Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (34): 6166-6172.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.34.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Optical properties of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposite and its conformational change
Tang Shi-hua1, 2, Li You-qun1, Wang Jun1, Wang Bai-yang1
- 1 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
2 Guangxi Key Laboratory of Chemistry and Engineering of Forest Products, Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2013-08-20Published:2013-08-20 -
About author:Tang Shi-hua, Master, Professor, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Shtang5@sohu.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 21067001*; Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, No. 0991083*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Shi-hua, Li You-qun, Wang Jun, Wang Bai-yang. Optical properties of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposite and its conformational change[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(34): 6166-6172.
share this article
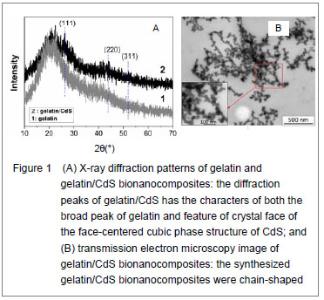
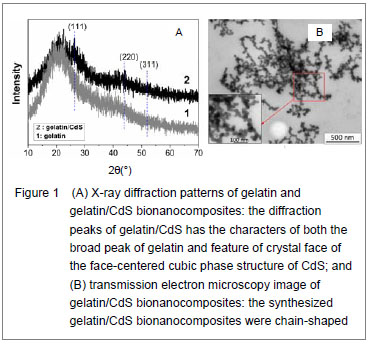
X-ray diffraction characteristics, ultrastructure and ζ potential of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites X-ray diffraction patterns of gelatin and the prepared gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites are presented in Figure 1A. Comparing with the broad peak of gelatin, the diffraction peaks of gelatin/CdS were broad and weak, and three main peaks at 2θ of 26.30°, 43.95°, and 52.03° were characteristics to the (111), (220) and (311) directions of the face-centered cubic phase structure of CdS, respectively. It could be well matched with the standard values (JCPDS Card No. 10-454). The positions of the peaks were in good agreement with literature values[8]. This result confirmed the existence of CdS nanoparticle as final product in gelatin. Microscopic observation showed that the size of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites was uniform with average diameters around 25 nm, and they were chain-shaped (Figure 1B). The same conclusions have been found by Sreekumari et al [9] and Oluwafemi et al [10] for preparation of the polyacrylamide-PbS nanocomposites, and gelatin capped Ag nanoparticles, respectively. When the concentrations of gelatin and S2- ion were 4.0×10-5 and 2.0×10-3 mol/L, respectively, the ζpotentials of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites were estimated to be circa -19.9, -19.4, -18.9 and -17.6 mV corresponding to the 0.0, 1.0×10-4, 4.0×10-4, and 1.4×10-3 mol/L of Cd2+. In another word, the ζ potentials of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites were decrease with the increasing concentration of CdS."
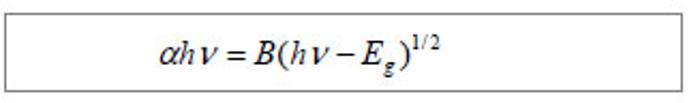
Optical properties of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites Figure 2A shows the optical transmission spectra of gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites for different concentrations of Cd2+. The optical transmittances of all the samples could reach to above 90% beyond the wavelength of 500 nm. It was observed that a shift toward longer wavelength with the increasing concentration of Cd2+. According to the related theories of semiconductor materials, the relation connecting the absorption coefficient α, the incident photon energy hv and optical band gap Eg obey Tauc’s formula[11]:"
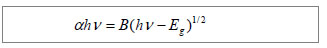

Where B was a constant. The band gaps have been calculated by extrapolating the linear region of the plots (αhν)2 vs. hν on the energy axis, as shown in Figure 2B, which were higher than that of the bulk CdS (2.42 eV at 27 ℃)[12]. The decreasing of band gap with the increase in Cd2+ concentration at different temperatures was observed as shown in Figure 2C."
