Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Streptococcus mutans gcp gene knockout strains expression profile gene chip
Xie Miao-miao1, Hu Xiao-cong2, Wu Bu-ling1, Yan Wen-juan1
- 1Department of Stomatology, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Baoan District People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518101, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2012-03-05Revised:2012-04-06Online:2013-08-13Published:2013-08-13 -
Contact:Wu Bu-ling, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Stomatology, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China wubuling@yahoo.com.cn Yan Wen-juan, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Stomatology, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China ywj918@sohu.com -
About author:Xie Miao-miao☆, Studying for doctorate, Department of Stomatology, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China medabc@163.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81100747*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Miao-miao, Hu Xiao-cong, Wu Bu-ling, Yan Wen-juan. Streptococcus mutans gcp gene knockout strains expression profile gene chip[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.33.014.
share this article
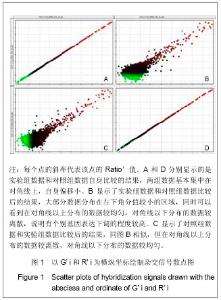
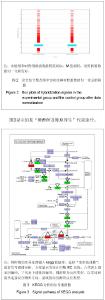
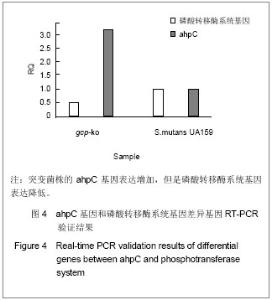
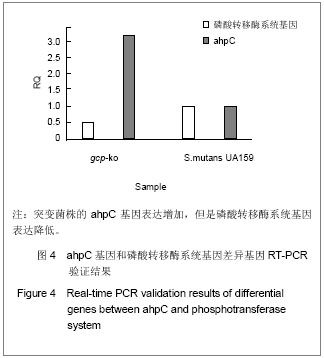
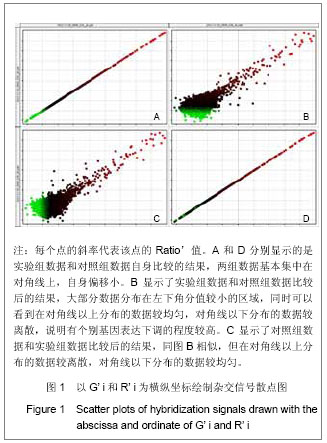
2.1 使用DEVA软件进行数据分析及标准化处理 首先将芯片对其网格,使用缩略图或者通过软件自带的“调整对齐”功能来查看手动对齐的效果,检查芯片的角落位置。从DEVA“项目管理器”对话框中选择“RMA分析功能”(多阵列分析功能)。用“RMA分析对话框”选择数据文件,设置计算方法和目标文件夹,点击“RUN”来进行数据分析。DEVA软件会自动运行每一个应用程序的默认分析,当分析工作完成后,可以查看结果。DEVA软件使用Bolstad描述的“位数正常化”的方法对表达的数据进行标准化。 通过标准化消除空间偏移误差后,这两列数据表示的就是实际表达水平。 2.2 上下调基因分析 差异基因的筛选标准为国内外基因芯片实验的常用标准Ratio’=2和Ratio’=0. 5,Ratio’值大于2或小于0.5的点被认为是有显著表达差异的基因。实验以G’ i和R’ i为横纵坐标绘制杂交信号散点图,见图1,图中每个点的斜率代表该点的Ratio’值。分别以实验组数据和对照组数据为横纵坐标,根据自身比较和相互比较的结果绘制杂交信号散点图。通过标准化消除空间偏移误差后,这两列数据表示的就是实际表达水平。图1A和图1D分别显示的是实验组数据和对照组数据自身比较的结果,两组数据基本集中在对角线上,自身偏移小。图1B显示了实验组数据和对照组数据比较后的结果,大部分数据分布在左下角分值较小的区域,同时可以看到在对角线以上分布的数据较均匀,对角线以下分布的数据较离散,说明有个别基因表达下调的程度较高。图1C显示了对照组数据和实验组数据比较后的结果,同图1B相似,大部分数据分布在左下角分值较小的区域,但是与图1B不相同的是,在对角线以上分布的数据较离散,对角线以下分布的数据较均匀。"
| [1] Yamada T, Kose H, Ohta T, et al. Genetic dissection of complex genetic factor involved in NIDDM of OLETF rat. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012:582546.[2] Mueller TF, Mas VR. Microarray applications in nephrology with special focus on transplantation. J Nephrol. 2012;25(5): 589-602.[3] Fujita K, Fukuda M, Iwahashi H. Significance of comprehensive gene expression analysis for evaluation of biological effects of manufactured nanomaterials. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2012;67(3):390-395.[4] 闫文娟.外源性单磷酸鸟苷环二聚体抑制变形链球菌生物膜的形成能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(16): 2939-2942.[5] 闫文娟,徐树军,谢苗苗,等.外源性单磷酸鸟苷环二聚体对变形链球菌基因表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(8): 1451-1454.[6] Li Z, Chen JH, Hao Y, et al. Structures of the PelD cyclic diguanylate effector involved in pellicle formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(36): 30191-30204.[7] Zaade D, Schmitz J, Benke E, et al. Distinct signal transduction pathways downstream of the (P)RR revealed by microarray and ChIP-chip analyses. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57674. [8] Zhou J, Sayre DA, Wang J, et al. Endo-S-c-di-GMP analogues-polymorphism and binding studies with class I riboswitch. Molecules. 2012;17(11):13376-13389.[9] Li W, He ZG. LtmA, a novel cyclic di-GMP-responsive activator, broadly regulates the expression of lipid transport and metabolism genes in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(22):11292-11307.