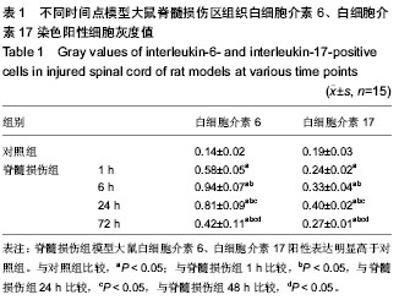
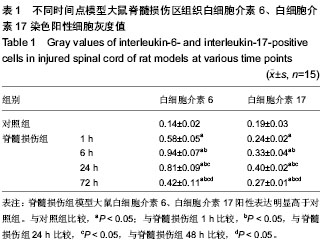
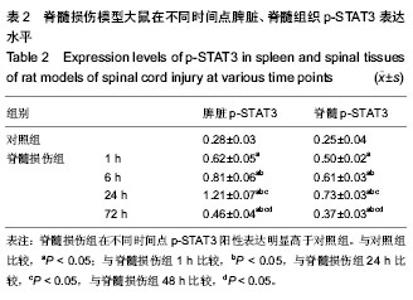
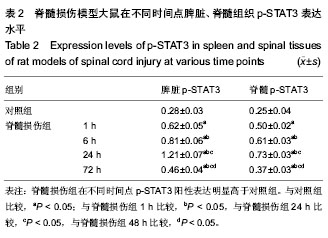
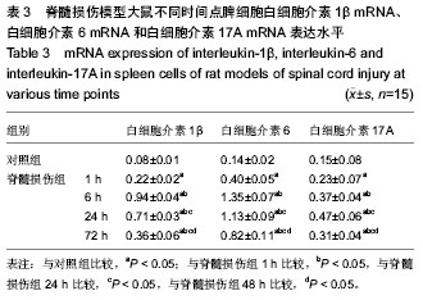
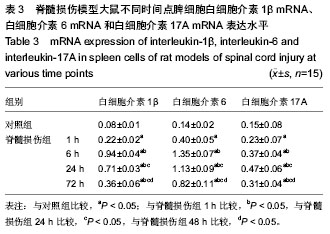
| [1] Gupta R, Bathen ME, Smith JS, et al.Advances in the management of spinal cord injury. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(4):210-222.
[2] Baptiste DC, Fehlings MG.Pharmacological approaches to repair the injured spinal cord. J Neurotrauma.2006;23(3-4): 318-334.
[3] 飞翔,锁志刚,丁惠强,等.JAK2/STAT3信号转导通路在大鼠急性脊髓损伤中对细胞凋亡的调控作用[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2011, 28(11): 993-997.
[4] 郭宗铎,孙晓川.白介素-6与颅脑损伤[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2006, 32(3):282-283.
[5] 庄志,顾红兵,朱灿宏.IL-1和IL-6 在脊髓损伤大鼠神经细胞中的表达及其动态变化[J].医药论坛杂志,2010,31(23):38-40.
[6] Frei K, Nadal D, Fontana A, et al. Intracerebral Synthesis of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-6 in Infectious Meningitisa. Ann NY Acad Sci.1990; 594(1): 326-335.
[7] 郑晶晶,姚安会,刘芳芳,等.小鼠脊髓损伤早期不同炎症因子的表达变化[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2012, 28(4):391-394.
[8] 史立敏,张云波,董坚,等. IL-17及其与疾病关系研究进展[J].中国热带医学,2012,12(1):109-111.
[9] Cua DJ, Tato CM.Innate IL-17-producing cells: the sentinels of the immune system.Nature Reviews Immunology.2010; 10(7): 479-489.
[10] Ankeny DP, Popovich PG.Mechanisms and implications of adaptive immune responses after traumatic spinal cord injury.Neuroscience.2009;158(3): 1112-1121.
[11] 温玉婷,刘伟,杨爱军,等.IL-17 和 STAT3 在结直肠癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].第三军医大学学报, 2011, 33(17): 1812-1815.
[12] 宗少晖,韦波,曾高峰,等.白介素-1 受体拮抗剂对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后 BDNF 表达的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(002): 205-206.
[13] 杨影,罗英,李春林,等. IL-23/Th17轴在变应性哮喘中的研究进展[J].生命科学,2011, 23(3): 286-290.
[14] 黄国祥,王玉忠,周文斌,等.外源性TGF-β1对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎模型小鼠中IL-23/Th17炎症轴的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2010,26(5): 413-416.
[15] 汪占文,杨金凤,孔庆飞,等.骨化三醇对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的治疗作用及相关机制[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2012,24(11): 1325-1328.
[16] 董梅,张美月,陈欣,等.Thl7 细胞在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎大鼠发病中的表达及依达拉奉的保护作用研究[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2013,29(2): 140-143.
