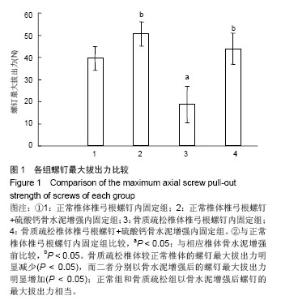
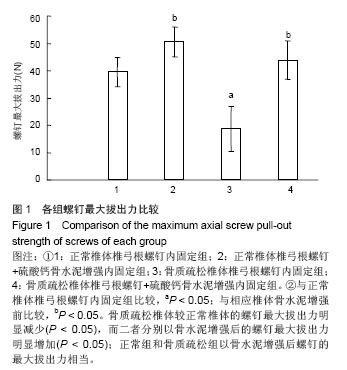
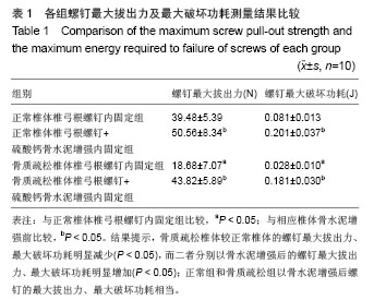
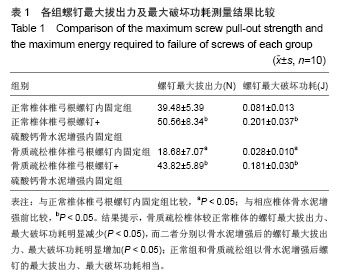
| [1]Kannus P, Niemi S, Parkkari J, et al. Why is the age-standardized incidence of low-trauma fractures rising in many elderly populations? J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(8): 1363-1367.
[2]Curtis R, Goldhahn J, Schwyn R, et al. Fixation principles in metaphyseal bone--a patent based review. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16 Suppl 2:S54-64.
[3]曹涌,张烽,姚羽,等.快速建立小牛椎体骨质疏松模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(39):7288-7291.
[4]Kawagoe K, Saito M, Shibuya T, et al. Augmentation of cancellous screw fixation with hydroxyapatite composite resin (CAP) in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;53(6):678-684.
[5]Koval KJ, Meek R, Schemitsch E, et al. An AOA critical issue. Geriatric trauma: young ideas. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A(7):1380-1388.
[6]Augat P, Simon U, Liedert A, et al. Mechanics and mechano-biology of fracture healing in normal and osteoporotic bone. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16 Suppl 2:S36-43.
[7]Meyer RA Jr, Tsahakis PJ, Martin DF, et al. Age and ovariectomy impair both the normalization of mechanical properties and the accretion of mineral by the fracture callus in rats. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(3):428-435.
[8]Bergman RJ, Gazit D, Kahn AJ, et al. Age-related changes in osteogenic stem cells in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(5): 568-577.
[9]汤亭亭,岳冰,陆斌,等.年龄因素对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞数量及组织中BMP2含量的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2005, 11(2): 156-158.
[10]Seebeck J, Goldhahn J, Morlock MM, et al. Mechanical behavior of screws in normal and osteoporotic bone. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16 Suppl 2:S107-111.
[11]Perren SM. Backgrounds of the technology of internal fixators. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 2:B1-3.
[12]Turner IG, Rice GN. Comparison of bone screw holding strength in healthy bovine and osteoporotic human cancellous bone. Clin Mater. 1992;9(2):105-107.
[13]von der Linden P, Gisep A, Boner V, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a new augmentation method for enhanced screw fixation in osteoporotic proximal femoral fractures. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(12):2230-2237.
[14]Lieberman IH, Togawa D, Kayanja MM. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: filler materials. Spine J. 2005;5(6 Suppl): 305-316S.
[15]Jansen J, Ooms E, Verdonschot N, et al. Injectable calcium phosphate cement for bone repair and implant fixation. Orthop Clin North Am. 2005;36(1):89-95.
[16]Oda H, Nakamura K, Matsushita T, et al. Clinical use of a newly developed calcium phosphate cement (XSB-671D). J Orthop Sci. 2006;11(2):167-174.
[17]Peters CL, Hines JL, Bachus KN, et al. Biological effects of calcium sulfate as a bone graft substitute in ovine metaphyseal defects. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;76(3): 456-462.
[18]Valimaki VV, Aro HT. Molecular basis for action of bioactive glasses as bone graft substitute. Scand J Surg. 2006;95(2): 95-102.
[19]Larsson S. Cement augmentation in fracture treatment. Scand J Surg. 2006;95(2):111-118.
[20]Carroll M, Lewis G, Xu J, et al. Evaluation of a synthetic bone defect test model to aid in the selection of materials for use in vertebral body compression fracture repair. Orthopedics. 2004; 27(1 Suppl):s119-122. |