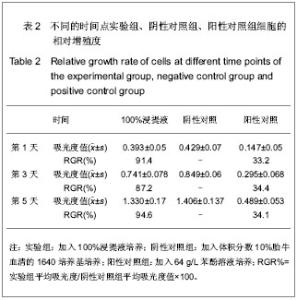
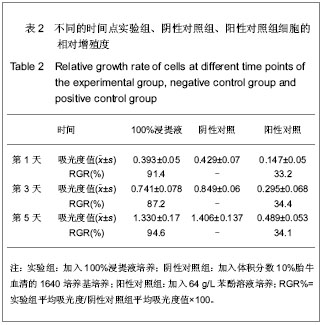
| [1] 刘祖国,张慧.重视我国角膜病的基础研究[J] .中华眼科杂志, 2006, 42(8):673-675. [2] Kuwabara Y. Studies on heterotransplantation of corneas. Am J Ophthalmol.1962; 53 (6):911-917.[3] Werblin TP, Kaufman HE, Friedlander MH,et al. Epikerato-phakia: the surgical correction of aphakia. III. Preliminary results of a prospective clinical trial. Arch Ophthamlol.1981;99(11):1957-1960.[4] McDonald MB, Koenig SB, Safir A, et al. Epikeratophakia: the surgical correction of aphakia.Ophthamlology. 1983;90(6): 668-672.[5] 徐锦堂, 李辰, 杜晶. 蜂蜜脱水低温保存同种和异种板层角膜片移植后植片的命运[J]. 眼科研究, 1986, 4(4):193-197.[6] 王雪, 颜华. 组织工程角膜上皮支架材料研究进展[J]. 眼科研究, 2010, 28(10):998-1001.[7] 樊廷俊,杨洪收,胡修忠,等. 组织工程人角膜上皮体外重建的研究进展[J]. 山东大学学报:医学版, 2010, 48(7):7-11.[8] 侯江平,李国星,李玉莉,等. 角膜内不同部位植入壳聚糖-胶原复核膜的生物相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(34): 6319-6322.[9] Wilson SE, Liu JJ, Mohan RR.Strom al-epithelial interactions in the cornea. Prog Retina Eye Res.1999;18(3):293-309.[10] Keogh MB,O’BFJ,Daly JS.A novel collagen scallold supports human osteogenesis-applications for bone tissue engineening.Cell Tissue Res.2010;340(1):169-177.[11] 丁勇,徐锦堂,陈建苏.组织工程角膜材料研究进展[J].中国病理生理杂志,2002,18(12):1557-1560.[12] 陈根云,吴静,徐锦堂,等.异种角膜基质材料正位植入后神经再生的研究[J].眼科新进展, 2005, 25(6):485-491.[13] 吴静,徐锦堂,赵松滨.培养角膜上皮移植的实验研究[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2001,19(3): 178-179.[14] 傅瑶,陈苹,陆雯娟.异种角膜脱细胞基质为供体进行角膜前板层移植的初步研究[J].眼科, 2009, 18(6):398-401.[15] 吴连胜, 陈建苏, 徐锦堂, 等. 脱细胞角膜材料的生物相容性研究[J]. 眼科研究, 2009,27(5):359-363.[16] 郭梁, 刘源, 张勇杰,等.脱细胞猪角膜的制备及其生物学性能观察[J]. 山东医药, 2010, 50 (42):4-5.[17] 张燕. 异种角膜移植的伦理考量[J]. 医学与哲学:人文社会医学版,2011, 32(12):26-27.[18] 刘丽敏,接英,潘志强.供体骨髓细胞输注诱导免疫耐受延长猪-猴异种角膜移植植片存活的研究[J]. 首都医科大学学报,2010, 31(1):20-25.[19] 王智崇,葛坚,徐锦堂,等.角膜不同组织免疫原性分析[J].中华眼科志, 2002, 38(9):535-539.[20] 孙雷, 张富强, 高益鸣,等.二部烧结牙科氧化锆陶瓷细胞毒性评价[J].口腔颌面修复杂志,2008, 9(1): 1-2.[21] Terada S, Sato M, Sevy A, et al. Tissue engineering in the twenty- first century. Yonsei Med J. 2000;41(6):685-691.[22] 胡晓洁,王敏,柴岗,等.组织工程技术构建兔角膜基质组织的实验研究[J].中华眼科杂志,2004,40(8):517-521.[23] 余克明, 王智崇, 葛坚, 等. 组织工程化角膜基质的构建与移植实验[J]. 眼科研究, 2005, 23(1) :1 - 3.[24] Koizumi N, Inatomi T, Quantock AJ, et al.Amniotic membrane as a substrate for cultivating limbal corneal epithelialcells for autologous transplantation in rabbits. Cornea.2000:19(1):65- 71.[25] Ishino Y, Sano Y, Nakamura T,et al.Amniotic membrane as a carrier for cultivated human corneal endothelial cell transplantation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2004;45(3): 800- 806.[26] Espana EM, He H, Kawakita T, et al.Human keratocytes cultured on amniotic membrane stroma preserve morphology and express keratocan. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2003;44(12): 5136- 5141.[27] 徐锦堂,陈建苏,吴静, 等. 异种角膜基质的研究现状及问题[J]. 眼科新进展, 2010, 30(7): 603.[28] Amano S. Transplantation of cultured human corneal endothelial cells.Cornea. 2003, 22(7Suppl): S66-74.[29] Ponce-Márquez S, Martínez VS, McIntosh-Ambrose W,et al. Decellularization of bovine corneas for tissue engineering application. Acta Biomater.2009;5(6): 1839-1847.[30] Xu YG, Xu YS, Huang C, et al. Development of a rabbit corneal equivalent using an acellular corneal matrix of a porcine substrate.MolVis.2008;14(18): 2180-2189.[31] 傅瑶, 陈苹, 陆雯娟.异种角膜脱细胞基质为供体进行角膜前板层移植的初步研究[J].眼科, 2009, 18(6):398-401.[32] 林旭初,金岩,惠延年.脱细胞猪角膜表面基底膜成分的检测[J].中国组织工程研究 2012, 16(25):4682-4684.[33] 王春晓, 王起振, 苏英梅,等. 鸵鸟心脏色素细胞C的制备及性质[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2002, 19(5):359-364.[34] Ofri R, Millodot R, Shimoni R, et al. Development of the refractive state in eyes of ostrich hicks (Struthio camelus). Am J Vet Res.2001;62 (5): 812-815.[35] 潘东艳, 柳林, 刘银萍. 鸵鸟角膜对兔板层角膜移植的排斥反应[J]. 国际眼科杂志,2005, 5(4): 651.[36] 刘先宁,朱秀萍,银勇,等. 以干燥脱水法保存的异种角膜基质为载体构建人工生物角膜上皮组织[J].国际眼科杂志,2008, 8(11): 2214-2216.[37] 吴贺勇,李娟,李亚玲.水溶性乌梢蛇总蛋白的提取方法及细胞毒性检测[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14 (50 ): 9403-9406. |