Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (35): 6314-6320.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.35.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relative factors for osteonecrosis in the Chinese systemic lupus erythematosus patients: Meta-analysis
Luo Zheng-liang, Shang Xi-fu, Li Xu, Hu Fei, He Rui
- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Anhui Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230001, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2013-04-02Revised:2013-04-10Online:2013-08-27Published:2013-08-27 -
Contact:Shang Xi-fu, M.D., Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Anhui Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230001, Anhui Province, China shangxifu@163.com -
About author:Luo Zheng-liang★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Anhui Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230001, Anhui Province, China luozl0551@gmail.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Zheng-liang, Shang Xi-fu, Li Xu, Hu Fei, He Rui. Relative factors for osteonecrosis in the Chinese systemic lupus erythematosus patients: Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(35): 6314-6320.
share this article

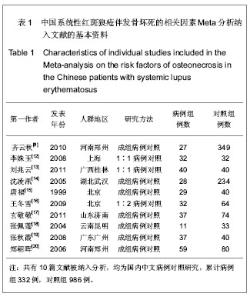
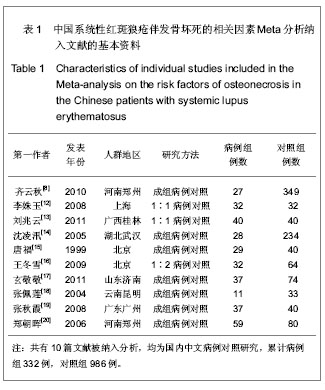
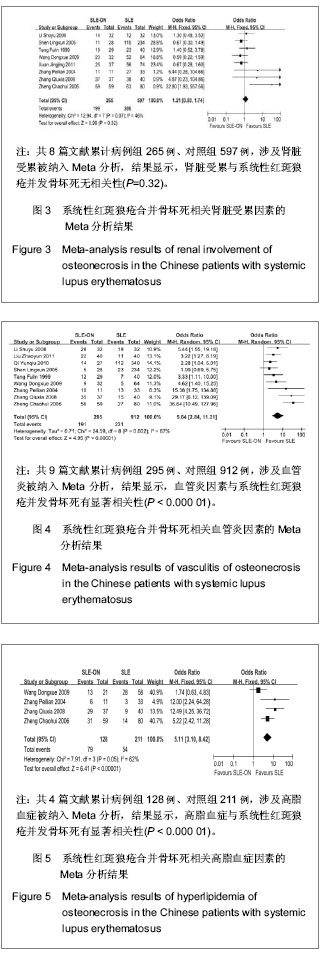
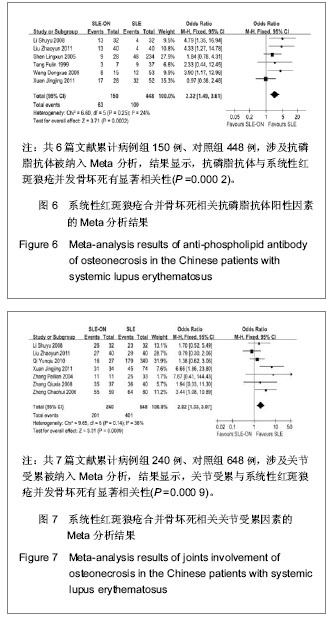
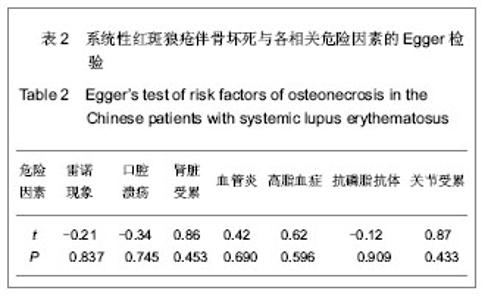
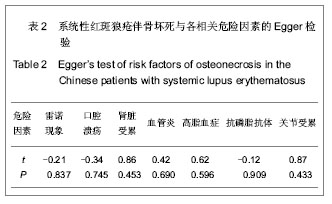
2.2 系统性红斑狼疮合并骨坏死各危险因素的Meta分析 将纳入的文章数据提取后,经RevMan 5.0软件检验各相关危险因素的异质性结果如下:雷诺现象(P < 0.0001,I2=77%),口腔溃疡(P=0.08,I2=47%),肾脏受累(P=0.07,I2=46%),血管炎因素(P=0.002,I2=67%),高脂血症(P=0.05,I2=62%),抗磷脂抗体(P=0.25,I2=24%),关节受累(P=0.14,I2=38%)。由此可见,雷诺现象和血管炎因素研究间存在明显的异质性,余研究因素的各研究间无明显异质性;故前二者采用随机效应模型进行分析,其余采用固定效应模型进行分析,见图1-7。经RevMan 5.0软件分析后各个相关危险因素的合并OR值、95%CI及P值如下:雷诺现象3.28(1.69-6.38),P=0.000 5;口腔溃疡2.95(2.13-4.09),P < 0.000 01;肾脏受累1.21(0.83-1.74),P=0.32;血管炎因素5.64 (2.84-11.21),P < 0.000 01;高脂血症5.11(3.10-8.42),P < 0.000 01;抗磷脂抗体2.32(1.49-3.61),P=0.000 2;关节受累2.02(1.33-3.07),P=0.000 9。因此,除肾脏受累未显示统计学意义外,余系统性红斑狼疮患者的自身因素均提示与系统性红斑狼疮并发骨坏死有显著相关性,见图1-7。"
| [1] Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(22): 2110-2121.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22129255[2] Pickering MC, Botto M, Taylor PR, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus, complement deficiency, and apoptosis. Adv Immunol. 2001;76: 227-324.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11079100[3] Gordon C. Long‐term complications of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41(10): 1095-1100.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12364626[4] D'Cruz DP, 张卓莉. 系统性红斑狼疮[J]. 英国医学杂志: 中文版, 2006, 9(4): 236-241.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=12&CurRec=8&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=YGYX200604022&urlid=&yx=[5] Jones LC, Hungerford DS. The pathogenesis of osteonecrosis. Instr Course Lect. 2007;56:179-196.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Jones+L+C%2C+Hungerford+D+S.+The+pathogenesis+of+osteonecrosis%5BJ%5D.+Instructional+course+lectures%2C+2007%2C+56%3A+179.[6] Zizic TM, Hungerford DS, Stevens MB. Ischemic bone necrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. II. The early diagnosis of ischemic necrosis of bone. Medicine. 1980;59(2): 134-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7360041[7] Abu-Shakra M, Buskila D, Shoenfeld Y. Osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2003;25(1): 13-24.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?cmd=HistorySearch&querykey=7[8] 齐云秋, 程敬亮, 潘芦翎, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮患者并发股骨头坏死危险因素研究[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2010, 27(12): 1937-1939.http://210.45.242.22/WFknowledgeServer_Mirror/D/Periodical_zhsywk201012060.aspx[9] Johnson AE, Gordon C, Palmer RG, et al. The prevalence and incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus in Birmingham, England. Relationship to ethnicity and country of birth. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38(4): 551-558.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7718010[10] Hedges LV, Pigott TD. The power of statistical tests in meta-analysis. Psychol Methods. 2001;6(3):203-217.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=(%22Psychological%20methods%22%5BJournal%5D)%20AND%20Fixed-and%20random-effects%20models%20in%20meta-analysis[11] Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109): 629-634.