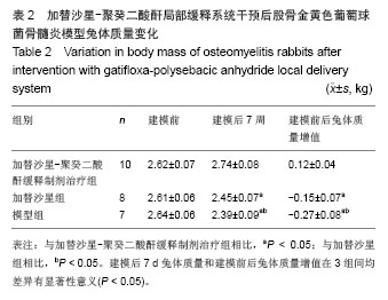
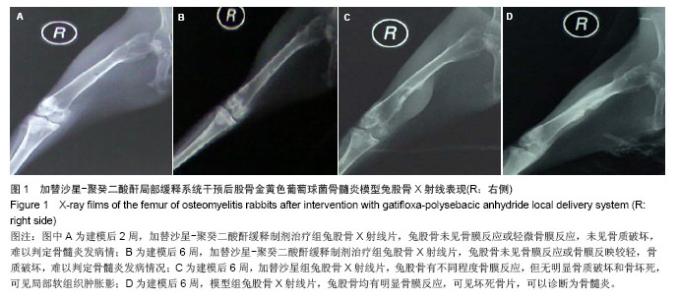
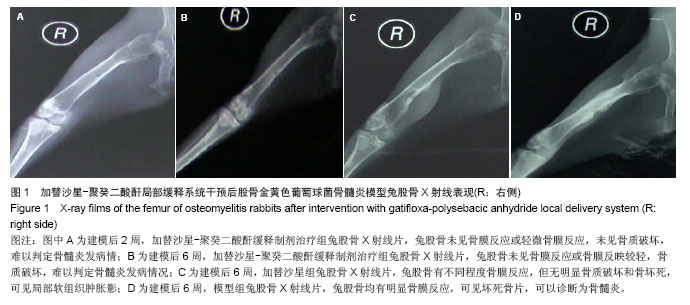
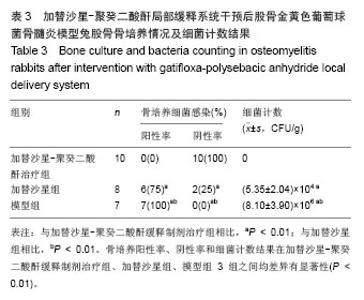
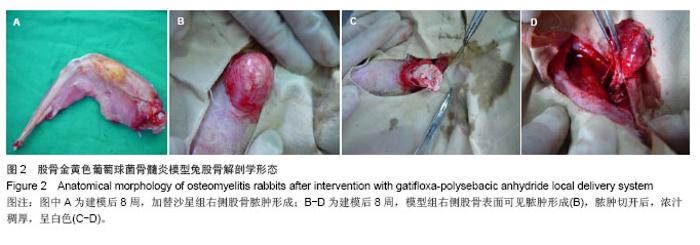
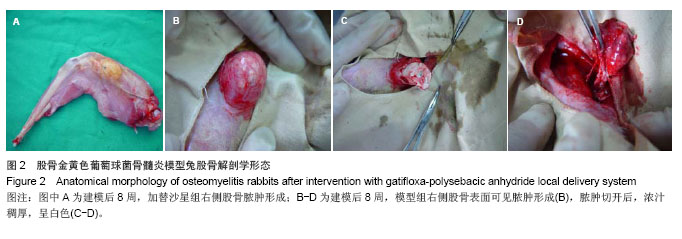
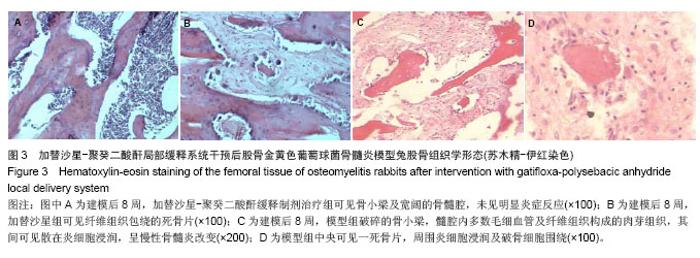
| [1]Domb AJ, Rock M, Perkin C. Excretion of a radiolabeled anticancer biodegradable polymeric implant from the rabbit brain. Biomaterials. 1995;16(14):1069-1072.
[2]Norden CW, Shafferm M. Experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a radiographic-pathological correlative analysis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980;61(4):451-460.
[3]Laurence ED, Charle H. Gentamicin-loaded plaster of Paris as a treatment of experimental osteomyelitis in rabbits. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(219):278-282.
[4]鲁锋,张鸿图.马术友.加替沙星-聚癸二酸酐局部缓释系统的体内释药特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(29):5351-5356.
[5]鲁锋,张鸿图,马术友.加替沙星-聚癸二酸酐局部缓释系统的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(25):4623-4628.
[6]Ostermann PA, Seligson D, Henry SL. Local antibiotic therapy for severe open fractures. A review of 1085 consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(1):93-97.
[7]Grace EJ, Bryoson V. Modern treatment of chronic osteomyelitis with topical detergent antibiotic therapy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1950;91(3):333-342.
[8]Perry CR, Kitterbusch JK, Rice SH, et al. Antibiotics delivered by an implantable drug pump; a new application for treating osteomyelitis. Am J Med. 1986;80(6B):222-227.
[9]陈爱民,侯春林.几丁糖庆大霉素药物释放系统的研制及体外释放实验[J].中华骨科杂志,1997;17(9):592.
[10]Kahn DS, Pritzker KP. The pathophysiology of bone infection. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1973;8(96):12-19.
[11]Mayberry-Carson KJ, Tober-Meyer B, Smith JK, et al. Bacterial adher ence and glycocalyx formation in osteomyelitis experimentally induced with staphlococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984;43(3):825-833.
[12]Nickel JC, Ruseska I, Wright JB, et al. Tobramycin resistance of pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985; 27(4):619-624.
[13]Taylor AR, Maudsley RH. Instillation-suction technique in chronic osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970;52(1): 88-92.
[14]Wahlig H, Dingledein E, Bergmann R, et al. The release of gentamicin from polymethylmethacrylate beads-an experimental and pharmacokinetic study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1978;60:270-275.
[15]Walenkamp GH, Vree TB, van Rens TJ. Gentamicin - PMMA beads. pharmacokinetic and nephrotoxicological study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(205):171-183.
[16]Wei G, Kotoura Y, Oka M, et al. A bioabsorbable delivery system for antibiotic treatment of osteomyelitis: the use of lactic acid pligomer as a carrier. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73(2):246-252. |