Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (26): 3938-3945.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.26.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of titanium plate and elastic intramedullary nail in the treatment of midshaft clavicular fractures
Ye Yong, Li Jun, Jing Jue-hua
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China
-
Revised:2016-04-07Online:2016-06-24Published:2016-06-24 -
Contact:Li Jun, M.D., Associate professor, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Ye Yong, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from the Anhui Medical University, No. 2013xkj032; the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, No. 1308085MH156
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ye Yong, Li Jun, Jing Jue-hua. Meta-analysis of titanium plate and elastic intramedullary nail in the treatment of midshaft clavicular fractures
share this article
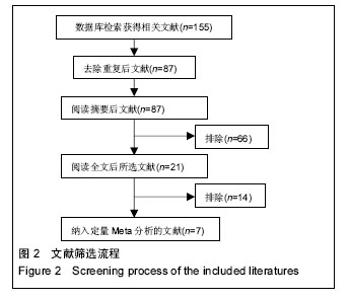
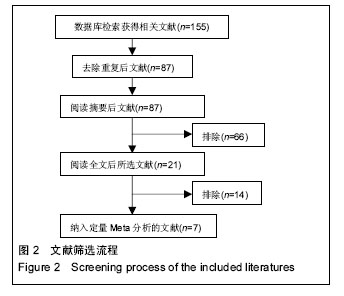
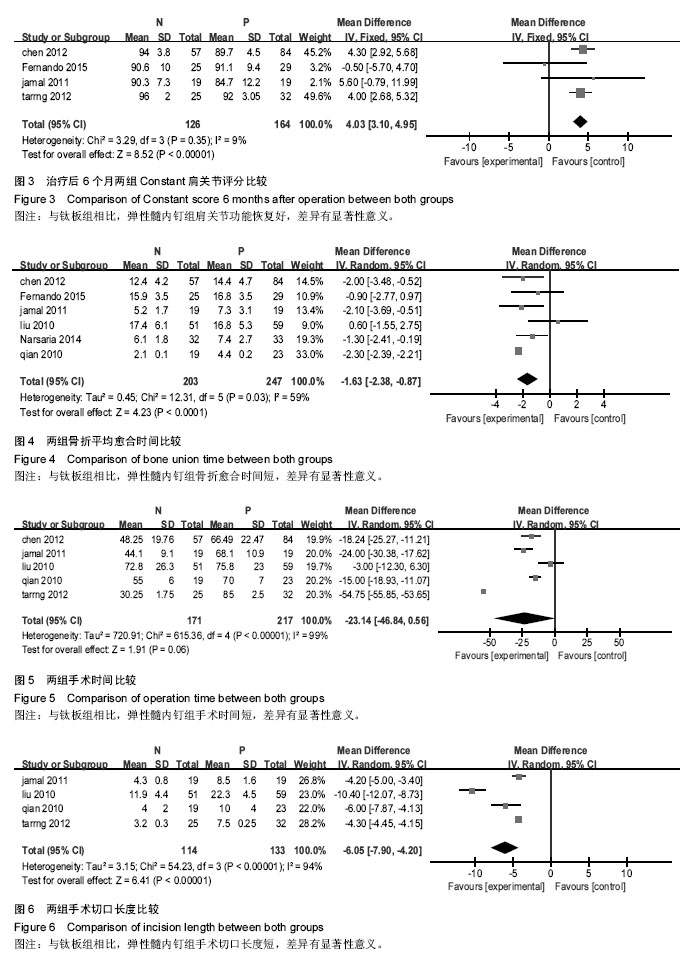
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 肩关节评分 纳入4项研究[11,15,17-18],研究间无异质性(P=0.35,I2=9%),使用固定效应模型。两组差异有显著性意义(WMD=4.03,95%CI:3.10-4.95,P < 0.000 01),表示弹性髓内钉组比钛板组肩关节功能恢复好,见图3。 2.2.2 骨折愈合时间 纳入6项研究[10-11,14,16-18],研究间存在异质性(P=0.03,I2=59%),使用随机效应模型。两组差异有显著性意义(MD=-1.63,95%CI:-2.38至-0.87,P < 0.000 1),表示弹性髓内钉组比钛板组的骨折愈合时间短,见图4。 2.2.3 手术时间 纳入5项研究[10-11,15-17],研究间存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=99%),使用随机效应模型。两组差异有显著性意义(MD=-19.35,95%CI:-46.84至0.56,P < 0.000 01),表示弹性髓内钉组比钛板组的手术时间短,见图5。 2.2.4 切口长度 纳入4项研究[10,15-17],研究间存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=94%),使用随机效应模型。两组差异有显著性意义(MD=-6.05,95%CI:-7.9至-4.2,P < 0.000 01),表示弹性髓内钉组比钢板组的手术切口长度短,见图6。"
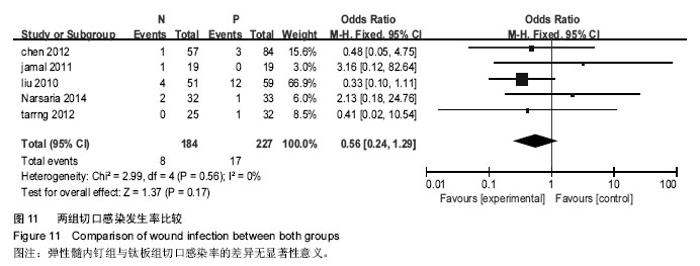
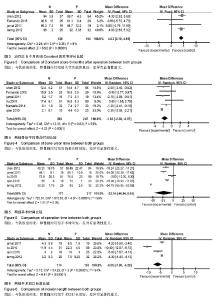
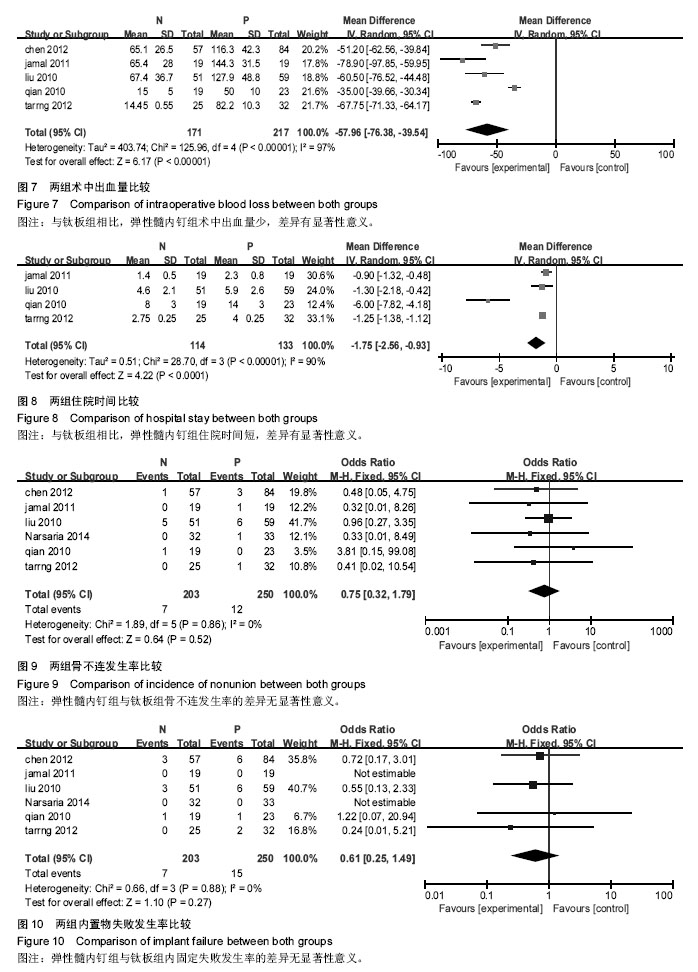
2.2.5 术中出血量 纳入5项研究[10-11,15-17],研究间存在异质性(P <0.000 01,I2=97%),使用随机效应模型。两组差异有显著性意义(MD=-55.99,95%CI:-76.38至-39.54,P < 0.000 01),表示弹性髓内钉组比钢板组的术中出血量少,见图7。 2.2.6 住院时间 纳入4项研究[10,15-17],研究间存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=90%),使用随机效应模型。两组差异有显著性意义(MD=-1.75,95%CI:-2.56至-0.93,P < 0.000 1),表示弹性髓内钉组比钛板组的住院时间短,见图8。 2.2.7 骨不连发生率 纳入6项研究[10-11,14-17],研究间无异质性(P=0.86,I2=0%),使用固定效应模型。两组差异无显著性意义(OR=0.75,95%CI:0.32-1.79,P=0.52),见图9。 2.2.8 内固定失败发生率 纳入6项研究[10-11,14-17],研究间无异质性(P=0.88,I2=0%),使用固定效应模型。两组差异无显著性意义(RR=0.61,95%CI:0.25-1.49,P=0.27),见图10。 2.2.9 切口感染率 纳入5项研究[10-11,14-15,17],研究间无异质性(P=0.56,I2=0%),使用固定效应模型。两组差异无显著性意义(OR=0.56,95%CI:0.24-1.29,P=0.17),见图11。"