[17] 肖瑶,方宁,陈代雄,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞对大鼠胶原性关节炎的疗效及免疫调节作用[J].免疫学杂志, 2013,29(6): 461-466.
[18] Kolls JK, Lindén A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21(4): 467-476.
[19] 周娟,张梦军,郭嘉伟,等.TPA致小鼠耳肿胀模型的中性粒细胞聚集及 IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α,IL-17A 的表达水平研究[J].免疫学杂志, 2012, 28(10): 872-876.
[20] 廖满林,廖穗波,陈霭平,等.类风湿性关节炎患者 IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-17 与护骨因子水平检测及临床意义[J].广东医学, 2007, 28(1):59.
[21] 罗英,黄为民.慢性肺疾病患儿外周血17个免疫细胞因子的研究[J].南方医科大学学报, 2010,30(2): 331-333.
[22] 万春平,熊尤龙,祁燕,等.肠系膜淋巴结Th1, Th17细胞在小鼠结肠炎模型发病中作用的研究[J].胃肠病学, 2013, 18(8): 477-481.
[23] 高长春,戴存才.急性胰腺炎患者血清Th17相关因子IL-17, IL-6 与 TNF-α 水平变化及意义[J].中国医药导报, 2009,6(35): 15-16.
[24] 李小琳,邹峥.甲基强的松龙对急性期川崎病外周血单个核细胞 NF-κB活化和IL-6, IL-17表达的干预[J].江西医学院学报, 2009, 49(3): 69-72.
[25] 陈骏,熊春霖,郭文超.依达拉奉对急性脑梗死患者血清IL-17, IL-6和TNF-α的影响[J].赣南医学院学报, 2009, 29(3):399-401.
[26] 王祥贵,许祖芳,许自兴.病毒性心肌炎患儿血清IL-17, IL-6 和 IL-8 水平的变化及临床意义[J].江西医学院学报,2009, 49(2): 116-118.
[27] 张慧琴,刘学军.IL-17和IL-6在大鼠肺纤维化过程中的动态表达及意义[J].中国医药导报, 2012, 9(10): 24-25.
[28] 沈朝斌,顾珺,夏尤佳,等.玉屏风散对气道变态反应性小鼠 IL-17 和 IL-6 的影响[J].上海中医药杂志,2009, 43(10): 58-61.
[29] 孟欣颖,马健,江晨,等.胃癌组织中IL-17, IL-6和TGF-β1 的表达及其临床意义[J].胃肠病学, 2012, 16(10): 593-596.
[30] 黄小霏,檀卫平,江润昌.手足口病患儿血清IL-6, IL-10, IL-17 水平的变化及其临床意义[J].重庆医学,2012, 41(30): 3157-3159.
[31] 徐国栋,张东军,袁劲涛,等.肾综合征出血热血浆IL-6, IL-17, TGF-β1与多器官损害的关系[J].热带医学杂志,2013,13(9): 1078-1081.
[32] 熊燚,王兴勇.脓毒症大鼠急性肺损伤血清 IL-6, IL-17的变化及其意义[J].儿科药学杂志,2010(1): 11-12.
[33] 齐育英,林振忠,明德松.IL-6, IL-10, IL-17在慢性乙型病毒性肝炎患者血中水平分析[J].中国免疫学杂志,2013, 29(11): 1177- 1180.
[34] Kortylewski M, Xin H, Kujawski M, et al.Regulation of the IL-23 and IL-12 balance by Stat3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment.Cancer cell.2009;15(2): 114-123.
[35] 寇巍,胡国华,姚红兵,等.STAT3及SOCS3在鼻息肉患者中对 Th17分化的作用观察[J].免疫学杂志, 2012,28(10): 888-891.
[36] 王国兵,李成荣,杨军,等.白细胞介素6/STAT3信号活化在急性免疫性血小板减少性紫癜患儿辅助性T淋巴细胞17/调节性T淋巴细胞失衡中的作用[J].实用儿科临床杂志, 2012, 27(13): 1005- 1008.
[37] Yu LZ, Wang HY, Yang SP, et al.Expression of interleukin-22/ STAT3 signaling pathway in ulcerative colitis and related carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(17):2638- 2649.
[38] Wang L, Yi T, Kortylewski M, et al.IL-17 can promote tumor growth through an IL-6–Stat3 signaling pathway.J Exp Med. 2009;206(7):1457-1464.
[39] Liu H, Yao YM, Yu Y, et al.Role of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway in regulation of expression and inflammation-promoting activity of high mobility group box protein 1 in rat peritoneal macrophages. Shock. 2007;27(1): 55-60.
[40] Hilton DJ.Negative regulators of cytokine signal transduction. Cell Mol Life Sci.1999;55(12):1568-1577. |