Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (29): 4673-4679.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2817
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effect of crocin in ulcerative colitis rats and its related mechanism
Yang Minjie1, Liu Wei2, Tu Hongfei2, Li Li2, Fei Sujuan2
- 1Gastroenterology Research Center, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Gastroenterology, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-12Revised:2020-02-22Accepted:2020-03-18Online:2020-10-18Published:2020-09-14 -
Contact:Fei Sujuan, Master, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Gastroenterology, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Yang Minjie, Master candidate, Gastroenterology Research Center, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Program of the Jiangsu Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission, No. H2017082; Xuzhou Science and Technology Key Research & Development Plan Project, No. KC17184
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Minjie, Liu Wei, Tu Hongfei, Li Li, Fei Sujuan. Protective effect of crocin in ulcerative colitis rats and its related mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4673-4679.
share this article
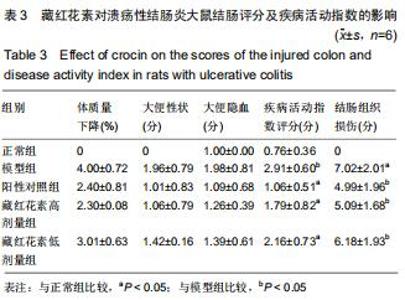
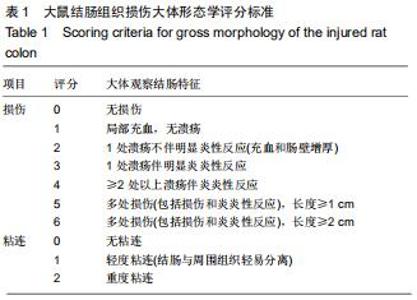
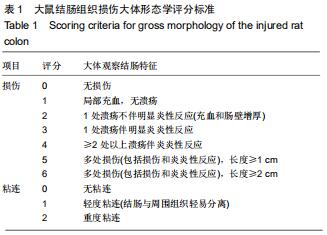
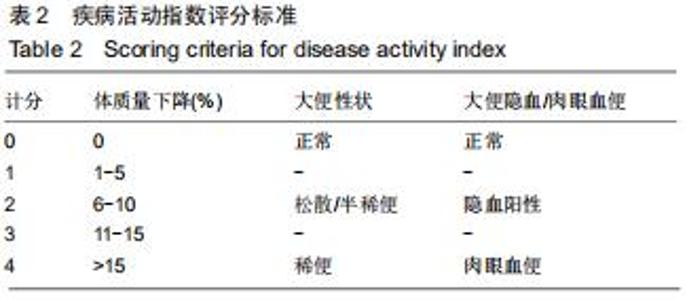
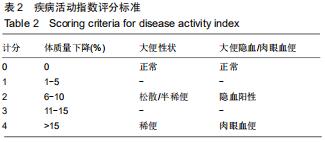
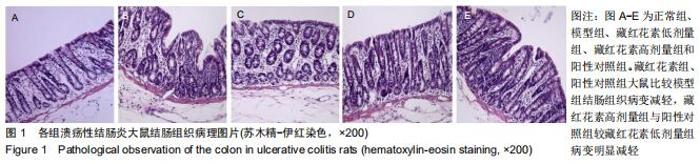
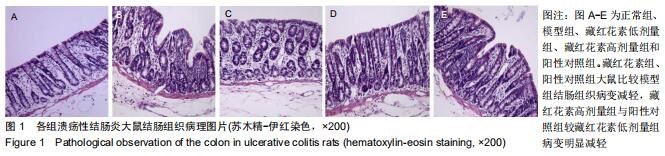
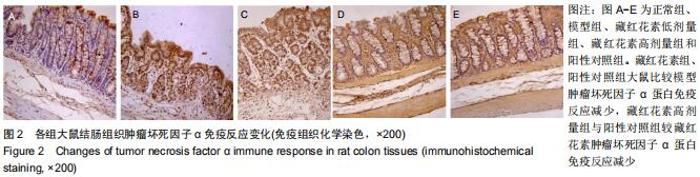
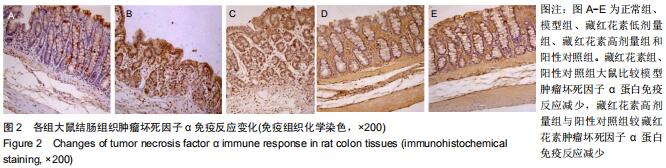
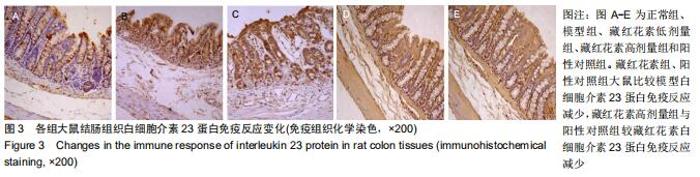
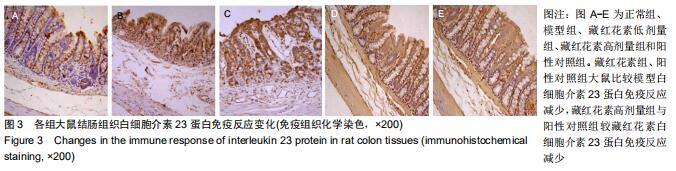
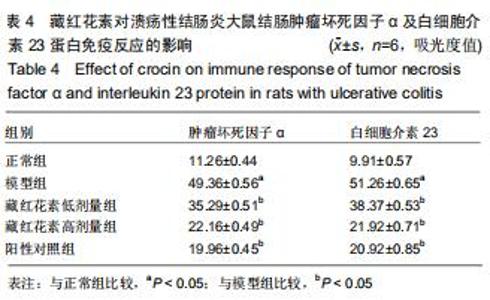
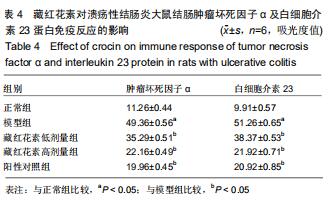
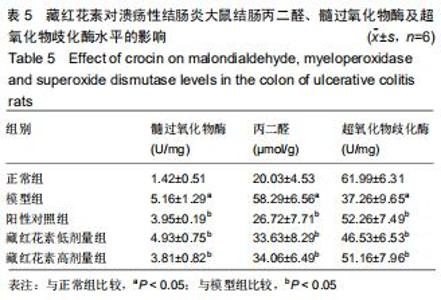
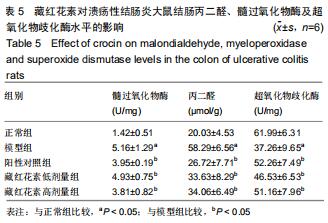
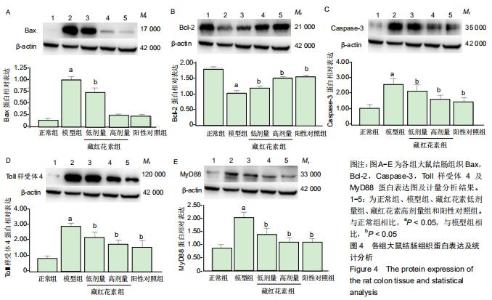
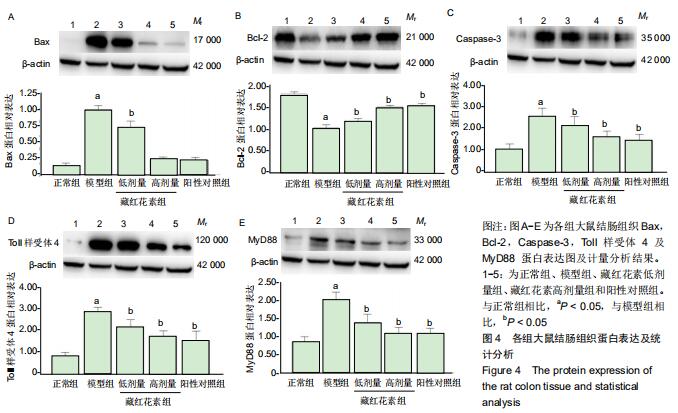
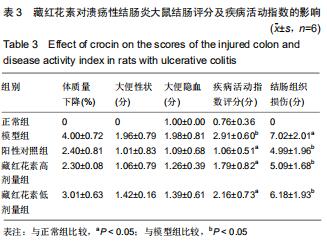
2.2 藏红花素对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠行为学的影响 与正常组比较,模型组于饮用葡聚糖硫酸钠后3 d出现活动量减少,不喜进食,聚成一团,萎靡态,粪便有潜血,肛周黏性物增多且污浊,毛发颜色暗沉;5 d后出现肉眼血便、稀便。大鼠体质量均在第1天有所减轻,但第2天开始体质量增加,各组间无明显差异。藏红花素组及阳性对照组大鼠行为对比模型组,大鼠状态、体质量减轻及腹泻便血症程度较轻。与模型组相比,正常组结肠组织评分及疾病活动指数评分降低(P < 0.05),藏红花素各组及阳性对照组与模型组相比结肠组织评分及疾病活动指数评分降低(P < 0.05)。藏红花素高剂量组与阳性对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表3。 "