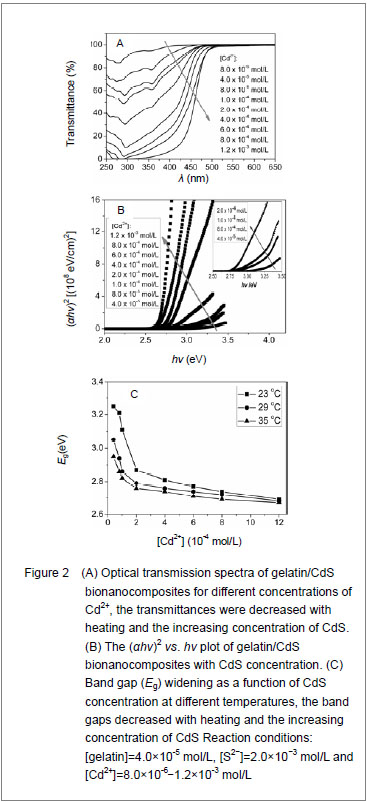
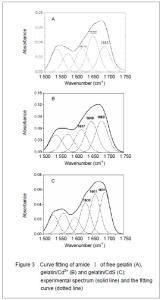
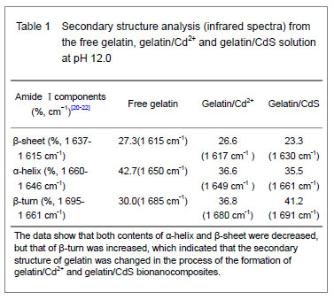
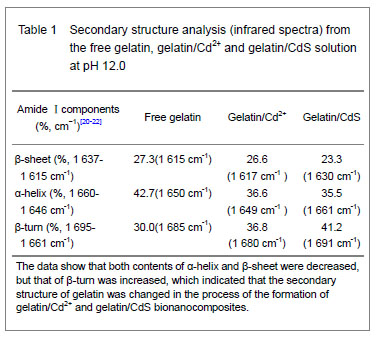
It was clear that the band gaps decreased due to an increasing of particle size with heating and the increasing concentration of Cd2+, and this was known as the quantum size effect[13-14]. The lower Eg value corresponded to the higher temperature, which indicated that the increasing temperature was favorable to the increasing of particle size, as predicted by the kinetic and the thermodynamic behavior of growth of CdS nanoparticles[15]. The similar phenomenon was observed for the synthesis of the mercaptoacetic acid modified CdSe quantum dots and the gelatin-PbS nanocomposites by Mi et al [16], and Wang et al [17], respectively. Conformational change of gelatin The binding of protein to nanoparticles often induced significant changes in secondary structure, which made it essential to understand the effect of nanoparticles on fundamental biological process[18]. The amideⅠband (1 600-1 700 cm-1) has been widely used for conformational studies[19]. To visualize the spectral changes more clearly, deconvolution of the amideⅠband was used for further analysis of the actual deformation on gelatin structure. The component peaks, their location and percentage of areas are showed in Figure 3 and Table 1. It was clear from the significantly differing band shapes and the shift of the peak maxima that the conformations of gelatin have changed due to its interaction with the Cd2+ and CdS."
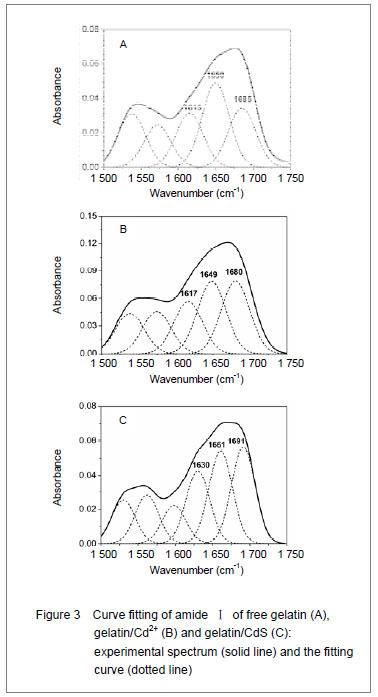
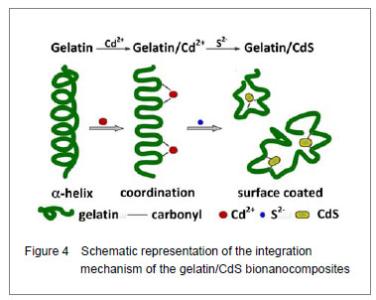
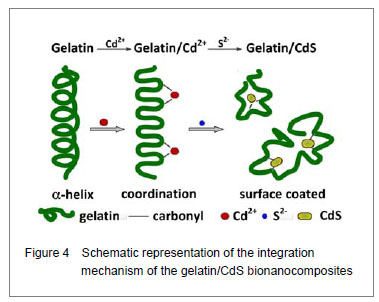
Curve fitting analysis of component bands showed that gelatin lose a large percentage of its α-helix and β-sheet characters[23], showed by a decreasing in the percentage of area of the component band centered at 1 650 and 1 615 cm-1, respectively. In contrast, the fraction of β-turn was 30.0% in pure gelatin but increased up to 36.8% in gelatin/Cd2+ solution, and increased to 41.2% in gelatin/CdS solution (Table 1), respectively. These findings indicated that Cd2+ and CdS combined with gelatin, could weaken or break the hydrogen bond, respectively. In other words, the formations of gelatin/Cd2+ complex and gelatin/CdS nanocomposites resulted in that the secondary structures of gelatin were changed from α-helix and β-sheet to β-turn, and the peptide chains of gelatin macromolecules were stretched. This changed conformation of the gelatin formed a configuration, which was well suitable for the formation of gelatin/Cd2+, and also the growth of CdS nanoparticles in gelatin matrix[24]. Similar feature that has been previously reported for the formation of CdS nanocrystals in pepsin solution by Yang et al [25]. The conformational changes may affect the biological function of gelatin protein[26-27]. Integration mechanism of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites Based on the results of discussion above, the schematic representation of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites formation is illustrated in Figure 4. It was speculated that the synthesis reaction of the gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites consisted of two steps as follows: First, there was a coordination interaction between the Cd2+ and carbonyl group (C=O) in gelatin macromolecular peptide chain to form initial precursor complexes (gelatin/Cd2+), and gelatin played the roles as oxygen source and structure-directing reagents[5]. At the same time, the interaction caused the gelatin conformation change from α-helix to β-turn, and the β-turn secondary structure formed a suitable conformation for the oriented growth of CdS nanoparticles. Second, when the S2− was added to gelatin/Cd2+ solution, the gelatin/Cd2+ interacted with S2− to form gelatin/CdS bionanocomposites, and the excess S2− could be adsorbed on the surface of CdS nanoparticles[18, 28]. In this reaction process, gelatin macromolecular conformation was changed from α-helix and β-sheets to β-turns, and coated on the surface of CdS nanoparticles, which may foreshow the biological functional change of protein."
