Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (13): 2407-2414.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.13.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation for midshaft clavicular fractures: A Meta-analysis
Chen Hao, Zhang Jin-hong, He Zeng-liang
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Nanjing, Southeast University, Nanjing 210003, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2012-09-04Revised:2012-09-16Online:2013-03-26Published:2013-03-26 -
Contact:Zhang Jin-hong, Master, Associate chief physician, the Second Hospital of Nanjing, Southeast University, Nanjing 210003, Jiangsu Province, China zhangjinhong1998@163.com -
About author:Chen Hao★, Master, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Nanjing, Southeast University, Nanjing 210003, Jiangsu Province, China hch838@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Hao, Zhang Jin-hong, He Zeng-liang. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation for midshaft clavicular fractures: A Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(13): 2407-2414.
share this article
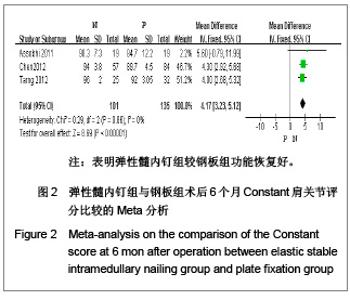
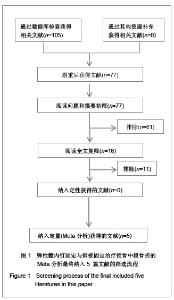
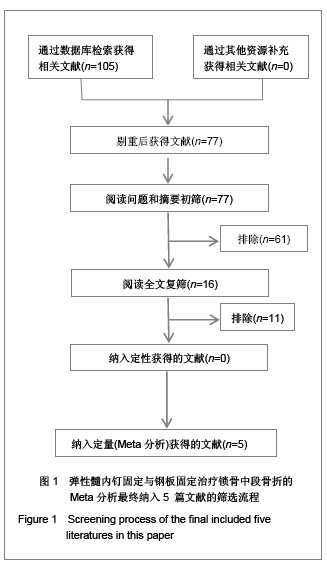
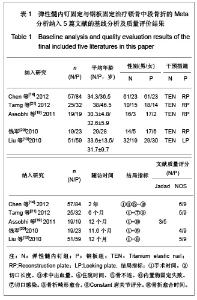
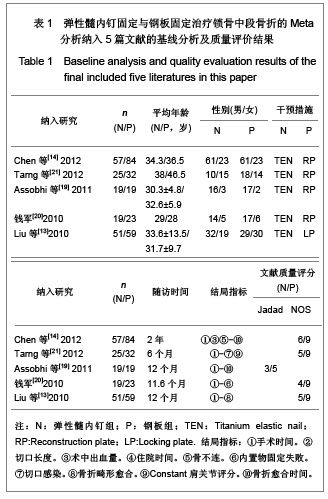
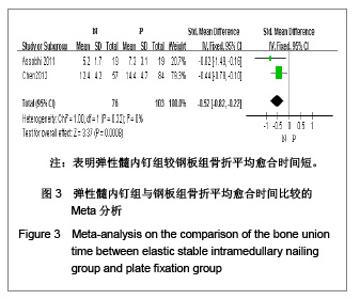
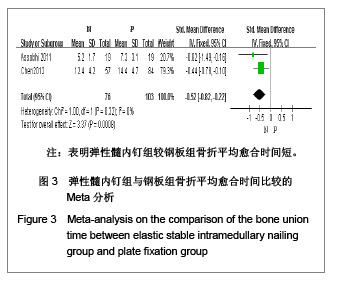
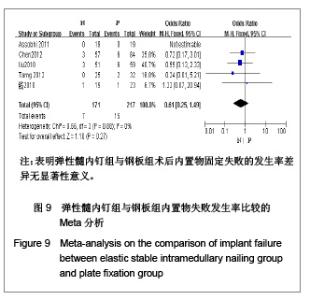
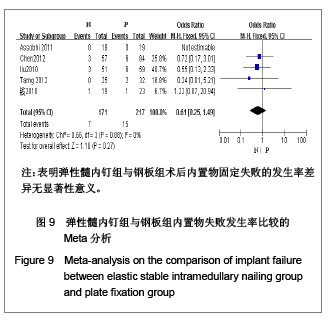
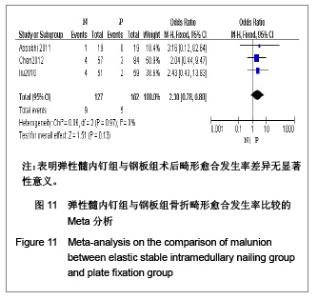
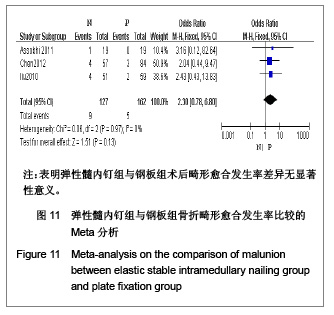
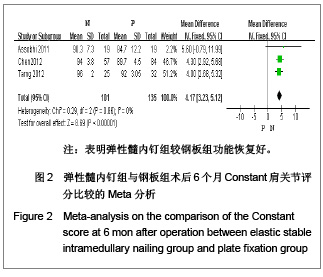
纳入的5篇文献中,只有1篇为随机对照试验[19],其余4篇为回顾性队列研究[13-14, 20-21],评价结果见表1。 2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 术后Constant肩关节评分 3项研究报道了术后6个月Constant肩关节评分[14,19,21],异质性检验示各项研究间无异质性(P < 0.86,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析。结果显示两组术后功能恢复Constant评分差异有显著性意义(WMD=4.17,95%CI:3.23-5.12,P < 0.000 01),表明弹性髓内钉组较钢板组功能恢复好,见图2。 2.3.2 骨折愈合时间 2项研究报道了骨折愈合时间[14,19],异质性检验示各项研究间有质性(P=0.32,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析。结果显示两组骨折愈合时间差异有显著性意义[MD=-0.52,95%CI:0.82-0.22,P=0.000 8],表明表明弹性髓内钉组较钢板组骨折平均愈合时间短,见图3。"
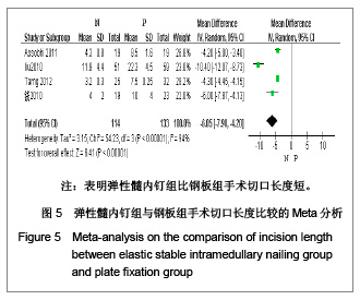
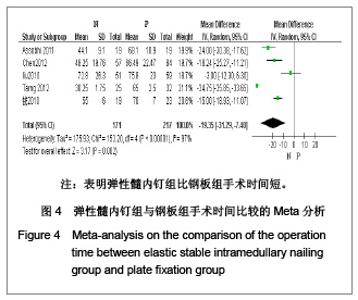
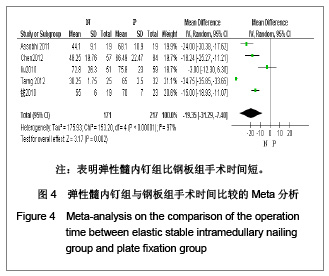
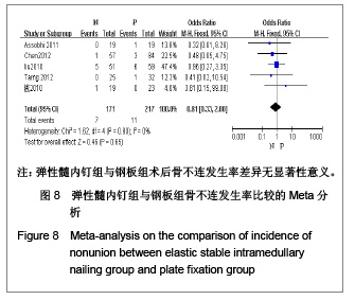