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Egger+M%2C+Smith+G+D%2C+Schneider+M%2C+et+al.+Bias+in+meta-analysis+detected+by+a+simple%2C+graphical+test%5BJ%5D.+Bmj%2C+1997%2C+315(7109)%3A+629-634.[12] 李姝玉, 胡大伟. 系统性红斑狼疮并发无菌性股骨头坏死的相关因素分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2008, 14(5): 324-327.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=3&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=ZGZS200805007&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhdkF0Rk4yakozWGhobUVseDZVRTNVOXZhQ3NFTGFsWU1YK0NlbU1RTzM1eUxpdSs0PQ==[13] 刘兆云, 赵铖, 米存东, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头缺血性坏死相关因素分析[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2011, 27(7): 1226-1228.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=9&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD1112&filename=SYYZ201107041&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhdkF0Rk4yakozWGhobUVseDZVRTNVOXZhQ3NFTGFsWU1YK0NlbU1RTzM1eUxpdSs0PQ==[14]沈凌汛, 夏菲, 余立凯, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮患者并发无菌性骨坏死的调查分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2005, 9(1):20-23.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=3&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0305&filename=FSBZ200501007&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhcEFjU3VlY3FPeExNZlpyYVNGRWFZM0FKd2kwbEJhc2RRNGhwV2ttOTFMRTMvLzk4PQ==[15] 唐福林, 金聂, 吴敏, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮并发无菌性骨坏死的危险因素分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 1999, 3(3):166-168.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=3&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD9902&filename=FSBZ199903010&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[16]王冬雪, 李桂叶, 马丽, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮并发无菌性股骨头坏死的临床研究[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2009, 48(11):926-929.http://210.45.242.22/WFknowledgeServer_Mirror/D/Periodical_zhnk200911009.aspx[17]玄敬敬, 张源潮, 杨清锐. 系统性红斑狼疮合并无菌性股骨头坏死的危险因素分析[J]. 山东大学学报: 医学版, 2011, 49(3):109-114.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=23&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD1112&filename=SDYB201103027&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[18]张佩莲, 冒长峙, 李学平, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死11例[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2004, 37(6):366.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=28&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0305&filename=ZHPF200406026&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[19]张秋霞, 陈镇秋. 系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头缺血性坏死的相关性临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2008, 40(8):27-28.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=34&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=REND200808018&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[20]郑朝晖, 赵占正, 刘章锁. 系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头坏死相关因素分析[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2006, 6(17):3311-3312.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=38&CurRec=1&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD0608&filename=ZWZX200617024&urlid=&yx=&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FiNDFMOWU4V3Q2RjNUU094bCtGYkRGK24rTmRDckZ1TnRmOUc4MEdXbHhRNHExa2trPQ==[21] Asherson RA, Liote F, Page B, et al. Avascular necrosis of bone and antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(2): 284-288.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8474066[22] Gladman DD, Chaudhry-Ahluwalia V, Ibañez D, et al. Outcomes of symptomatic osteonecrosis in 95 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(10): 2226-2229.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Gladman+DD%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+Outcomes+of+symptomatic+osteonecrosis+in+95+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus[23] Sayarlioglu M, Yuzbasioglu N, Inanc M, et al. Risk factors for avascular bone necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(1): 177-182.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Sayarlioglu+M%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+Risk+factors+for+avascular+bone+necrosis+in+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus[24] Weinstein RS. Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis. Endocrine. 2012;41(2): 183-190.