| [1]Katz E, Willner I. Integrated nanoparticle-biomolecule hybrid systems: synthesis, properties, and applications. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004;43(45):6042-6108.[2]Ruiz-Hitzky E, Darder M, Aranda P, et al. Bionanocomposites as new carriers for in?uenza vaccines. Adv Mater. 2009;21(41):4167-4171.[3]Bakshi MS, Thakur P, Kaur G, et al. Stabilization of PbS nanocrystals by bovine serum albumin in its native and denatured states. Adv Funct Mater. 2009;19(9):1451-1458.[4]Ruiz-Hitzky E, Darder M, Aranda P, et al. Advances in biomimetic and nanostructured biohybrid materials. Adv Mater. 2010;22(3):323-336.[5]Darder M, Aranda P, Ruiz-Hitzky E. Bionanocomposites: a new concept of ecological, bioinspired, and functional hybrid materials. Adv Mater. 2007;19(10):1309-1319.[6]Tang SH, Xiao XG, Fang CJ, et al. Interaction between water-soluble nano-CdS and gelatin. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(38): 7587-7592.[7]Goormaghtigh E, Cabiaux V, Ruysschaert JM. Secondary structure and dosage of soluble and membrane proteins by attenuated total reflection Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy on hydrated films. Eur J Biochem. 1990; 193(2): 409-420. [8]Rafati AA, Borujeni ARA, Najafi M, et al. Ultrasonic/ surfactant assisted of CdS nano hollow sphere synthesis and characterization. Mater Charact. 2011;62(1):94-98.[9]Sreekumari Nair P, Radhakrishnan T, Revaprasadu N, et al. Structure and properties of PbS–polyacrylamide nanocomposites. Appl Phys A. 2005;81(4):835-838. [10]Oluwafemi OS, Lucwaba Y, Gura A, et al. A facile completely 'green' size tunable synthesis of maltose-reduced silver nanoparticles without the use of any accelerator. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;102: 718-723.[11]Caglar M, Ilicana S, Caglar Y, et al. Boron doped nanostructure ZnO ?lms onto ITO substrate. J Alloys Compd. 2011;509(6):3177-3182. [12]Kumar V, Kumar S, Kumar S, et al. Optical studies of electrochemically synthesized CdS nanowires. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 2011;22(4):335-338. [13]Liji-obhana SS, Vimala-evi M, Sastry TP, et al. CdS quantum dots for measurement of the size-dependent optical properties of thiol capping. J Nanopart Res. 2011; 13(4):1747-1757.[14]Seoudi R, Shabaka AA, Kamal M, et al. Dependence of spectroscopic and electrical properties on the size of cadmium sul?de nanoparticles. Physica E. 2012;45:47-55.[15]Bakiyaraj G, Gopalakrishnan N, Dhanasekaran R. Influences of thermal annealing on the structural, optical and electrical properties of nanostructured cadmium sulphide thin films. Chalcogenide Lett. 2011;8(7):419-426.[16]Mi W, Tian JT, Tian WG, et al. Temperature dependent synthesis and optical properties of CdSe quantum dots. Ceramics International. 2012;38(7):5575-5583.[17]Wang J, Li YQ, Mao XJ, et al. One-pot synthesis and formation mechanism of water-soluble PbS/gelatin micro-nano biocomposite. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(25):4605-4610.[18]Fei L, Perrett S. Effect of nanoparticles on protein folding and fibrillogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2009;10(2):646-655.[19]Magyari K, Baia L, Popescu O, et al. The anchoring of fibrinogen to a bioactive glass investigated by FT-IR spectroscopy. Vibrational Spectroscopy. 2012;62:172-179.[20]Roach P, Farrar D, Perry CC. Interpretation of protein adsorption: surface-induced conformational changes. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(22):8168-8173.[21]Tsai DH, Delrio FW, Keene AM, et al. Adsorption and Conformation of Serum Albumin Protein on Gold Nanoparticles Investigated Using Dimensional Measurements and in Situ Spectroscopic Methods. Langmuir. 2011;27(6):2464-2477.