Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanical and biodegradable properties of absorbable hydroxyapatite/ poly-DL-lactide screws
Fu Rong1, You Xiao-bo1, Zhong Zhen-dong2, Li Yan3, 4
- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; 2Experimental Animal Research Institute, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Chengdu Army General Hospital, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China; 4Disease Prevention and Control Center of Chengdu Military Region, Chengdu 610021, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2013-02-18Revised:2013-02-26Online:2013-09-17Published:2013-09-17 -
Contact:Li Yan, Attending physician, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Chengdu Army General Hospital, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China; Disease Prevention and Control Center of Chengdu Military Region, Chengdu 610021, Sichuan Province, China doctoryanli@yahoo.cn -
About author:李焰,主治医师,解放军成都军区总医院口腔科,四川省成都市 610083 doctoryanli@yahoo.cn -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, No. 2001Z021*; the Health Department of Sichuan Province, No. 100526*, 100086*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fu Rong, You Xiao-bo, Zhong Zhen-dong, Li Yan. Mechanical and biodegradable properties of absorbable hydroxyapatite/ poly-DL-lactide screws[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.38.002.
share this article
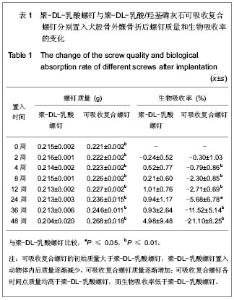
2.1 实验动物数量分析 42只犬均进入结果分析。 2.2 各组大体观察结果 置入后1周内所有动物能够站立行走,2周时所有动物关节功能基本恢复正常,肢体无短缩等畸形。动物左后肢和右后肢的恢复时间及功能表现无明显差异。所有受试犬生活状态良好,进食进水、尿便、体质量正常,精神状态良好,未见深部组织感染,未见异物炎性反应表现。 2.3 各组X射线摄片结果 各组动物手术后当天X射线显示双侧内固定良好,骨折线清晰,复合螺钉显影稍明显,可见螺钉孔道影。第2周时,实验组与对照组骨折固定佳,均无移位,骨折线稍模糊,骨痂生长不明显,“+”-“++”;第4周时,两组骨折无移位,骨痂量稍增多,螺钉孔道开始模糊,“++”-“+++”;第8周时,骨折区密度增高,螺钉孔道影模糊,“+++”-“++++”;第12周时,骨痂密度增高,仍可见螺钉孔道影,“+++”-“++++”。第24周时,两组骨折区新骨生长良好,骨折愈合,螺钉孔道影不明显,“++++”。第36,48周显示双侧骨折区新骨生长良好。 2.4 两种螺钉质量和生物吸收率的比较 两种螺钉置入后质量和生物吸收率随时间的变化情况,见表1。"
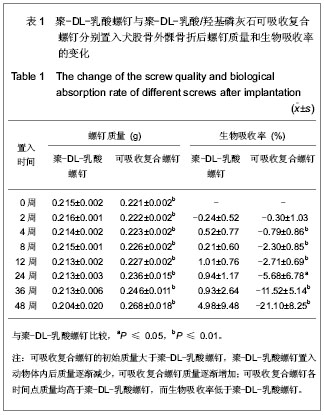

由表1可以看出,可吸收复合螺钉的初始质量大于聚-DL-乳酸螺钉,聚-DL-乳酸螺钉置入动物体内后质量逐渐减少,可吸收复合螺钉质量逐渐增加。聚-DL-乳酸螺钉置入后质量下降缓慢,生物吸收率缓慢增加;可吸收复合螺钉置入动物体后质量逐渐增加,各时间段与聚-DL-乳酸螺钉比较差异有非常显著性意义(P ≤ 0.01),提示可吸收复合螺钉在材料上改进对生物吸收率产生了一定影响。 2.5 两种螺钉抗弯强度及强度衰减率的比较 两种螺钉置入后抗弯强度及强度衰减率随时间变化情况,见表2。 由表2可以看出,可吸收复合螺钉的初始抗弯强度高于聚-DL-乳酸螺钉,置入后两组螺钉强度均逐渐降低。聚-DL-乳酸螺钉抗弯强度置入后2周开始下降,在前8周强度衰减较平缓,8周后强度衰减速度加快,至第48周时强度降至最低,衰减率为39.51%。可吸收复合螺钉强度衰减在前4周较平缓,4周后衰减速度加快,至第48周时衰减率为58.42%,可吸收复合螺钉的抗弯强度与聚-DL-乳酸螺钉比较,在骨折固定前8周能维持较高水平。"
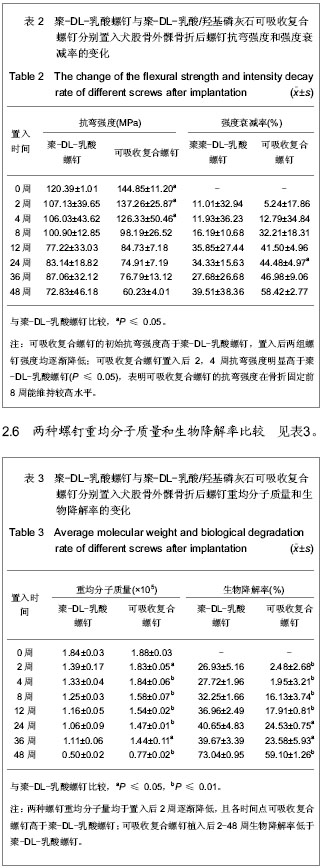
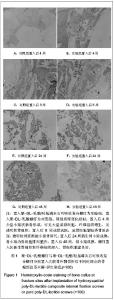