[10] Petrova OE, Sauer K. Dispersion by Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires an unusual posttranslational modification of BdlA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(41):16690- 16695. [11] Stelitano V, Brandt A, Fernicola S, et al. Probing the activity of diguanylate cyclases and c-di-GMP phosphodiesterases in real-time by CD spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(7): e79. [12] Chen Y, Chai Y, Guo JH,et al. Evidence for cyclic Di-GMP-mediated signaling in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 2012;194(18):5080-5090.[13] Smith KD,Lipchock SV,Livingston AL,et al. Structural and biochemical determinants of ligand binding by the c-di-GMP riboswitch . Biochemistry. 2010;49(34):7351-7359. [14] Tschowri N, Lindenberg S, Hengge R. Molecular function and potential evolution of the biofilm-modulating blue light-signalling pathway of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 2012;85(5):893-906. [15] Cruz DP, Huertas MG, Lozano M, et al. omparative analysis of diguanylate cyclase and phosphodiesterase genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:139.[16] Chen MW, Kotaka M, Vonrhein C, et al. Structural insights into the regulatory mechanism of the response regulator RocR from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cyclic Di-GMP signaling. J Bacteriol. 2012;194(18):4837-4846.[17] Miller MB, Tang YW. Basic concepts of microarrays and potential applications in clinical microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009;22(4):611-633.[18] Procop GW. Molecular diagnostics for the detection and characterization of microbial pathogens. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45 Suppl 2:S99-S111. [19] Charoenlap N, Shen Z, McBee ME, et al. Alkyl hydroperoxide reductase is required for Helicobacter cinaedi intestinal colonization and survival under oxidative stress in BALB/c and BALB/c interleukin-10-/- mice. Infect Immun. 2012;80(3): 921-928.[20] Higuchi M, Yamamoto Y, Kamio Y. Molecular biology of oxygen tolerance in lactic acid bacteria: Functions of NADH oxidases and Dpr in oxidative stress. J Biosci Bioeng. 2000; 90(5):484-493.[21] Mohammadian T, Doosti M, Paknejad M, et al. Preparative SDS-PAGE Electroelution for Rapid Purification of Alkyl Hydroperoxide Reductase from Helicobacter pylori. Iran J Public Health. 2010;39(1):85-91.[22] Lechardeur D, Fernandez A, Robert B, et al. The 2-Cys peroxiredoxin alkyl hydroperoxide reductase c binds heme and participates in its intracellular availability in Streptococcus agalactiae. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(21):16032-16041.[23] Yamamoto Y, Higuchi M, Poole LB, et al. Identification of a new gene responsible for the oxygen tolerance in aerobic life of Streptococcus mutans.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2000; 64(5):1106-1109.[24] Wasim M, Bible AN, Xie Z, et al. Alkyl hydroperoxide reductase has a role in oxidative stress resistance and in modulating changes in cell-surface properties in Azospirillum brasilense Sp245. Microbiology. 2009;155(Pt 4):1192-1202.[25] Jönsson TJ, Ellis HR, Poole LB. Cysteine reactivity and thiol-disulfide interchange pathways in AhpF and AhpC of the bacterial alkyl hydroperoxide reductase system. Biochemistry. 2007;46(19):5709-5721.[26] Yamamoto Y, Sato Y, Takahashi-Abbe S, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of the pfl gene encoding pyruvate formate-lyase from Streptococcus mutans.Infect Immun. 1996;64(2):385-391.[27] Elizarov SM, Alekseeva MG, Novikov FN, et al. Identification of phosphorylation sites in aminoglycoside phosphotransferase VIII from Streptomyces rimosus. Biochemistry.2012;77(11):1258-1265.[28] Neumann S, Grosse K, Sourjik V. Chemotactic signaling via carbohydrate phosphotransferase systems in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(30):12159-12164.[29] Zeng L, Burne RA. Multiple sugar: phosphotransferase system permeases participate in catabolite modification of gene expression in Streptococcus mutans. Mol Microbiol. 2008;70(1):197-208.[30] Webb AJ, Homer KA, Hosie AH. A phosphoenolpyruvate- dependent phosphotransferase system is the principal maltose transporter in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 2007;189(8):3322-3327. |
