Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (32): 5091-5096.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.32.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mangiferin protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia
Cheng Jian-wen, Zhao Jin-min, Li Xiao-feng, Tan Zhen
- Department of Traumatic Orthopaedics and Hand Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2014-07-08Online:2014-08-06Published:2014-09-18 -
Contact:Zhao Jin-min, M.D., Professor, Department of Traumatic Orthopaedics and Hand Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Cheng Jian-wen, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopaedics and Hand Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Special Scientific Fund for Traditional Chinese Medicine in Guangxi Health Bureau, No. GZKZ 10-011, GZKZ-Z1104; the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, No. 20104503110002; Key Technology Research and Development Projects of Population Health and Food Safety of Guangxi Science and Technology Bureau, No. guikegong 1140003A-31; Self-Funded Research Projects of Guangxi Health Bureau, No. guiweiZ2012058, guiweiZ2012061; Projects of Guangxi Education Bureau, No. guijiao201010LX050
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Jian-wen, Zhao Jin-min, Li Xiao-feng, Tan Zhen. Mangiferin protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(32): 5091-5096.
share this article
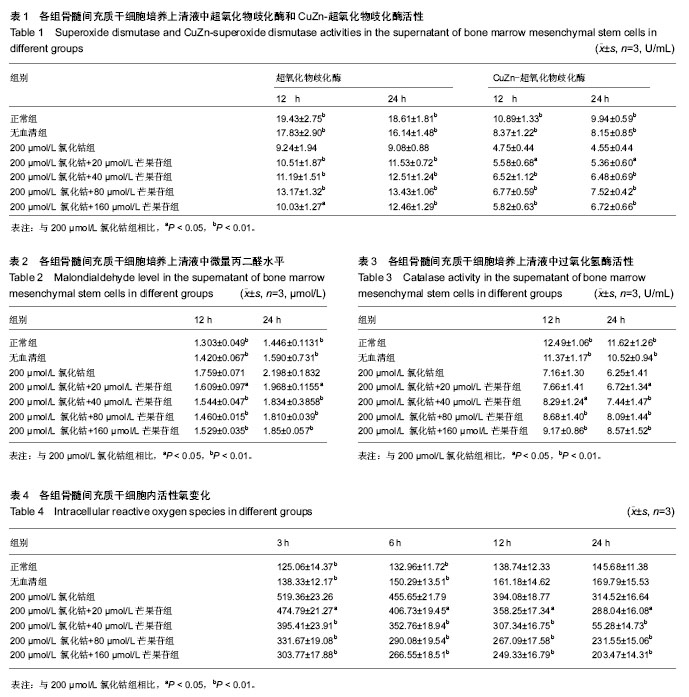
2.1 氯化钴对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的细胞毒性实验 具体结果参见作者前期研究[11]。 2.2 缺氧损伤12,24 h各组骨髓间充质干细胞培养上清液中超氧化物歧化酶活性 应用氯化钴建立细胞缺氧模型,以芒果苷进行预保护,测定大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤12 h及24 h的总超氧化物歧化酶和CuZn-超氧化物歧化酶活性,观察芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的保护作用。结果可见,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的超氧化物歧化酶作用呈时间依赖性及浓度依赖性。用200 μmol/L氯化钴处理细胞12,24 h,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞总超氧化物歧化酶活性下降。20,40,80 μmol/L芒果苷组总超氧化物歧化酶活性明显高于200 µmol/L氯化钴组(P < 0.01),随着芒果苷浓度的升高,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的保护作用逐渐增强。但是芒果苷浓度为160 μmol/L时总超氧化物歧化酶活性有所降低,但仍高于200 µmol/L氯化钴组(P < 0.05),见表1。 用200 μmol/L氯化钴处理细胞12,24 h,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞CuZn-超氧化物歧化酶活性下降。 20 μmol/L芒果苷组CuZn-超氧化物歧化酶活性高于 200 µmol/L氯化钴组(P < 0.05),随着芒果苷浓度的升高,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的保护作用逐渐增强。40,80,160 μmol/L芒果苷组CuZn-超氧化物歧化酶活性与200 µmol/L氯化钴组比较,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表1。 2.3 各组骨髓间充质干细胞培养上清液中微量丙二醛水平 应用氯化钴建立细胞缺氧模型,以芒果苷进行预保护,测定大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤12 h及24 h的微量丙二醛水平,观察芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的保护作用。可见,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的微量丙二醛作用呈时间依赖性及浓度依赖性。用200 μmol/L氯化钴处理细胞12,24 h,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞微量丙二醛水平上升。20 μmol/L芒果苷组丙二醛水平低于200 µmol/L氯化钴组(P < 0.05),随着芒果苷浓度的升高,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的保护作用逐渐增强。40,80,160 μmol/L芒果苷组丙二醛水平与 200 µmol/L氯化钴组比较,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表2。 2.4 各组骨髓间充质干细胞培养上清液中过氧化氢酶活性 应用氯化钴建立细胞缺氧模型,以芒果苷进行预保护,测定大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤12 h及24 h的过氧化氢酶活性,观察芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的保护作用。可见,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的过氧化氢酶作用呈时间依赖性及浓度依赖性。用200 μmol/L氯化钴处理细胞12 h及24 h,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞过氧化氢酶活性下降。处理12 h时20 μmol/L芒果苷组过氧化氢酶活性与200 μmol/L CoCl2组比较未见明显变化(P > 0.05),随着芒果苷浓度的升高,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的保护作用逐渐增强,40 μmol/L芒果苷组过氧化氢酶活性高于200 µmol/L氯化钴组(P < 0.05),80,160 μmol/L芒果苷组过氧化氢酶活性明显高于 200 µmol/L氯化钴组(P < 0.01)。处理24 h时20 μmol/L芒果苷组过氧化氢酶活性高于200 μmol/L 氯化钴组(P < 0.05);随着芒果苷浓度的升高,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的保护作用逐渐增强,40,80,160 μmol/L芒果苷组丙二醛水平与200 µmol/L氯化钴组比较,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表3。 2.5 各组骨髓间充质干细胞内活性氧变化 应用氯化钴建立细胞缺氧模型,以芒果苷进行预保护,测定大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤3,6,12,24 h的细胞内活性氧变化,观察芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的保护作用。可见,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺氧损伤的活性氧作用呈时间依赖性及浓度依赖性。用 200 μmol/L氯化钴处理细胞3,6,12,24 h,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞活性氧上升,第3小时为最高值,随着时间的延长,活性氧水平逐渐下降。20 μmol/L芒果苷组活性氧水平低于200 µmol/L氯化钴组(P < 0.05),随着芒果苷浓度的升高,芒果苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的保护作用逐渐增强。40,80,160 μmol/L芒果苷组活性氧水平与 200 µmol/L氯化钴组比较,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表4。"