| [1] BEVIVINO G, MONTELEONE G. Advances in understanding the role of cytokines in inflammatory boweldisease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;12(9):907-915. [2] CASTRO-DOPICO T, DENNISON TW, FERDINAND JR, et al. Anti-commensal IgG drives intestinal inflammation and type 17 immunity in ulcerative colitis. Immunity. 2019;50(4): 1099-1114. [3] FRIEDRICH M, POHIN M, POWRIE F. Cytokine networks in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Immunity. 2019;50(4):992-1006. [4] NI Y, LIU M, YU H, et al. Desmethylbellidifolin from gentianella acuta ameliorate TNBS-Induced ulcerative colitis through antispasmodic effect and anti-inflammation. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10(9):1-12. [5] NING L, LOU X, ZHANG F, et al. Nuclear receptors in the pathogenesis and management of inflammatory bowel disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019(1):1-13. [6] FAGUNDES DJ, CARRARA FL, TEIXEIRA WA, et al. The role of the exogenous supply of adenosine triphosphate in the expression of Bax and Bcl2L1 genes in intestinal ischemia and reperfusion in rats 1. Acta Cir Bras. 2018;33(10):889-895. [7] HASAN A, AKHTER N, AL-ROUB A, et al. TNF-α in combination with palmitate enhances IL-8 production via The MyD88- Independent TLR4 signaling pathway: potential relevance to metabolic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(17): E4112. [8] LI Z, WANG G, FENG D, et al. Targeting the miR-665-3p-ATG4B-autophagy axis relieves inflammation and apoptosis in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):483. [9] WATANABE T, HIGUCHI K, KOBATA A, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small intestinal damage is Toll-like receptor 4 dependent. Gut. 2007;57(2):181-187. [10] LARUSSA T, IMENEO M, LUZZA F. Olive tree biophenols in inflammatory bowel disease: when bitter is better. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6):1-13. [11] KIM WS, SONG HY, MUSHTAQ S, et al. Therapeutic potential of gamma-irradiated resveratrol in ulcerative colitis via the anti-inflammatory activity and differentiation of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(5):1117-1138. [12] GEDIK S, ERDEMLI ME, GUL M, et al. Investigation of the protective effects of crocin on acrylamide induced small and large intestine damage in rats. Biotech Histochem. 