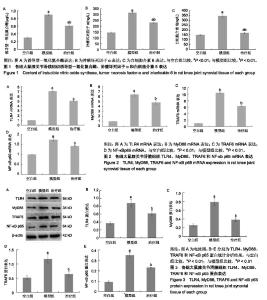
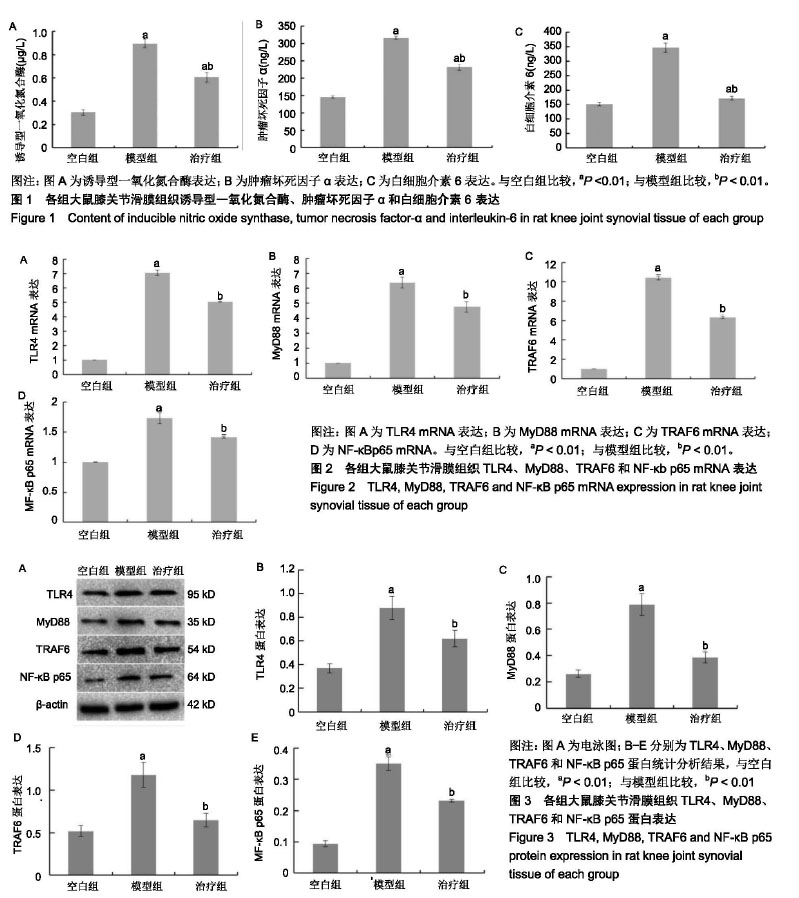
| [1]向川.软骨细胞凋亡与骨关节炎[J].国外医学:免疫学分册, 2003, 26(2):110-111.[2]Radstake TR, Roelofs MF, Jenniskens YM, et al.Expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue and regulation by proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 via interferon-gamma. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50(12):3856-3865.[3]Sohn DH, Sokolove J, Sharpe O, et al.Plasma proteins present in osteoarthritic synovial fluid can stimulate cytokine production via Toll-like receptor 4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(1):R7.[4]Yamamoto Y,Gaynor RB.Role of the NF-kappa B pathway in the pathogenesis of human disease states. CurrMol Med. 2001;1(3):287-296.[5]王永福,林剑,詹宏刚.CD14/TLR-4-NF-κB信号通路参与骨关节炎发病机制的研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(6):528-530.[6]韦嵩,申茜茸,李晓昊,等.经筋微创松解术治疗膝骨关节炎对TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号转导通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志, 2018,33(10):4637-4641.[7]曹云祥.基于miRNA-21/TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB信号通路探讨新风胶囊改善RA心功能的机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学, 2018.[8]董小君.风湿宁对风寒湿痹证CIA模型TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的作用机制研宄[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2018.[9]焦永亮,刘慧敏,顾海伦,等.白藜芦醇对肥胖者骨性关节炎软骨细胞的作用及对TLR4?NF- κBmRNA表达的影响[J].东南大学学报, 2015,34(3):342-346.[10]付长龙,梅阳阳,叶锦霞,等.乌头汤治疗寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎:与双氯芬酸钠的比较[J].风湿病与关节炎,2017,6(4):12-16.[11]林洁,陈俊,付长龙,等.乌头汤治疗骨关节炎的系统评价[J].风湿病与关节炎,2017,6(5):35-38,50.[12]郑春松,林洁,付长龙,等. 基于计算机模拟乌头汤治疗疼痛的药效物质基础与分子作用机制[J].福建中医药大学学报, 2016,1(26): 33-37.[13]陈俊,叶锦霞,林洁,等.乌头汤对膝骨关节炎大鼠细胞因子IL-1β?IL-6?TNF-α?MMP-3的影响[J].福建中医药,2017,18(5):27-29.[14]刘献祥,李西海,周江涛.改良Hulth造模法复制膝骨关节炎的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2005,25(12):1104-1108.[15]黄继汗,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2004,9(9):1069-1072.[16]Wakamatsu K,Nanki T,Miyasaka N, et al. Effect of a small molecule inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear translocation in a murine model of arthritis and cultured human synovial cells.Arthritis Res Ther.2005;7:1348-1359.[17]Kosinska MK, Liebisch G, Lochnit G,et al.A Lipidomic Study of Phospholipid Classes and Species in Human Synovial Fluid.Arthritis Rheum.2013;65(9):2323-2333.[18]Ritter SY, Subbaiah R, Bebek G, et al.Proteomic analysis of synovial fluid from the osteoarthritic knee: comparison withrtranscriptome analyses of joint tissues.Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(4):981-992.[19]张鹏,石关桐,郑昱新.膝骨关节炎滑膜细胞体外培养及生物学特性观察[J].中国骨伤,2006,19(11):656-658.