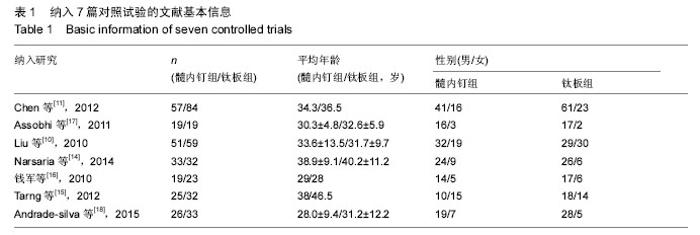
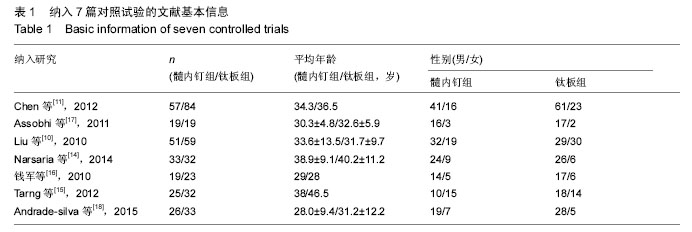
| [1] Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM, et al. Estimating the risk of nonunion following nonoperative treatment of a clavicular fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(7):1359-1365. [2] Postacchini R, Gumina S, Farsetti P, et al. Long-term results of conservative management of midshaft clavicle fracture. Int Orthop. 2010;34(5):731-736. [3] Smekal V, Oberladstaetter J, Struve P, et al. Shaft fractures of the clavicle: current concepts. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(6):807-815. [4] Wang XH, Guo WJ, Li AB, et al. Operative versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: a meta-analysis based on current evidence. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015;70(8):584-592. [5] Khorami M, Fakour M, Mokarrami H, et al. The Comparison of Results of Treatment of Midshaft Clavicle Fracture between Operative Treatment with Plate and Non-Operative Treatment. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2014;2(3):210-214. [6] Postacchini F, Gumina S, De Santis P, et al. Epidemiology of clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):452-456. [7] Nowak J, Mallmin H, Larsson S. The aetiology and epidemiology of clavicular fractures. A prospective study during a two-year period in Uppsala, Sweden. Injury. 2000;31(5):353-358. [8] Böstman O, Manninen M, Pihlajamäki H. Complications of plate fixation in fresh displaced midclavicular fractures. J Trauma. 1997;43(5):778-783. [9] Duncan SF, Sperling JW, Steinmann S. Infection after clavicle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;439: 74-78. [10] Liu HH, Chang CH, Chia WT, et al. Comparison of plates versus intramedullary nails for fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Trauma. 