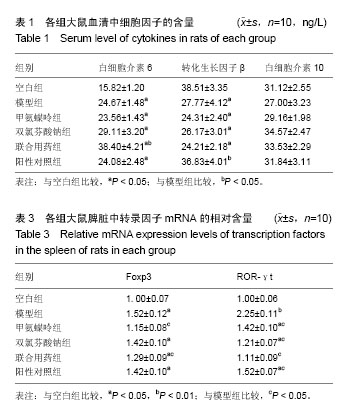
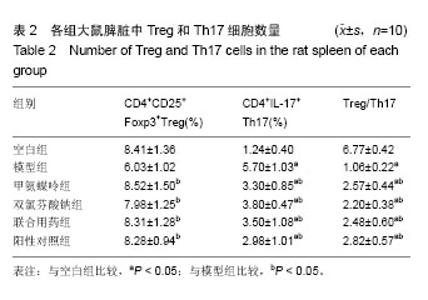
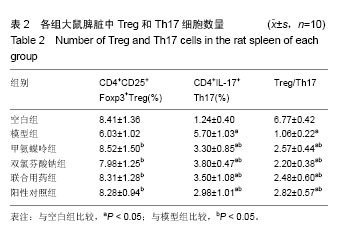
| [1] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.类风湿关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(4):265-270.[2] 池里群,周彬,高文远,等.治疗类风湿性关节炎常用药物的研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2014,39(15):2851-2858.[3] 李培培,邰宇,黄传兵,等.美洛昔康片联合甲氨蝶呤片治疗类风湿关节炎的临床研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2016,32(22):2023-2026.[4] 毕丹艳,李芹,张虹,等.雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床疗效研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2016,32(10):880-882.[5] 任晓明.双氯芬酸钠缓释胶囊与布洛芬缓释胶囊治疗类风湿性关节炎比较[J].医药导报,2003,22(12):860-861.[6] 宾驰.双氯芬酸制剂研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂,2010,19(23): 2983-2985.[7] 孙玉玲,吴慧,李家才,等.英太青缓释胶囊治疗类风湿性关节炎62例疗效观察[J].临床荟萃,2002,17(1):37-37.[8] 杨金娜,刘晓光,李覃,等.Th17/Treg平衡在类风湿关节炎中作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2013,29(8):1045-1048.[9] 周茹,杨以阜,左建平,等.Ⅱ型胶原诱导的小鼠关节炎动物模型的建立及影响因素[J].中国药理学通报, 2006,22(12):1532-1535.[10] 李艳玲,祁芳,许明,等.常用类风湿关节炎动物模型研究概况及展望[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2015,35(4):63-66.[11] 张玲玲,沈玉先,魏伟,等.类风湿关节炎动物模型与临床的关系[J].中国药理学通报,2002,18(5):502-506.[12] 樊丹平,郭晴晴,郑康,等.雷公藤甲素对胶原诱导关节炎大鼠MIP-1α、Eotaxin和MCP-1表达的影响[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2016,18(6): 1027-1032.[13] 张磊,努尔艾•沙吾塔力,阿依娜孜•巴达力汗,等.类风湿关节炎单独甲氨蝶呤与三联疗法治疗的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(52): 9049-9054.[14] 张俊宇,杜文静,吉鹏,等.胶原诱导性关节炎模型大鼠炎性细胞因子表达及白喉乌头的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(18):2794-2799.[15] 温博,曾升平.类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2014, 9(9):1014-1016,1019.[16] 李云春,方忠俊,钟立,等.滤泡辅助性T细胞在类风湿关节炎发病中的临床意义[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2015,36(16):2324-2325,2328.[17] 殷文,叶丛,于飞,等.CD4+ T细胞亚群在类风湿关节炎中的研究[J].医学分子生物学杂志,2017,14(1):44-48.[18] 张莹,周小莉.Th17/Treg平衡在类风湿关节炎发病和治疗中的意义[J].中国医药导报,2015,12(24):48-52.[19] 张义浜,刘志敏,熊凌霜,等.类风湿关节炎发病机制及其治疗方法研究进展[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2005,21(z1):88-90,94.[20] 伍斌,鲁延富,姜凤良,等.类风湿关节炎发病机制的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2014,29(23):4249-4251.[21] 魏蕾.类风湿关节炎病因和发病机制研究进展[J].医学综述, 2015,21(9): 1548-1551.[22] 杨明峰,丁瑜,王艺文,等.二甲双胍通过腺苷酸活化蛋白酶-哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路调节胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠辅助性T细胞17/调节性T细胞的分化及细胞因子的表达[J].中华风湿病学杂志, 2016,20(9):614-618.[23] 兰瑛,胡蝶,宋海宁,等.甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎有效性与安全性的系统评价[J].中国药房,2016,27(21):2928-2932,2933.[24] Liu DY,Lon HK, Wang YL,et al.Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and toxicities of methotrexate in healthy and collagen-induced arthritic rats.Biopharm Drug Dispos.2013;34(4):203-214.[25] Sun Y,Yao Y,Ding CZ,et al.A combination of Sinomenine and Methotrexate reduces joint damage of collagen induced arthritis in rats by modulating osteoclast-related cytokines.International immunopharmacology.2014;18(1):135-141.