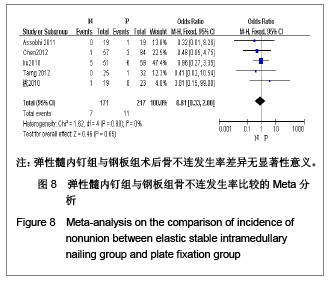
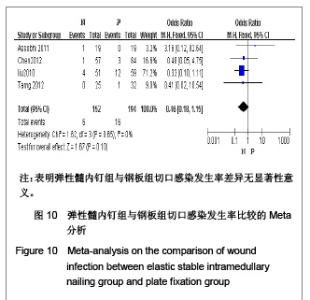
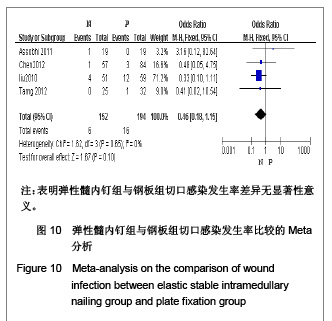
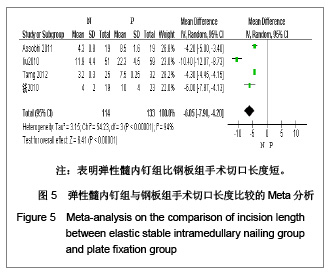
5项研究报道了手术时间[13-14, 19-21],异质性检验示各项研究间有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=97%),排除随机对照试验[19],回顾性队列研究组有异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=98%),再排除低质量队列研究仍存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=97%),故采用随机效应模型进行分析。结果显示两组手术时间差异有显著性意义[MD=-19.35,95%CI:-31.29- -7.4,P < 0.000 01],表明弹性髓内钉组比钢板组手术时间短。 2.3.4 切口长度 4项研究报道了手术时间[13, 19-21],异质性检验示各项研究间有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=94%),排除随机对照试验[19],回顾性队列研究组有异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),在排除低质量队列研究仍存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=98%),故采用随机效应模型进行分析。结果显示两组手术时间差异有显著性意义[MD=-6.05,95%CI:-7.9- -4.2,P < 0.000 01],表明弹性髓内钉组比钢板组手术切口长度短,见图5。"
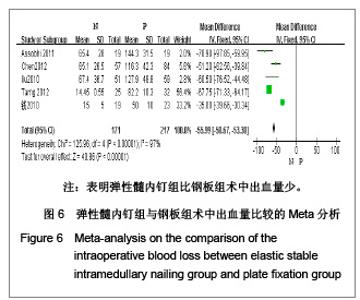
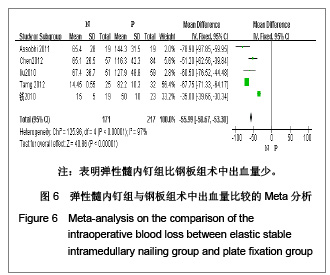
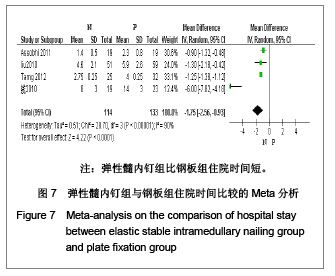
5项研究报道了手术时间[13-14, 19-21],异质性检验示各项研究间有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=97%),排除随机对照试验[19],回顾性队列研究组有异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=98%),再排除低质量队列研究仍存在异质性(P < 0.02,I2=75%),故采用随机效应模型进行分析。结果显示两组术中出血量差异有显著性意义[MD=-55.99,95%CI:-58.67- -53.3,P < 0.000 01],表明弹性髓内钉组比钢板组术中出血量少。 2.3.6 住院时间 4项研究报道了住院时间[13, 19-21] ,异质性研究示各项研究间有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2= 90%),考虑住院时间异质性来源与各国医疗水平、医疗环境及医疗卫生制度存在明显差异有关,故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示两组住院时间差异有显著性意义[MD=-1.75,95%CI:-2.56- -0.93,P < 0.000 1],表明弹性髓内钉组比钢板组住院时间短,见图7。"
| [1] McKee MD. Clavicle fractures in 2010: sling/swathe or open reduction andinternal fixation? Orthop Clin North Am. 2010; 41(2):225-231.[2] Wijdicks FJ, Van der Meijden OA, Millett PJ, et al. Systematic review of thecomplications of plate fixation of clavicle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(5):617-625.[3] Postacchini F, Gumina S, De Santis P, et al. Epidemiology of clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5): 452-456.[4] Nowak J, Mallmin H, Larsson S. The aetiology and epidemiology of clavicular fractures. A prospective study during a two-year period in Uppsala, Sweden. Injury. 2000; 31(5):353-358.