[20]Deng LL, Yuan D, Zhou ZY, et al.Saponins from Panax japonicus attenuate age-related neuroinflammation via regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways.Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(11):1877-1884.[21]陈宁,叶静,汤特,等.共有序列寡核苷酸竞争结合NF-κB以减少TNF产生的实验研究[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2003,19(5): 619-621. [22]Rigoglou S,Papavassiliou AG.The NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2013;45(11):2580-2584.[23]Yang H, Cheng X, Yang YL, et al.Ramulus Cinnamomi extract attenuates neuroinflammatory responses via downregulating TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in BV2 cells.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(11):1860-1864. [24]Kawai T,Akira S.The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity:update on Toll-like receptors.Nature Immunology. 2010;11(5):373-384.[25]Bobacz K,Sunk IG,Hofstaetter JG,et al.Toll-like receptors and chondrocytes:the lipopolysaccharide-induced decrease in cartilage matrixsynthesis is dependent on the presence of toll-like receptor 4 and antagonized by bone morphogenetic protein 7.Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(6):1880-1893.[26]Bahtiar A, Nurazizah M, Roselina T,et al.Ethanolic extracts of babandotanleaves(Ageratum conyzoides L.) prevents inflammation and proteoglycan degradation by inhibiting TNF-αand MMP-9 on osteoarthritis rats induced by monosodium iodoacetate. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017;10(3): 270-277. [27]Campo GM, Avenoso A, Campo S, et al.Molecular size hyaluronan differently modulates toll-like receptor-4 in LPS-induced inflammation in mouse chondrocytes. Biochimie. 2009;92(2):204-215.[28]钦丹萍,周毅骏,孙佩娜,等.雷公藤多苷对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠TLR4/MyD88非依赖信号通路的作用研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2016,41(6):1093-1099.[29]Bortolotto V, Grilli M.Not only a bad guy: potential proneurogenic role of the RAGE/NF-κB axis in Alzheimer's disease brain.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(12):1924-1925. [30]Li T,Hu J,Thomas JA,et al.Differential induction of apoptosis by LPS and taxol in monocytic cells. Molecular Immunology. 2005; 42(9):1049-1055.[31]Kopp EB, Medzhitov R. The Toll-receptor family and control of innate immunity. Current Opinion in Immunology. 1999;11(1): 13-18.[32]Modlin RL,Brightbill HD,Godowski PJ.The toll of innate immunity on microbial pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(23): 1834-1835.[33]Dunne A, Carpenter S, Brikos C, et al.IRAK1 and IRAK4 promote phosphorylation,ubiquitination,and degradation of MyD88 adaptor-like(Mal). J Biol Chem. 2010 ;285(24): 18276-18282. |