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22169965[25] Assouline-Dayan Y, Chang C, Greenspan A, et al. Pathogenesis and natural history of osteonecrosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002;32(2): 94-124.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=(Assouline-Dayan%20Y%5BAuthor%5D)%20AND%20(Pathogenesis%20and%20natural%20history%20of%20osteonecrosis)[26] Jones JP Jr. Intravascular coagulation and osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;277: 41-53.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1532547[27] Oinuma K, Harada Y, Nawata Y, et al. Osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus develops very early after starting high dose corticosteroid treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(12): 1145-1148.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11709458[28] Colwell CW Jr, Robinson CA, Stevenson DD, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients with inflammatory arthritis or asthma receiving corticosteroid therapy. Orthopedics. 1996;19(11): 941-946.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8936529[29] Mok CC, Lau CS, Wong RW. Risk factors for avascular bone necrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol.1998;37(8): 895-900.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9734682[30] Leventhal GH, Dorfman HD. Aseptic necrosis of bone in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1974;4(1): 73-93.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4846262[31] Fialho SCMS, Bonfa E, Vitule LF, et al. Disease activity as a major risk factor for osteonecrosis in early systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2007;16(4): 239-244.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Fialho+SCMS%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+(Disease+activity+as+a+major+risk+factor+for+osteonecrosis+in+early+systemic+lupus+erythematosus)[32] Sari RA, Polat MF, Taysi S, et al. Serum lipoprotein (a) level and its clinical significance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2002;21(6): 520-524.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=(Sar%C4%B1+RA%5BAuthor%5D)+AND+(Serum+lipoprotein+(a)+level+and+its+clinical+significance+in+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus)[33] Houssiau FA, Toukap ANZ, Depresseux G, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-detected avascular osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: lack of correlation with antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37(4): 448-453.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Magnetic+resonance+imaging-detected+avascular+osteonecrosis+in+systemic+lupus+erythematosus%3A+lack+of+correlation+with+antiphospholipid+antibodies[34] Mok MY, Farewell VT, Isenberg DA. Risk factors for avascular necrosis of bone in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Is there a role for antiphospholipid antibodies? Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(6): 462-467.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Risk+factors+for+avascular+necrosis+of+bone+in+patients+with+systemic+lupus+erythematosus%3A+Is+there+a+role+for+antiphospholipid+antibodies[35] Tektonidou MG, Malagari K, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, et al. Asymptomatic avascular necrosis in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome in the absence of corticosteroid use: a prospective study by magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(3): 732-736.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Asymptomatic+avascular+necrosis+in+patients+with+primary+antiphospholipid+syndrome+in+the+absence+of+corticosteroid+use%3A+a+prospective+study+by+magnetic+resonance+imaging[36] Nagasawa K, Ishii Y, Mayumi T, et al. Avascular necrosis of bone in systemic lupus erythematosus: possible role of haemostatic abnormalities. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989;48(8): 672-676.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2506841[37] Nagasawa K, Tada Y, Koarada S, et al. Prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus by anti-coagulant. Lupus. 2006;15(6): 354-357.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16830881[38] Smith FE, Sweet DE, Brunner CM, et al. Avascular necrosis in SLE. An apparent predilection for young patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976;35(3): 227-232.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Avascular+necrosis+in+SLE.