Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (28): 4440-4445.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1329
Previous Articles Next Articles
Risk assessment of hemiarthroplasty and internal fixation of proximal femoral nail antirotation for treating hip fractures in older adults
- Zhengzhou Orthopaedics Hospital, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Online:2019-10-08Published:2019-10-08 -
About author:Zuo Sili, Master, Zhengzhou Orthopaedics Hospital, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zuo Sili. Risk assessment of hemiarthroplasty and internal fixation of proximal femoral nail antirotation for treating hip fractures in older adults[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4440-4445.
share this article
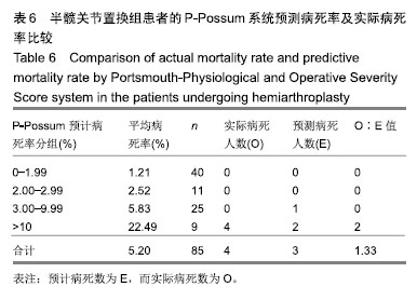
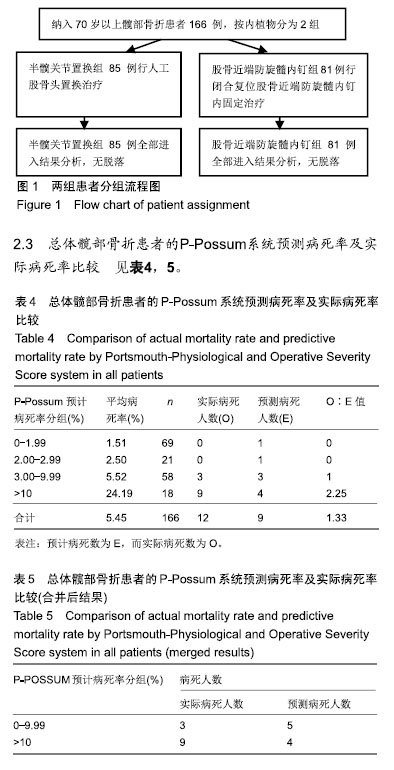
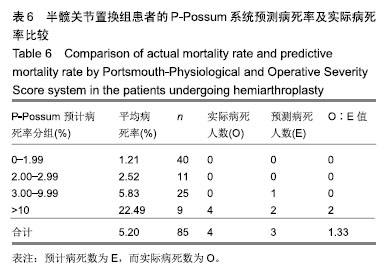
如表4所示,应用P-Possum评分系统计算出每例患者的预测病死率,将它们分为0-1.99%,2.00%-2.99%,3.00%-9.99%,10%以上共计4组,算出对应每组人数分别为69,21,58,18例。各组所有死亡率之和与该组人数的比值即为每组平均病死率,计算出4组分别为1.51%,2.50%,5.52%,24.19%。各组平均病死率×各组人数=各组预测病死人数,各为1,1,3,4例。总的预计病死数为E=9,而实际病死数为O=12,O∶E值为1.33。总预测病死率为5.4%,实际病死率为7.2%。 如表5所示,将O,E分别做χ2检验,因预计病死人数前2个分组中实际病死人数为0,故跟第3组3.00-9.99合并为1组。只对合并后的2个分组做χ2检验,由于总数n < 40,所以用确切概率法,得出P=0.203,差异无显著性意义。表明P-Possum评分系统对2组患者内植物置入的风险都有良好的预测能力。 2.4 半髋关节置换组患者的P-Possum系统预测病死率及实际病死率比较 见表6,7。 如表6所示,用P-Possum评分系统算出半髋关节置换组患者的单个预计病死率,同理将其分为4组分别为0-1.99%,2.00%-2.99%,3.00%-9.99%,10%以上,算出每组人数分别为40,11,25,9例。各组所有病死率叠加之和与该组人数比值=平均病死率,平均病死率各为1.21%,2.52%,5.83%,22.49%,各组平均病死率×该组人数=每组预测病死人数,各为0,0,1,2例。总预计病死人数E=3,查到实际病死人数O=4,O∶E值为1.33。总预测病死率即预计病死人数与总人数比值为3.5%,实际病死率为4.7%。"
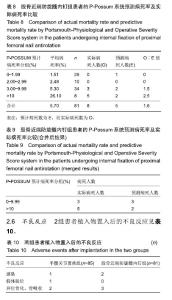
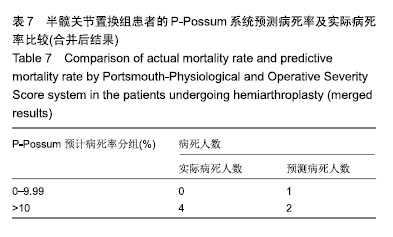
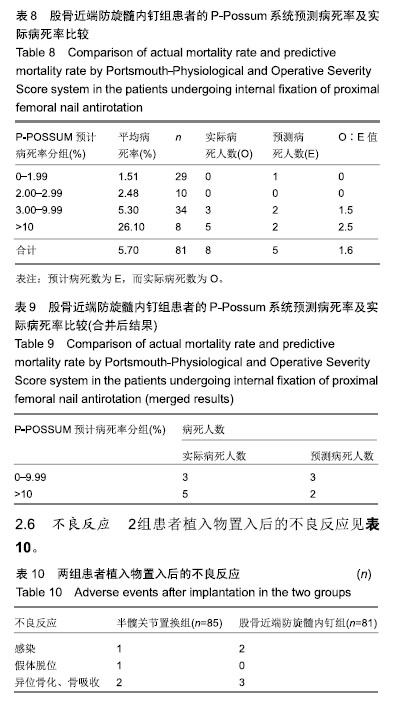
2.5 股骨近端防旋髓内钉组患者的P-Possum系统预测病死率及实际病死率比较 见表8,9。 如表8所示,通过系统算出股骨近端防旋髓内钉组患者中单个患者的预测病死率,将其分为4组分别为0-1.99%,2.00%-2.99%,3.00%-9.99%,10%以上,算出各组人数分别为28,10,33,8例。各组平均病死率=各组所有病死率之和除以该组人数所得值,分别为1.51%,2.48%,5.30%,26.10%,4组平均病死人数=4组平均病死率× 4组人数,分别为1,0,2,2。总预测病死人数E=5,实际病死人数O=8,O∶E值为1.6。总预测病死率为两者比值算出为6.2%,实际病死率为9.9%。 如表9所示,O与E做χ2检验,由于预计病死人数第2组实际与预测病死人数都为0,所以舍弃。另外2组中实际病死人数为0,2组合二为一。只对合并组做χ2检验,由于总数n < 40,所以用确切概率法,得出P > 0.05,差异无显著性意义。说明P-POSSUM评分系统在股骨近端防旋髓内钉组患者病死率预测中同样有良好的预测能力。"
| [1]Neary WD, Heather BP, Earnshaw JJ. The physiological and operative severity score for the enumeration of mortality and morbidity( possum). Br J Surg. 2003;90:157-165.[2]Copeland GP Jones D, Walters M. POSSUM: a scoring system for surgical audit. Br J Surg.1991;78:355-360.[3]Whiteley MS, Prytherch DR, Higgins B, et al. An evaluation of the POSSUM surgical scoring system. Br J of Surg. 1996; 83: 812-815.[4]白晓冬,李强,郭艾. POSSUM系统对老年患者骨科手术风险的预测研究[J]. 中国骨科肿瘤病,2009,8(3):149-153.[5]Mohamed K, Copeland GP. An assessment of the POSSUM system in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg. 2002; 84-B:735-739.[6]de Cássia Braga Ribeiro K, Kowalski LP.APACHE II, POSSUM, and ASA scores and the risk of perioperative complications in patients with oral or oropharyngeal cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;129(7):739-745. [7]Tekkis PP, Kocher HM, Kessaris NJ, et al. How accurate is POSSUM and p-POSSUM in predictingmortality in emergency surgery and in old age. Br J of Surg. 2001;88 (Supp l1): 42-43.