[5] Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM, et al. Estimating the risk of nonunion following nonoperative treatment of a clavicular fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(7):1359-1365.[6] Postacchini R, Gumina S, Farsetti P, et al. Long-term results of conservative management of midshaft clavicle fracture. Int Orthop. 2010;34(5):731-736.[7] Smekal V, Oberladstaetter J, Struve P, et al. Shaft fractures of the clavicle: current concepts. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(6):807-815.[8] Smekal V, Irenberger A, Struve P, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures-a randomized, controlled, clinical trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(2):106-112.[9] Smekal V, Irenberger A, Attal RE, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing is best for mid-shaft clavicular fractures without comminution: Results in 60 patients. Injury. 2011; 42(4): 324-329.[10] Bernstein J. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(8):1866-1867.[11] Bostman O, Manninen M,Pihlajamaki H. Complications of plate fixation in fresh displaced midclavicular fractures. J Trauma. 1997;43(5):778-783.[12] Duncan SF, Sperling JW,Steinmann S. Infection after clavicle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;439:74-78.[13] Liu HH, Chang CH, Chia WT, et al. Comparison of plates versus intramedullary nails for fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Trauma. 2010;69(6):E82-87.[14] Chen YF, Wei HF, Zhang C, et al. Retrospective comparison of titanium elastic nail (TEN) and reconstruction plate repair of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(4):495-501.[15] Fernandez FF, Egenolf M, Carsten C, et al. Unstable diaphyseal fractures of both bones of the forearm in children: plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2005;36(10):1210-1216.[16] Mueller M, Rangger C, Striepens N, et al. Minimally invasive intramedullary nailing of midshaft clavicular fractures using titanium elastic nails. J Trauma. 2008;64(6):1528-1534.[17] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12.[18] Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. URL: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp[19] Assobhi JEH. Reconstruction plate versus minimal invasive retrograde titanium elastic nail fixation for displaced midclavicular fractures. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(4):185- 192.[20] Qian J. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(43):8024-8027. 钱军.钛制弹性髓内钉与重建钢板应用于锁骨中段骨折髓内外固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(43): 8024-8027.[21] Tarng YW, Yang SW, Fang YP, et al. Surgical management of uncomplicated midshaft clavicle fractures: a comparison between titanium elastic nails and small reconstruction plates. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(6):732-740.[22] Keller HW, Huber R,Rehm KE. Intramedullary nailing of fractures during the growth period with a new implant. Chirurg. 1993;64(3):180-184.[23] Niemeier U,Zimmermann HG. Kuntscher's open intramedullary nailing of the clavicle. An alternative in the treatment of an old clavicular fracture. Chirurg. 1990;61(6): 464-466.[24] Jubel A, Andermahr J, Schiffer G, et al.Technique of intramedullary osteosynthesis of the clavicle with elastic titanium nails. Unfallchirurg. 2002;105(6):511-516.[25] Kettler M, Schieker M, Braunstein V, et al. Flexible intramedullary nailing for stabilization of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: Technique and results in 87 patients. Acta Orthopaedica. 2007;78(3):424-429.[26] Jubel A, Andermahr J, Bergmann H, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of midclavicular fractures in athletes. Br J Sports Med. 2003;37(6):480-483.[27] Duan X, Zhong G, Cen S, et al. Plating versus intramedullary pin or conservative treatment for midshaft fracture of clavicle: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(6):1008-1015.[28] Houwert RM, Wijdicks FJ, Steins Bisschop C, et al. Plate fixation versus intramedullary fixation for displaced mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2012;36(3): 579-585. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [6] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [7] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [9] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [10] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [11] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [12] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [13] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [14] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [15] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||