2010;69(6):E82-87. [11] Chen YF, Wei HF, Zhang C, et al. Retrospective comparison of titanium elastic nail (TEN) and reconstruction plate repair of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012; 21(4):495-501. [12] Fernandez FF, Egenolf M, Carsten C, et al. Unstable diaphyseal fractures of both bones of the forearm in children: plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2005;36(10):1210-1216. [13] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary. Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1): 1-12. [14] Narsaria N, Singh AK, Arun GR, et al. Surgical fixation of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: elastic intramedullary nailing versus precontoured plating. J Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15(3):165-171. [15] Tarng YW, Yang SW, Fang YP, et al. Surgical management of uncomplicated midshaft clavicle fractures: a comparison between titanium elastic nails and small reconstruction plates. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(6):732-740. [16] 钱军.钛制弹性髓内钉与重建钢板应用于锁骨中段骨折髓内外固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(43): 8024-8027. [17] Assobhi JE. Reconstruction plate versus minimal invasive retrograde titanium elastic nail fixation for displaced midclavicular fractures. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(4):185-192. [18] Andrade-Silva FB, Kojima KE, Joeris A, et al. Single, superiorly placed reconstruction plate compared with flexible intramedullary nailing for midshaft clavicular fractures: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(8):620-626. [19] Virtanen KJ, Remes V, Pajarinen J, et al. Sling compared with plate osteosynthesis for treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(17): 1546-1553. [20] 张亚峰,张作君.重建钢板内固定治疗成人锁骨粉碎性骨折[J].中医正骨,2006,18(9):35-36. [21] Robinson CM, Goudie EB, Murray IR, et al. Open reduction and plate fixation versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(17):1576-1584. [22] Ferran NA, Hodgson P, Vannet N, et al. Locked intramedullary fixation vs plating for displaced and shortened mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a randomized clinical trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(6): 783-789. [23] van der Meijden OA, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Treatment of clavicle fractures: current concepts review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(3):423-429. [24] van der Meijden OA, Houwert RM, Hulsmans M, et al. Operative treatment of dislocated midshaft clavicular fractures: plate or intramedullary nail fixation? A randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(8):613-619. [25] Duan X, Zhong G, Cen S, et al. Plating versus intramedullary pin or conservative treatment for midshaft fracture of clavicle: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(6):1008-1015. [26] Houwert RM, Wijdicks FJ, Steins Bisschop C, et al. Plate fixation versus intramedullary fixation for displaced mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2012;36(3):579-585. [27] McKee MD. Clavicle fractures in 2010: sling/swathe or open reduction and internal fixation. Orthop Clin North Am. 2010;41(2):225-231. [28] Shin SJ, Do NH, Jang KY. Risk factors for postoperative complications of displaced clavicular midshaft fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012; 72(4):1046-1050. [29] Zehir S, Zehir R, ?ahin E, et al. Comparison of novel intramedullary nailing with mini-invasive plating in surgical fixation of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(3):339-344. [30] Wijdicks FJ, Van der Meijden OA, Millett PJ, et al. Systematic review of the complications of plate fixation of clavicle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132(5):617-625. [31] Wijdicks FJ, Houwert M, Dijkgraaf M, et al. Complications after plate fixation and elastic stable intramedullary nailing of dislocated midshaft clavicle fractures: a retrospective comparison. Int Orthop. 2012;36(10):2139-2145. [32] King PR, Ikram A, Lamberts RP. The treatment of clavicular shaft fractures with an innovative locked intramedullary device. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015; 24(1):e1-6. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Li Jing, Yang Long, Wang Jian-ji, Liu Qin, Zou Qiang, Sun Yu, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Three-dimensional reconstruction based on DICOM data and its application for orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1046-1051. |
| [9] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [10] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [12] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [13] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [14] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [15] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||