| [1] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147. [2] Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart.Circulation. 2002;105(1):93-98. [3] Malherbe CJ, Willenburg E, de Beer D,et al. Iriflophenone-3-C-glucoside from Cyclopia genistoides: isolation and quantitative comparison of antioxidant capacity with mangiferin and isomangiferin using on-line HPLC antioxidant assays.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014;951-952:164-171. [4] Telang M, Dhulap S, Mandhare A,et al.Therapeutic and cosmetic applications of mangiferin: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2013;23(12):1561-1580. [5] Kavitha M, Manivasagam T, Essa MM,et al.Mangiferin antagonizes rotenone: induced apoptosis through attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells.Neurochem Res. 2014;39(4):668-676. [6] Rodeiro I, Delgado R, Garrido G. Effects of a Mangifera indica L. stem bark extract and mangiferin on radiation-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes and lymphoblastoid cells.Cell Prolif. 2014;47(1):48-55. [7] Zhao J, Zhang B, Li S,et al. Mangiferin increases Nrf2 protein stability by inhibiting its ubiquitination and degradation in human HL60 myeloid leukemia cells.Int J Mol Med. 2014; 33(5):1348-1354. [8] Lin H, Chen R, Liu X,et al. Study on interaction of mangiferin to insulin and glucagon in ternary system.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2010;75(5):1584-1591. [9] Ang E, Liu Q, Qi M,et al. Mangiferin attenuates osteoclastogenesis, bone resorption, and RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and ERK.J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(1): 89-97. [10] 李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(10):1721-1725. [11] 李晓峰,罗世兴,赵劲民,等. 芒果苷对缺氧损伤骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡的保护[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(49):8481-8487. [12] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL,et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow.Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49. [13] Pereira RF, Halford KW, O'Hara MD,et al. Cultured adherent cells from marrow can serve as long-lasting precursor cells for bone, cartilage, and lung in irradiated mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(11):4857-4861. [14] Azizi SA, Stokes D, Augelli BJ,et al. Engraftment and migration of human bone marrow stromal cells implanted in the brains of albino rats--similarities to astrocyte grafts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(7):3908-3913. [15] Hernandez P, Rodriguez PC, Delgado R,et al. Protective effect of Mangifera indica L. polyphenols on human T lymphocytes against activation-induced cell death.Pharmacol Res. 2007;55(2):167-173. [16] Leiro JM, Alvarez E, Arranz JA,et al. In vitro effects of mangiferin on superoxide concentrations and expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta genes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;65(8):1361-1371. [17] Muruganandan S, Lal J, Gupta PK.Immunotherapeutic effects of mangiferin mediated by the inhibition of oxidative stress to activated lymphocytes, neutrophils and macrophages. Toxicology. 2005;215(1-2):57-68. [18] Rodeiro I, Donato MT, Martínez I,et al. Potential hepatoprotective effects of new Cuban natural products in rat hepatocytes culture.Toxicol In Vitro. 2008;22(5):1242-1249. [19] Satish Rao BS, Sreedevi MV, Nageshwar Rao B. Cytoprotective and antigenotoxic potential of Mangiferin, a glucosylxanthone against cadmium chloride induced toxicity in HepG2 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009;47(3):592-600. [20] Amazzal L, Lapôtre A, Quignon F, et al. Mangiferin protects against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium toxicity mediated by oxidative stress in N2A cells.Neurosci Lett. 2007;418(2): 159-164. [21] Campos-Esparza MR, Sánchez-Gómez MV, Matute C. Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotection by two natural antioxidant polyphenols.Cell Calcium. 