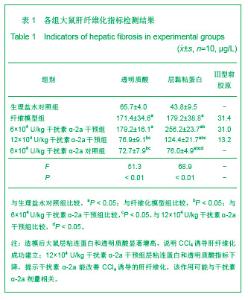
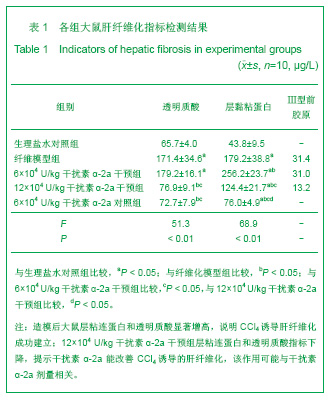
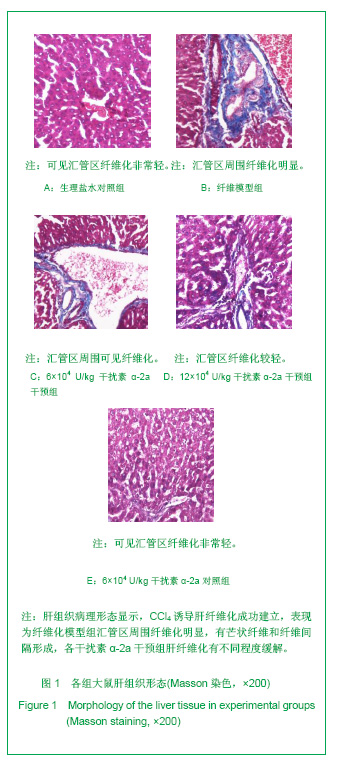
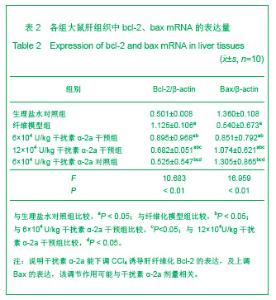
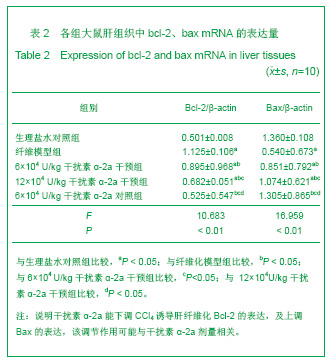
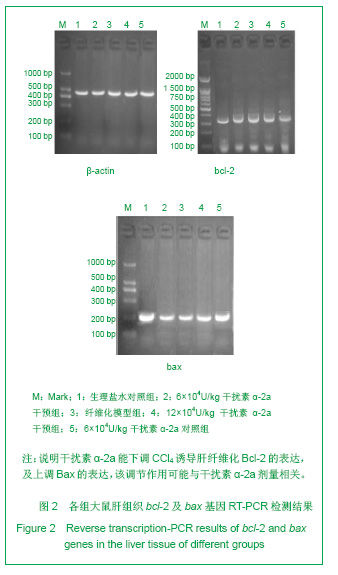
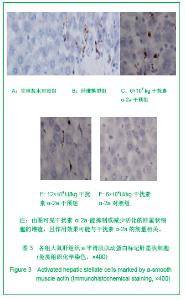
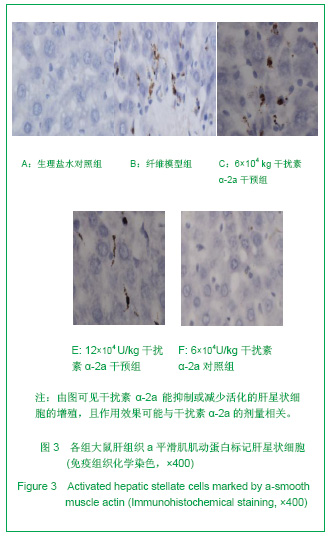
| [1] Wang PG,Liu WW,Liu XQ,et al.Zhongguo Linchuang Yanjiu. 2011;24(5):424-426. 汪培国,刘文武,刘溪泉,等.干扰素抗肝纤维化机制的研究进展[J].中国临床研究,2011,24(5):424-426.[2] Okazaki I,Watanabe T,Inagaki Y,et al. Recent advance in understanding mechanisms of fibrogenesis and fibrolysis in hepatic fibrosis.Nippon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2002; 99(4):353-364. [3] Adinolfi L E,Utili R,Tonziello A,et al.Effects of alpha interferon induction plus ribavirin with or without amantadine in the treatment of interferon non-responsive chronic C:a randomised trial.Gut.2003;52(5):701-705.[4] Mallat A, Preaux AM, Blazejewski S, et al. Interferon alfa and gamma inhibit proliferation and collagen synthesis of human Ito cells in culture. Hepatology. 1995; 21(4): 1003-1010.[5] Zhang W,Yi Z,Ye CG,et al.Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2011; 19(31):3207-3211. 张伟,易珍,叶长根,等.IFNa-2a对CCL4诱导肝纤维化的作用及影响因素[J].世界华人消化杂志,2011,19(31):3207-3211.[6] Friedman SL.Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology.2008;134(6):1655-1669. [7] Reeves HL,Friedman SL.Activation of hepatic stellate cells--a key issue in liver fibrosis.Front Biosci.2002;7:808-826. [8] Urtasun R, Nieto N. Hepatic stellate cells and oxidative stress. Rev Esp Enferm Dig.2007;99(4): 223-230.[9] Xu WH,Lü XX,Zhu JR,et al.Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi. 许伟华,吕晓霞,朱菊人,等.α干扰素对肝星状细胞凋亡及其基因表达的影响[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2003, 11(10): 633-634.[10] Huang Y,Huang C,Li J.Zhongguo Yaoli Tongbao. 2010,26(1): 9-13. 