[22]Shi XJ, Li D, Xie J, et al. Spectroscopic investigation of the interactions between gold nanoparticles and bovine serum albumin. Chin Sci Bull. 2012;57(10):1109-1115.[23]Peng X, Yao D, Pan Y, et al. Study on the structural changes of bovine serum albumin with effects on polydatin binding by a multitechnique approach. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2011;81(1):209-214.[24]Ghosh D, Mondal S, Ghosh S, et al. Protein conformation driven biomimetic synthesis of semiconductor nanoparticles. J Mater Chem. 2012;22(2):699-706.[25]Yang L, Shen QM, Zhou JG, et al. Biomimetic synthesis of CdS nanocrystals in aqueous solution of pepsin. Mater Chem Phys. 2006;98(1):125-130.[26]Deng ZJ, Liang M, Toth I, et al. Molecular interaction of poly(acrylic acid) Gold nanoparticles with human fibrinogen. ACS Nano. 2012;6(10):8962-8969. [27]Gagner JE, Qian X, Lopez MM, et al. Effect of gold nanoparticle structure on the conformation and function of adsorbed proteins. Biomaterials. 2012;33(33):8503-8516.[28]Li CL, Chen W, Yuan J, et al. Biomolecule-assisted synthesis of nanocrystalline CdS and Bi2S3 for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. World J Nano Sci Eng. 2011;1(3):79-83.[29]Mahmoudi M, Lynch I, Ejtehadi MR, et al. Protein-nanoparticle interactions: opportunities and challenges. Chem Rev. 2011;111(9):5610-5637.[30]Shemetov AA, Nabiev I, Sukhanova A. Molecular interaction of proteins and peptides with nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2012;6(6):4585-4602. |
| [1] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [2] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [3] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [4] | Xie Jian, Su Jiansheng. Advantages and characteristics of electrospun aligned nanofibers as scaffolds for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2575-2581. |
| [5] | Ji Qi, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Problems and trends of technique and clinical application of metallic biomaterials prepared by three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [6] | Qian Nannan, Zhang Qian, Yang Rui, Ao Jun, Zhang Tao. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: cell therapy and combination of new drugs and biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2114-2120. |
| [7] | Jia Wei, Zhang Mandong, Chen Weiyi, Wang Chenyan, Guo Yuan. Effects of femoral prosthetic materials on artificial knee arthroplasty performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1477-1481. |
| [8] | Wang Qian, Li Lu, Shu Jingyuan, Dong Zhiheng, Jin Youshi, Wang Qingshan. Micro-morphology and phase of zirconia-based nano-hydroxyapatite functional gradient biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1517-1521. |
| [9] | Zhou Liyu, Ma Yanxia, Qi Shibin, Saijilafu, Wei Shanwen, Ni Li. Regulatory effects of ADT-OH on the proliferation of neural precursor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 96-100. |
| [10] | Zhao Chuntao, Qing Mingsong, Yu Langbo, Peng Jiachen . Meta-analysis of total knee arthroplasty guided by kinematic alignment and mechanical alignment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1435-1442. |
| [11] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [12] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [13] | He Yujie, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Cai Yongqiang, Dai Lina, Xu Yangyang, Wang Yidan, Xu Xuebin. Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| [14] | Yan Shu, Lu Yan, Ouyang Zhaolian. Analysis of programs on tissue engineering funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China between 2013 and 2018 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 731-735. |
| [15] | Qin Wenpin, Yang Yujie, Zhao Laihe, Shi Xiaowei, Lu Lei, Yang Hongxu, Huang Jinghui. Hemorrhage control of fluid gelatin SurgifloTM versus gelatin sponge in lumbar spine fusion surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 561-565. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||