[26] 李晖.双氯芬酸钠缓释胶囊改善类风湿关节炎关节症状的作用[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(9):1435-1435.[27] 陆志华,徐红,孙荣新.双氯芬酸钠乳胶剂缓解关节炎等疾病患者关节肿胀、压痛、活动受限症状的疗效评价[J].中国临床康复, 2004,8(27):5865.[28] 陈瑞林,陶怡,黄文辉,等.大鼠胶原诱导性关节炎关节滑膜Treg/Th17平衡及TNF-α拮抗剂的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2012,28(6):1071-1075.[29] 牛倩,黄卓春,蔡蓓,等.类风湿性关节炎患者外周血Th17/Treg细胞比率失衡的研究[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2010,26(3):267-269,272.[30] 刘运夏,朱彦锋,刘杨,等.类风湿关节炎患者外周血 Th17细胞及Treg细胞数量的 meta分析[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2015,50(5):606-610.[31] Lubberts EW.Th17 cytokines and arthritis.Semin Immunopathol.2010; 32(1):43-53.[32] 龚建玲.Th细胞相关因子在类风湿关节炎中的检测意义[J].中国中医药科技,2014,21(z1):276-276.[33] 安乐美,李娟,季兰岚等.类风湿关节炎患者外周血滤泡辅助性T细胞水平检测[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2016,48(6):951-957.[34] Wang Y,Cai W,Zhang G,et al.Discoveryof novel N-(5-(arylcarbonyl) thiazol-2-yl)amides and N-(5-(arylcarbonyl)thiophen-2-yl)amidesas potent RORγt inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem.2014;22(2):692-702.[35] 元绍苓,李洋.不同类型的调节性T细胞在类风湿关节炎中的作用[J].国际免疫学杂志,2014,37(3):231-233.[36] Tong B,Yu J,Wang T, et al.Sinomenine suppresses collagen-induced arthritis by reciprocal modulation of regulatory T cells and Th17 cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Mol Immunol. 2015;65(1):94-103.[37] 王建.Th细胞在类风湿关节炎发病作用的研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志, 2015,35(2):263-266.[38] 李鸿斌,铁宁,贾永峰,等.类风湿关节炎患者滑膜抗环瓜氨酸肽表位表达与Th17/调节性T细胞的失衡和滑膜炎症的相关性分析[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2012,16(4):224-228.[39] 余黄合,魏艳霞,林也,等.IL-23/IL-17炎症轴在类风湿关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2016,13(31):37-41.[40] 邵勤,吴斌.辅助性T细胞22/白细胞介素-22在类风湿关节炎中的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2016,20(4):274-278.[41] Dallenbach K,Maurer P,Röhn T,et al.Protective effect of a germline, IL-17-neutralizing antibody in murine models of autoimmune inflammatory disease.Eur J Immunol.2015;45(4):1238-1247.[42] Yao Y,Ding CZ,Fang Y,et al.Combination of MTX and LEF attenuates inflammatory bone erosion by down-regulation of receptor activator of NF-kB ligand and interleukin-17 in type II collagen-induced arthritis rats. Rheumatol Int.2013;33(7):1845-1853.[43] 高勇,宋月,安万新,等.类风湿关节炎患者Th17细胞与调节性T细胞失衡的研究[J].国际免疫学杂志,2011,34(2):160-164.[44] Ivanova I, Seledtsova G, Mamaev S, et al.Immune responses induced by T-cell vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Vaccin Immunother.2014;10(5):1221-1227.[45] 姚寿林,徐建华,连莉,等.类风湿关节炎患者外周血Th17细胞/调节性T细胞变化及其临床意义[J].中华风湿病学杂志, 2011,15(5):309-313.[46] 武瑜.生物制剂靶向治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].医学综述,2015, 21(9):1540-1543.[47] 任茜,何成松.针对Th17细胞及IL-17的靶向生物制剂在类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2016,45(8):1124-1127. |