黄艳,黄成,李俊.肝纤维化病程中Kupffer细胞分泌的细胞因子对肝星状细胞活化增殖、凋亡的调控[J].中国药理学通报,2010, 26(1): 9-13.[11] Yang H,Yi YR.Curative effect of interferon-αon rat liver fibrosis induced by CCL4. J Cent South Univ(Med Sci).2008;33(10): 919-925.[12] Giannelli G, Ant onaci S. Imm unological and molecular aspects of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Histol Histopathol.2005;20(3):939-944.[13] Che L, Li ZW. Guoji Xiaohuabing Zazhi. 2007,27(4): 247-249. 车雷,李智伟.α-干扰素抗肝纤维化的研究现状[J].国际消化病杂志,2007,27(4):247-249.[14] Rao HY,Wei L,Fei R,et al.Inhibitory effect of interferon-beta on the activation of LX-2 and rHSC-99 hepatic stellate cells in culture. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.2006;14(7): 550-552.[15] Chang XM,Chang Y,Jia A.Effects of interferon-alpha on expression of hepatic stellate cell and transforming growth factor-betal and alpha-smooth muscle actin in rats with hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol.2005; 11(17):2634-2636. [16] Li JQ, Liu Y, Liu WZ,et al.Zhonghua Xiaohua Zazhi.2006; 28(8): 539-554. 李继强,柳怿,刘文忠,等.依那普利对肝组织bax和bcl-2基因表达的影响[J].中华消化杂志,2006;28(8):539-554.[17] Le Bousse-Kerdiles MC,Martyre MC,Samson M,Cellula and molecular mechanisms underlying bone marrow and liver fibrosis:a review.Eur Cytokine Netw.2008;19(2):69-80.[18] Sreelekha TT, Pradeep VM, Vijayalakshmi K, et al. In situ apoptosis in the thyroid.Thyroid.2000;10(2):117-122.[19] Novo E, Marra F, Zamara E, et al. Overexpression of Bcl-2 by activated human hepatic stellate cells: resistance to apoptosis as a mechanism of progressive hepatic fibrogenesis in humans. Gut.2006; 55(8):1174-1182.[20] Xin-Ming Chang, Ying Chang, Ai Jia.Effects of interferon-alpha on expression of hepatic stellate cell and transforming growth factor-β1 and α-smooth muscle actin in rats with hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11(17): 2634-2636. |