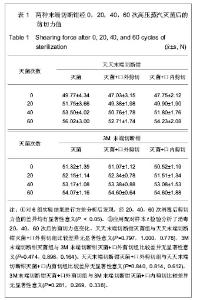
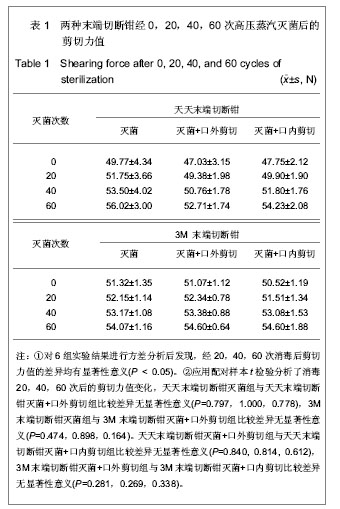
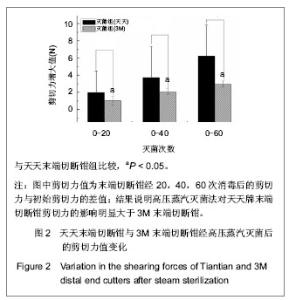
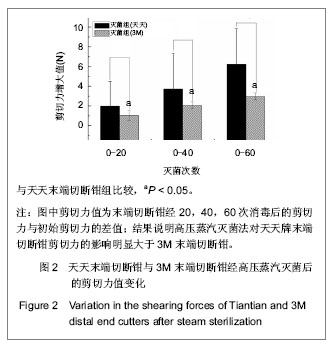
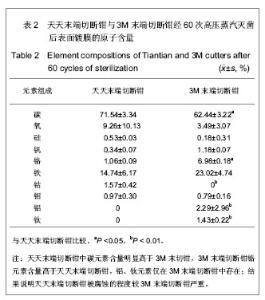
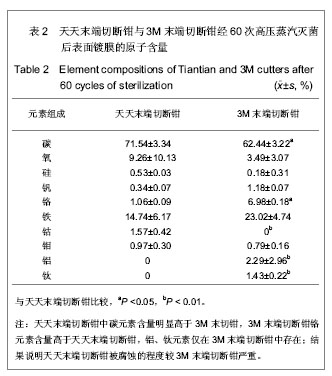
| [1] Liang XF,Chen YS,Wang XJ,et al.A study on the sero-epidemiology of hepatitis B in Chinese population aged over 3-years old. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi.2005; 26(9):655-658.
[2] Tao W,Jiang Y.Evaluation of promoting the oral cavity health measures of rural AIDS patients/HIV-carriers.Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011;46(5):293-296.
[3] Payne GS.Sterilization and disinfection in the orthodontic office: a practical approach. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1986;90(3):250-252.
[4] Crowell WS. Why dental instruments rust and how to prevent it.Dental Cosmo. 1925;67:752-755.
[5] Custer F,Andersen R.A study of surface changes on instruments during sterilization procedures. N Y J Dent. 1968; 38(1):8-17.
[6] Custer F,Coyle T.Instrument changes during sterilization.J Dent Res. 1970;49:487-95.
[7] Custer F,Addington L.Physical changes of instruments during sterilization. J Periodont.1965;36:382-386.
[8] Ginesberg F. High grade surgical instruments must be given high grade care. Mod Hosp.1960;95:96.
[9] Matlack RE. Instrument sterilization in orthodontic offices. Angle Orthod. 1979;49(3):205-211.
[10] Jones ML.An initial assessment of the effect on orthodontic pliers of various sterilization/dis- infection regimes. Br J Orthod. 1989;16:251-258.
[11] Vendrell RJ,Hayden CL,Taloumis LJ.Effect of steam versus dry-heat sterilization on the wear of orthodontic ligature-cutting pliers. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002; 121:467-471.
[12] Stach DJ,Cross-Poline GN,Newman SM, et al. Effect of repeated sterilization and ultrasonic cleaning on curet blades. J Dent Hyg. 1995;69:31-39.
[13] Tal H,Kozlovsky A,Green E,et al.Scanning electron microscope evaluation of wear of stainless steel and high carbon steel curettes.J Periodontol. 1989;60:320-324.
[14] Ward R, Borchert P, Wright A, et al.Hepatitis B antigen in saliva and mouth washings.Lancet. 1972;300(7780):726.
[15] Cottone JA.Hepatitis,in Emphasis.J Am Dent Assoc.1983; 107:918.
[16] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended infection control practices for dentistry MMWR.1993; 42 (RR-8): 1-12.
[17] Custer F,Coyle T.Instrument changes during sterilization,J Dent Res. 1970;49:487-495.
[18] Masunaga MI. Sterilization in orthodontics. Part 3. Corrosion of instruments. J Clin Orthod.1987;21:331-332.
[19] Wichelhaus A, Brauchle G, Mertmann M, et al. Corrosion of orthodontic pliers using different sterilization procedures. J Orofac Orthop.2004;65(6):501-511.
[20] Benyahia H,Merzouk N,Ebn Touhami M,et al.Effects of sterilization and disinfection Procedures on the corrosion of orthodontic ligature cutters.Int Orthod. 2012;10(1):1-15. |