+An+apparent+predilection+for+young+patients[39] Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Chaudhry-Ahluwalia V, et al. Predictive factors for symptomatic osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(4): 761-765.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11327247[40] Calvo-Alén J, McGwin G, Toloza S, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA): XXIV. Cytotoxic treatment is an additional risk factor for the development of symptomatic osteonecrosis in lupus patients: results of a nested matched case–control study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(6): 785-790.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Systemic+lupus+erythematosus+in+a+multiethnic+US+cohort+(LUMINA)%3A+XXIV.+Cytotoxic+treatment+is+an+additional+risk+factor+for+the+development+of+symptomatic+osteonecrosis+in+lupus+patients%3A+results+of+a+nested+matched+case%E2%80%93control+study[41] DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7(3): 177-188.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed |
| [1] | Ye Xiang-yang, Sun Xiang, Tang Li-xin, Zhen Ping, Geng Bin, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo. Acetabular liner wear of cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene for total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1143-1148. |
| [2] | Zhang Tai-liang, Zhang Lei, Lian Zhi-ming, Yang Guang-zhong. Effect of remnant preservation on recovery of knee proprioception in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 471-477. |
| [3] | Zha Yuan-yu, Yang Yang, Chen Shu-zhen, Wei Ren-xiong, Zhang Shu-wei, Jin Wei. Meta-analysis of posterior laminectomy and instrumented fusion versus laminoplasty in treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 485-492. |
| [4] | Hu Bing-yan, Ai Jin-wei, Chen Qiong, Yao Zhong-jun . InterTan nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for femoral intertrochanteric fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 8010-8021. |
| [5] | Zha Yuan-yu, Yang Yang, Zhou Yi-chi, Wei Ren-xiong, Zhang Shu-wei, Jin Wei. Meta-analysis of anterior screw fixation versus posterior cervical fusion in treatment of odontoid fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7288-7296. |
| [6] | Xie Yu, Zhang Cheng-huan, Liu Yun. Mechanical device for prevention of deep vein thrombosis on patient compliance: a meta-analysis based on observational studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5304-5312. |
| [7] | Zhou Kai-di, Wang Hong-yi, Yan Yu-fei, Hong Wei-xiang, Feng Jian-min. Clinical outcomes of intra-articular route versus intravenous route of tranexamic acid during total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5313-5320. |
| [8] | Wang Xin . Meta-analysis of death risk factors for hip fracture in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3929-3937. |
| [9] |
Ye Yong, Li Jun, Jing Jue-hua.
Meta-analysis of titanium plate and elastic intramedullary nail in the treatment of midshaft clavicular fractures
|
| [10] | Yang Sen, Xu Tao, Sheng Wei-bin, Wang Guo-qi, Guo Hai-long . A systematic review on unilateral versus bilateral kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1306-1312. |
| [11] | Li Zhong-hai, Hou Shu-xun, Li Li, Tang Jia-guang, Ren Dong-feng, Zhao Yan-tao. Biomechanical change in adjacent segments after cervical fusion and non-fusion: a meta-analysis of second surgery rate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 642-647. |
| [12] | Zhao Zhen-qun, Liu Wan-lin, Gong Yu-lin, Bai Rui, Wang Wen-xuan. DNA oxidative damage to bone marrow hematopoietic cells and apoptosis of osteocytes in early avascular necrosis of the femoral head induced by glucocorticoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1652-1657. |
| [13] | Lu Yun-xiang, Chen Yu-xian, Zhuang Ze, Ren Jian-hua, Peng You, Shi De-hai, Wang Kun, Li Zhi-yong. Medical TH adhesive embolism for establishing a rabbit model of ischemic necrosis of lunate bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 663-668. |
| [14] | Liu Bing-gen, Pang Qing-jiang. Meta-analysis of therapeutic effects of computer-assisted navigation versus conventional total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(40): 6542-6547. |
| [15] | Wang Zhi-zhou, Qu Guang-hua, Han Ya-jun, Xu Chao, Yilihamu•Tuoheti. Meta-analysis on endobutton plate versus the other fixation methods for acromioclavicular joint dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(40): 6553-6561. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||