2009;45(4):358-368. [22] Prabhu S, Jainu M, Sabitha KE,et al. Role of mangiferin on biochemical alterations and antioxidant status in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;107(1):126-133. [23] Viswanadh EK, Rao BN, Rao BS.Antigenotoxic effect of mangiferin and changes in antioxidant enzyme levels of Swiss albino mice treated with cadmium chloride.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2010;29(5):409-418. [24] Agarwala S, B NR, Mudholkar K,et al.Mangiferin, a dietary xanthone protects against mercury-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells.Environ Toxicol. 2012;27(2):117-127. [25] Ang E, Liu Q, Qi M,et al. Mangiferin attenuates osteoclastogenesis, bone resorption, and RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and ERK.J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(1): 89-97. [26] Karovic O, Tonazzini I, Rebola N,et al.Toxic effects of cobalt in primary cultures of mouse astrocytes. Similarities with hypoxia and role of HIF-1alpha.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007; 73(5):694-708. [27] Hong SM, Yang YS.A potential role of crystallin in the vitreous bodies of rats after ischemia-reperfusion injury.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2012;26(4):248-254. [28] Tammasakchai A, Reungpatthanaphong S, Chaiyasut C,et al. Red strain oryza sativa-unpolished thai rice prevents oxidative stress and colorectal aberrant crypt foci formation in rats.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(5):1929-1933. [29] Shukla SD, Bhatnagar M, Khurana S.Critical evaluation of ayurvedic plants for stimulating intrinsic antioxidant response. Front Neurosci. 2012;6:112. [30] Lee SH, Park MH, Kang SM,et al.Dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava protects against high-glucose induced damage to rat insulinoma cells by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(8):1445-1451. [31] Song MK, Seon HJ, Kim IG,et al.The effect of combined therapy of exercise and nootropic agent on cognitive function in focal cerebral infarction rat model.Ann Rehabil Med. 2012; 36(3):303-310. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [3] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [4] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [5] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [6] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [7] | Wang Buyu, Zhang Yong, Li Feifei, Dong Xiaoyu, Deng Jiang, Ruan Shiqiang. Role and application of bone morphogenetic protein 2 in the repair of osteochondral defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3259-3265. |
| [8] | Wu Ruiqi, Cui Wei, Yang Qipei, Zhou Yi, Zhang Xuan. Therapeutic mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of hormone-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2763-2771. |
| [9] | Ling Xuwei, Sun Jie, Liu Chang, Wang Yi, Shi Qin, Yang Huilin. Valproic acid promotes osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2304-2310. |
| [10] | Wen Hongjie, Chen Zhong, Yang Huagang, Xu Yongqing. Transcriptome sequencing analysis of osteogenic rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2333-2338. |
| [11] | He Zike, Wang Shangzeng. Eucommia ulmoides Oliver aqueous extract promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation through upregulating Nur77 protein expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2371-2378. |
| [12] | Yang Jun, Li Peng. Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into meniscus fibrochondrocytes induced by transforming growth factor beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2412-2419. |
| [13] | Ling Huajun, Cui Ruiwen, Wang Qiyou. 3D extracellular matrix hydrogel loaded with exosomes promotes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1900-1905. |
| [14] | Su Meng, Wang Xin, Zhang Jin, Bei Ying, Huang Yu, Zhu Yanzhao, Li Jiali, Wu Yan. Nanocellular vesicles loaded with curcumin promote wound healing in diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1877-1883. |
| [15] | Wu Xiaolei, Han Yu, Li Jialei, Wang Shuang, Cao Jimin, Sun Teng. piRNA-5938 can regulate cardiomyocyte apoptosis and mitochondrial fission [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1750-1757. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||