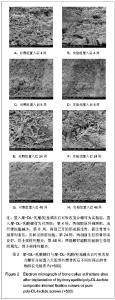
由表3可以看出,聚-DL-乳酸螺钉和可吸收复合螺钉的初始重均分子质量差别不大,均从置入后2周起逐渐降低,8周后降解加快,至48周时,两组螺钉重均分子质量均降至最低。聚-DL-乳酸螺钉的重均分子质量较可吸收复合螺钉降低速度快,生物降解率在各个时间段高于可吸收复合螺钉(P ≤ 0.05或P ≤ 0.01)。 2.7 各组组织学观察结果 骨折愈合:两组骨折均固定良好,无移位。置入后解剖观察实验组骨折处缝隙较小,随置入时间延长,骨折线逐渐模糊,直至基本消失,提示骨折愈合良好,无延迟愈合及不愈合情况。两组螺钉置入钉道清晰,提示螺钉固定良好。 螺钉观察:实验组螺钉初始外观呈乳白色,不透明,对照组螺钉初始外观呈透明状,光泽度良好。置入后2周时,两组螺钉固定良好,未出现断裂、弯曲现象,容易从固定部位完整取出,螺钉外观无明显变化。置入后4周时,两组螺钉固定良好,无断裂弯曲,能完整取出,对照组螺钉表面开始变白。 置入后8周时,两组螺钉固定良好,无断裂弯曲,表面螺纹吸收变钝,螺杆表面稍粗糙,对照组螺钉变白。随植入时间延长,两组螺钉表面螺纹吸收缺损明显,螺杆表面明显粗糙,对照组螺钉透明度明显降低呈白色。置入后12周时,两组螺钉表面粗糙,螺纹吸收缺损,对照组螺钉表面明显变白。 置入后24周时,两组螺钉表面明显粗糙,螺纹缺损,光泽度差,对照组螺钉透明度明显降低,呈乳白色,出现断裂。置入后36周时,两组螺钉取出困难,均出现断裂,表面明显粗糙,螺纹缺损明显,断裂面不平整,无光泽,对照组螺钉呈乳白色。置入后48周时,两组螺钉取出困难,断裂现象明显,表面螺纹缺损明显,无光泽,对照组螺钉呈明显乳白色。 骨组织光镜观察:两组置入后2周均可见炎症反应,肉芽组织内充满成纤维细胞,可见中性粒细胞,实验组炎症反应较轻。置入后4周少量小梁状新骨形成,可见大量成骨细胞,纤维组织增生,见透明软骨组织,类骨质薄。 置入后8周成骨活跃,成骨细胞紧贴类骨质表面,类骨质丰富,透明软骨逐渐被小梁骨替代。置入后12周新生骨小梁趋于成熟,互相连接,排列有序。骨小梁内骨细胞排列整齐,软骨基本被小梁骨取代。 置入后24周新生骨小梁成熟,互相连接,排列有序。可见较多的新生骨质和多核骨巨细胞,类骨质覆盖均匀,骨小梁内骨细胞排列整齐。置入后36周骨小梁成熟,粗大,互相连接,排列有序。置入后48周,骨小梁成熟,有序排列,螺钉置入区新生骨组织和纤维组织浸入,骨组织重建良好。两组呈现相似病理变化,骨折愈合,骨组织重建良好,见图1。"
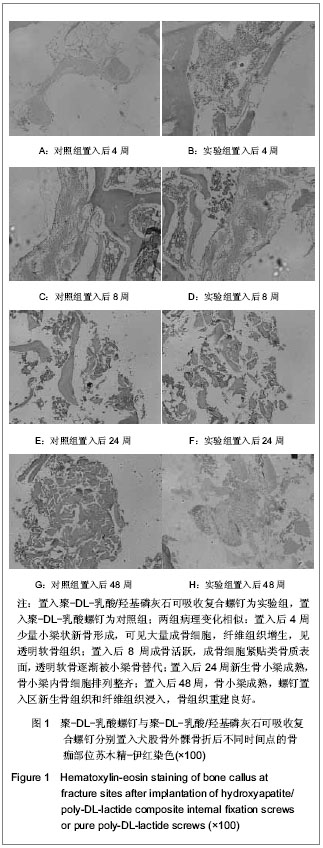
| [1] Bostman O,Vainionpaa S,Hirvensalo E,et al. Biodegradable internal fixation for malleolar fractures. J Bone Joint Surg. 1987;69(4): 615. [2] Dijkema AR,van der Elst M,Breederveld RS,et al. Surgical treatment of fracture-dislocations of the ankle joint with biodegradable implants: a prospective randomized study. J Trauma.1993;34(1): 82. [3] Landes CA,Ballon A.Indications and limitations in resorbable P(L70/30DL)LA osteosyntheses of displaced mandibular fractures in 4.5-year follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg.2006;117(2): 577-587; discussion 588-589. [4] Ferretti C.A prospective trial of poly-L-lactic/polyglycolic acid co-polymer plates and screws for internal fixation of mandibular fractures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2008;37(3): 242-248. [5] Habal MB.Triad of system applications for absorbable rigid fixation of the craniofacial skeleton.J Craniofac Surg.1996; 7(5): 394-398. [6] Cohen SR,Holmes RE,Amis P,et al, Tacks: a new technique for craniofacial fixation. J Craniofac Surg.2001;12(6): 596-602. [7] Brady JM,Cutright DE,Miller RA,et al. Resorption rate,route of elimination and ultrastructure of the implant site of polylactic acid in the abdominal wall of the rat. J Biomed Mater Res.1973;7(2):155. [8] Miller RA,Brady JM,Cutright DE.Degradation rates of oral resorbable implants(polylactates and polyglycolates): rate modification with changes in PLA/PGA copolymer ratios. J Biomed Mater Res.1977;11(5):711. [9] 王云华,何斌.DIKFIX可吸收螺钉治疗关节部位骨折的临床观察[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2006,3(3):37-38. [10] 张国富,柯雯县,段军.PDLLA可吸收螺钉治疗四肢松质骨骨折76例[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2005,26(6):775-777. [11] 彭国常.