[8]张延龄. 外科患者的危机:重点介绍 POSSUM 评分系统[J]. 国外医学(外科学分册),2003,30(5):275.[9]谷贵山,张德宝,白岩. P-POSSUM 评分系统预测骨科手术风险的价值[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2006,5(1):42-48.[10]Copeland GP, Sagar P, Brenaan J, et al. Risk-adjustd analysis of surgeon performance: a year study. Br J of Surg. 1995;85: 408-411 .[11]谷贵山,张博皓,李子川.POSS UM评分系统简介及在骨科推广应用的建议[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2005, 4(3):172-174.[12]饶忠,黄谦,周红菊. 改良POSSUM评分系统预测老年烧伤患者术后并发症的价值[J].广西医科大学学报, 2004,21(1):49-50.[13]谷贵山,张德宝,孙乃坤,等. P-POSSUM和POSSUM评分系统预测老年髋关节置换死亡率和并发症发生率的对比研究[J].中国老年学杂志,2005,25(12):1440-1442.[14]林岳平,林佩达,王友.高龄髋部骨折围手术期死亡原因及时间探讨[J]. 医学研究杂志,2007,36(9):77-79.[15]Rose FR,Oreffo RO.Bone tissue engineering: hope vs hype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2002;292(1):1-7.[16]Karres J, Heesakkers NA, Ultee JM, et al. Predicting 30-day mortality following hip fracture surgery: evaluation of six risk prediction models. Injury. 2015;46(2):371-377. [17]Toson B, Harvey LA, Close JC. The ICD-10 Charlson Comorbidity Index predicted mortality but not resource utilization following hip fracture. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68(1): 44-51. [18]Makary MA, Segev DL, Pronovost PJ, et al. Frailty as a predictor of surgical outcomes in older patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210(6):901-908. [19]van Zeeland ML, Genovesi IP, Mulder JW, et al. POSSUM predicts hospital mortality and long-term survival in patients with hip fractures. J Trauma. 2011;70(4):E67-72.[20]Merad F, Baron G, Pasquet B, et al. Prospective evaluation of in-hospital mortality with the P-POSSUM scoring system in patients undergoing major digestive surgery. World J Surg. 2012;36(10):2320-2327. [21]Midwinter MJ, Ashley S. An evaluation of the POSSUM surgical scoring system. Br J Surg. Br J Surg. 1996;83(11): 1653.[22]Revenig LM, Canter DJ, Taylor MD, et al. Initial results of a large multidisciplinary prospective study examining pre-operative variables predictive of poor surgical outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 2013.[23]Sohail I, Jonker L, Stanton A, et al. Physiological POSSUM as an indicator for long-term survival in vascular surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2013;46(2):223-226.[24]Menendez ME, Neuhaus V, van Dijk CN, et al. The elixhauser comorbidity method outperforms the charlson index in predicting inpatient death after orthopaedic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(9):2878-2886.[25]Hu F, Jiang C, Shen J, et al. Preoperative predictors for mortality following hip fracture surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Injury. 2012;43(6):676-685.[26]Gunasekera N, Boulton C, Morris C, et al. Hip fracture audit: the Nottingham experience. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(Suppl 4):S647-653.