2018; 93(4):267-276. [13] CAO L, XU H, WANG G, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;72(4): 264-274. [14] CHASSAING B, AITKEN JD, MALLESHAPPA M, et al. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2014;104(15):11-14. [15] GAO W, WANG C, YU L, et al. Chlorogenic Acid attenuates dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through MAPK/ERK/JNK pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019(18):1-13. [16] KORANI S, KORANI M, SATHYAPALAN T, et al. Therapeutic effects of Crocin in autoimmune diseases: a review. BioFactors. 2019;45(6):835-843. [17] BING X, XUELEI L, WANWEI D, et al. EGCG Maintains Th1/Th2 balance and mitigates ulcerative colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium through TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappab signaling pathway in rats. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 2017(11):1-9. [18] JEON YD, BANG KS, SHIN MK, et al. Regulatory effects of glycyrrhizae radix extract on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16(1):459. [19] CALABRESI MFF, TANIMOTO A, PRÓSPERO AG, et al. Changes in colonic contractility in response to inflammatory bowel disease: long-term assessment in a model of TNBS-induced inflammation in rats. Life Sci. 2019;236(9):1-8. [20] ZHENG JD, HE Y, YU HY, et al. Unconjugated bilirubin alleviates experimental ulcerative colitis by regulating intestinal barrier function and immune inflammation. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(15):1865-1878. [21] NEURATH MF. IL-23 in inflammatory bowel diseases and colon cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;45(12):1-8. [22] WONG U, CROSS RK. Expert opinion on interleukin-12/23 and interleukin-23 antagonists as potential therapeutic options for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019;28(5):473-479. [23] TOTH S, JONECOVA Z, MARETTA M, et al. The effect of Betanin parenteral pretreatment on Jejunal and pulmonary tissue histological architecture and inflammatory response after Jejunal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;110(10):1-9. [24] POPE MR, HOFFMAN SM, Tomlinson S, et al. Complement regulates TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses during intestinal ischemia reperfusion. Mol Immunol. 2010;48(1-3): 356-364. [25] KAWAI T, AKIRA S. The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int Immunol. 