使用聚D乳酸可吸收螺钉治疗内踝骨折的疗效观察[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2007,27(2):294-295. [12] 肖军,杨述华,许伟华,等.国产超高分子聚乳酸可吸收螺钉治疗髌骨骨折术后下肢功能评定[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(42):60-63. [13] 曾庆敏,张新潮,尹望平.国产聚-DL-乳酸可吸收螺钉治疗关节内股骨髁骨折探讨[J].中华现代外科学杂志,2005,2(1):25-27. [14] 唐根林,郭曙光,陈守来.国产可吸收螺钉在关节周围骨折内固定中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(12):852-853. [15] Jeon O,Rhie JW,Kwon IK,et al.In vivo bone formation following transplantation of human adipose-derived stromal cells that are not differentiated osteogenically. Tissue Eng Part A.2008;14(8): 1285-1294. [16] Sato M,Slamovich EB,Webster TJ.Enhanced osteoblast adhesion on hydrothermally treated hydroxyapatite/ titania/poly(lactide-co-glycolide) sol-gel titanium coatings. Biomaterials.2005;26(12): 1349-1357. [17] Blaker JJ,Gough JE,Maquet V,et al. In vitro evaluation of novel bioactive composites based on Bioglass-filled polylactide foams for bone tissue engineering scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A.2003;67(4): 1401-1411. [18] Mollaoglu N,Cetiner S,Alpaslan C,et al.The early tissue response to titanium and LactoSorb screws. Dent Traumatol. 2003;19(3): 139-144. [19] 邹季.骨折愈合实验研究中动物模型选择的有关问题[J].湖北中医学院学报,2002,4(2):25-27. [20] Prokop A, Höfl A, Hellmich M, et al.Degradation of poly-L/DL-Lactide versus TCP Composite Pins: A Three-Year Animal Study. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005; 75(2): 304-310. [21] 魏鸿文,蔡瑞莹,郑成功.可降解骨螺钉强度衰减体外测试模式的建立[J].医用生物力学,2000,15(3):130. [22] Wang WJ,Xu LW,Yu HP,et al.Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi.1998;4(9):35.王维佳,许林薇,俞杭平,等.补肾活血中药促进骨折愈合的实验研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,1998, 4(9): 35. [23] Tams J,Joziasse CA,Bos RR,et al.High-impact poly (L/D-lactide) for fracture fixation: in vitro degradation and animal pilot study. Biomaterials.1995;16: 1409-1415. [24] An YH,Friedman RJ,Powers DL,et al.Fixation of Osteotomies using Bioabsorbable Serews in the Canine Femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(355):300-311. [25] Tuompo P,Paritio EK,Pätiälä H,et al.Causes of the clinical tissue response to polyglycolide and polylactide implants with an emphasis on the knee. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2001; 121:261-264. [26] 林献章,金大地,王立,等.生物降解聚丙交酯(PLA)栓内固定治疗犬股骨髁部骨折的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1996,16(10): 659-661. [27] Honig S.Osteoporosis - new treatments and updates. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2010;68(3): 166-170. [28] Lacativa PG, Farias ML.Osteoporosis and inflammation. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2010;54(2): 123-132. [29] 孙仁贵,陈冠群.实验性骨折愈合的扫描电镜观察[J].中华骨科杂志,1993,13(2):368. [30] Uhthoff HK,Goto S,Cerckel PH. Influence of stable fixation on trabecular bone healing: a morphologic assessment in dogs.J Orthop Res.1987;5:14. [31] Miles BA,Goldstein DP,Gilbert RW,et al. Mandible reconstruction. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2010; 18(4): 317-322. [32] Eppley BL.Zygomaticomaxillary fracture repair with resorbable plates and screws. J Craniofac Surg.2000;11(4): 377-385. [33] 陈海云,王羽丰,林定坤,等.OBIF棒内固定治疗家兔股骨髁骨折的实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2007,36(7):786-790. [34] 丰强,闵思佳,张海萍,等.羟基磷灰石及其复合材料在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].蚕桑通报,2008,39(1):10. [35] Verheyen C,Wijn J,Blitterswijk C,et al. Hydroxylapatite poly(L-lactide) composite: an animal study on push-out strenths and interface histology. J Biomed Mater Res.1993;27: 433-434. [36] Deng X,Hao J,Wang C.Preparation and mechanical properties of nanocomposites of poly (D,L- lactide) with Ca- deficient hydroxyapatite nanocrystals. Biomaterials.2001; 22(21):2867-2873. [37] Wittwer G,Adeyemo WL,Voracek M,et al.An evaluation of the clinical application of three different biodegradable osteosynthesis materials for the fixation of zygomatic fractures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100(6): 656-660. [38] Bähr W,Stricker A,Gutwald R,et al.Biodegradable osteosynthesis material for stabilization of midface fractures: experimental investigation in sheep. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1999;27(1): 51-57. [39] Suuronen R,Kallela I,Lindqvist C.Bioabsorbable plates and screws: Current state of the art in facial fracture repair. J Craniomaxillofac Trauma. 2000;6(1): 19-27; discussion 28-30. [40] Collinge CA,Stern S,Cordes S,et al.Mechanical properties of small fragment screws. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2000;(373): 277-284. [41] Persons BL,Wong GB.Transantral endoscopic orbital floor repair using resorbable plate. J Craniofac Surg.2002;13(3): 483-488; discussion 488-489. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||