[27]Brooks MJ, Sutton R, Sarin S. Comparison of Surgical Risk Score, POSSUM and p-POSSUM in higher‐risk surgical patients. Br J Surg. 2005;92(10):1288-1292.[28]Makary MA, Segev DL, Pronovost PJ, et al. Frailty as a predictor of surgical outcomes in older patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210(6):901-908.[29]Wright DM, Blanckley S, Stewart GJ, et al. The use of orthopaedic POSSUM as an audit tool for fractured neck of femur. Injury. 2008;39(4):430-435.[30]Moppett IK, Parker M, Griffiths R, et al. Nottingham Hip Fracture Score: longitudinal and multi-assessment. Br J Anaesth. 2012;109(4):546-550. |
| [1] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [2] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [3] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [4] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| [5] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [6] | Cheng Shigao, , Wang Wanchun, Jiang Dong, Li Tengfei, Li Xun, Ren Lian. Comparison of the standard and long-stem bone cement prosthesis replacement in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 362-367. |
| [7] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [8] | Cai Qunbin, Yang Lijuan, Li Qiumin, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei . Feasibility of internal fixation removal of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients based on fracture mechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3313-3318. |
| [9] | Wang Hao, Wang Yitao, Lü Zexiang, Li Tengfei, Wang Shaolong, Wang Yehua. Effect of repeated intravenous tranexamic acid in the perioperative period of proximal femoral nail antirotation for femoral intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3319-3323. |
| [10] | Tian Kechao, Wang Lei, Tao Yong, Yao Tao. Proximal femoral nail antirotation combined with posteromedial wall reconstruction for the treatment of type A2 intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3337-3342. |
| [11] | Song Kaikai, Du Gangqiang, Li Peng, Jiang Shengyuan, Gong Zhihao, Zhang Zhiwei, Zhang Kai . Application of head-neck ratio in the treatment of femoral neck fracture in aged patients with artificial femoral head replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2805-2809. |
| [12] | Li Haifeng, Liu Yu, Yin Qudong, Sun Zhenzhong, Rui Yongjun, Gu Sanjun. Risk of complications of early postoperative weight-bearing after internal fixation of intracapsular femoral neck fractures: 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2875-2880. |
| [13] | Yang Kun, Fei Chen, Wang Pengfei, Zhang Binfei, Yang Na, Tian Ding, Zhuang Yan, Zhang Kun . Meta-analysis of the efficacy of robot-assisted and traditional manual implantation of cannulated screws in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2938-2944. |
| [14] | Fan Zhirong, Su Haitao, Zhou Lin, Huang Huida, Zhou Junde, Jiang Tao, Liu Zitao. Finite element analysis of novel femoral neck system for unstable femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2321-2328. |
| [15] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||