2009;21(4):317-337. [26] BARBALHO SM, BOSSO H, SALZEDAS-PESCININI LM, et al. Green tea: a possibility in the therapeutic approach of inflammatory bowel diseases? Complementary Ther Med. 2019;43(1):148-153. [27] LI B, YAO X, LUO Y, et al. Inhibition of Autophagy Attenuated Intestinal Injury After Intestinal I/R via mTOR Signaling. J Surg Res. 2019;243(3):363-370. [28] YAN Y, LV X, MA J, et al. Simvastatin alleviates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating Omi/HtrA2 signaling pathways. Transplant Proc. 2019;51(8):2798-2807. [29] FAN W, FEI G, LI X, et al. Sera with anti-enteric neuronal antibodies from patients with irritable bowel syndrome promote apoptosis in myenteric neuronsof guinea pigs and human SH-Sy5Y cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;30(12): 1-15. [30] ZU G, ZHOU T, CHE N, et al. Salvianolic Acid A Protects Against OxidativeStress and Apoptosis Induced by Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(6):2320-2332. |
| [1] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [2] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [3] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [4] | Shu Wenbo, Chen Mengchi, Li Hua, Huang Liqian, Huang Binbin, Zhang Wenhai, Wu Yachen, Wang Zefeng, Li Qiaoli, Liu Peng. Correlation between body fat distribution and characteristics of daily physical activity in college students [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1277-1283. |
| [5] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [6] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [7] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [8] | Zeng Zhen, Hu Jingwei, Li Xuan, Tang Linmei, Huang Zhiqiang, Li Mingxing. Quantitative analysis of renal blood flow perfusion using contrast-enhanced ultrasound in rats with hemorrhagic shock during resuscitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1201-1206. |
| [9] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [10] | Chai Le, Lü Jianlan, Hu Jintao, Hu Huahui, Xu Qingjun, Yu Jinwei, Quan Renfu. Signal pathway variation after induction of inflammatory response in rats with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [11] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [12] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [13] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||