| [1] | Shen Fu, Kuang Gaoyan, Yang Zhuo, Wen Meng, Zhu Kaimin, Yu Guizhi, Xu Wuji, Deng Bo . Immune infiltration mechanism of differential expression genes in rheumatoid arthritis and potential therapeutic prediction of Chinese herbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2183-2191. |
| [2] | Zhao Chuntao, Qing Mingsong, Yu Langbo, Peng Jiachen . Meta-analysis of total knee arthroplasty guided by kinematic alignment and mechanical alignment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1435-1442. |
| [3] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [4] | Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [5] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [6] | He Yujie, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Cai Yongqiang, Dai Lina, Xu Yangyang, Wang Yidan, Xu Xuebin. Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| [7] | Yan Shu, Lu Yan, Ouyang Zhaolian. Analysis of programs on tissue engineering funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China between 2013 and 2018 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 731-735. |
| [8] | Sun Jian, Fang Chao, Gao Fei, Wei Laifu, Qian Jun. Clinical efficacy and complications of short versus long segments of internal fixation for the treatment of degenerative scoliosis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 438-445. |
| [9] | Gao Yangyang, Che Xianda, Han Pengfei, Liang Bin, Li Pengcui. Accuracy of robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw placement: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 446-452. |
| [10] | Zhang Jian, Wang Xiaojian, Qin Dean, Zhao Zhongtao, Liang Qingyuan, An Qijun, Song Jiefu. Risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis after spinal deformity surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 460-468. |
| [11] | Xu Yangyang, Zhang Kai, Li Zhijun, Zhang Yunfeng, Su Baoke, Wang Xing, Wang Lidong, Wang Yidan, He Yujie, Li Kun, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe. Morphological analysis of optimal selection of lumbar pedicle screws in adolescents aged 12-15 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3321-3328. |
| [12] | He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Zheng Xiaolong, Shen Yingshan, Pang Fengxiang, Chen Lixin, Li Weifeng, Yang Fan, Liu Shaojun, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Trends in global research on bone and joint tuberculosis: bibliometrics and visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3234-3239. |
| [13] | Sui Xiang, Tian Guangzhao, Yang Zhen, Li Xu, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi. Application potential of CD146 positive subpopulation as seed cells for cartilage tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 2997-3003. |
| [14] | Qin Haikuo, Luo Shixing. Correlation of cortical bone thickness and X-ray gray value in different planes of proximal femur with brittle fracture of female hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2867-2872. |
| [15] | Wu Yuhang, Zheng Liqin, Zhang Biao, Li Fan, Chen Xinmin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Compression fracture simulation of osteoporotic trabecular bone in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(15): 2387-2392. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||