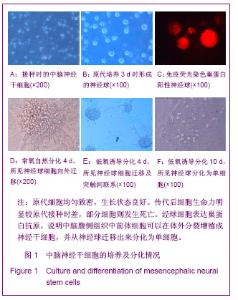
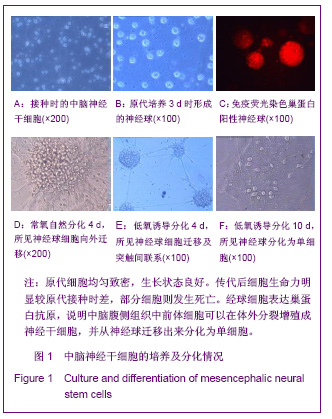
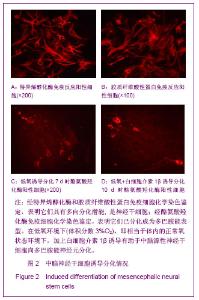
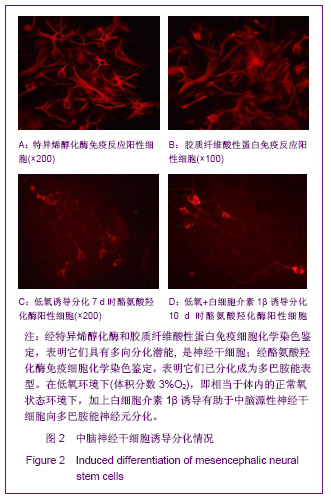
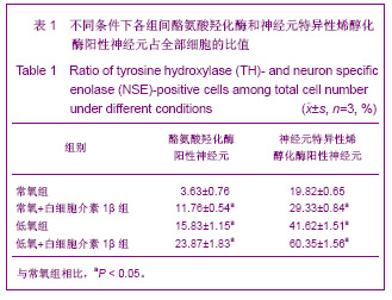
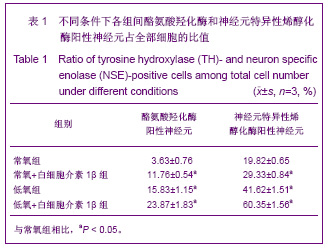
| [1] Moses D, Teper Y, Gantois I, et al. Murine embryonic EGF-responsive ventral mesencephalic neurospheres display distinct regional specification and promote survival of dopaminergic neurons. Exp Neurol.2006;18(1): 4-8.[2] Ding JG, Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2010; 14(10):1855-1860. 丁继固.中脑神经干细胞转基因治疗帕金森病:可能与可行?[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(10):1855-1860.[3] Ding JG,Ding WJ.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(40):7511-7514. 丁继固,丁文杰,低氧环境下胶质源性神经营养因子体外诱导中脑神经干细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(40):7511-7514.[4] Zhu C,Zhang CH,Liu ZH,et al.Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi. 2006;21(4):322-324. 祝畅,张传汉,刘志恒,等.人胚神经干细胞的长期贴壁培养和鉴定[J].中国康复医学杂志,2006,21(4):322-324.[5] Ding JG,Ding WJ,Li G.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2010;14(27):5033-5036. 丁继固,丁文杰,李光. 胶质源性神经营养因子与白细胞介素1β体外诱导中脑神经干细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010;14(27):5033-5036.[6] Ling ZD,Potter ED,Lipton JW,et al.Differentiation of mesencephalic progenitor cells into dopaminergic neurons by cytokines. Exp Neurol.1998;149(2):411-423. [7] Liu B,Dai YB,Peng CH,et al. Shuli Yiyanxue Zazhi.2004;17(5): 393-395. 刘兵,戴冀斌,彭超华,等.IL-1β诱导中脑NSCs向DA能神经元分化的研究[J].数理医药学杂志,2004,17(5):393-395. [8] Andersson K, Blum M, Chen Y, et al. Perinatal asphyxia increases bFGF mRNA levels and DA cell body number in the mesencephalon of rats. NeuroReport.1995;6 (2):375-378.[9] Csete M, Rodriguez L, Wilcox M, et al. Erythropoietin receptor is expressed on adult rat dopaminergic neurons and erythropoietin is neurotrophic in cultured dopaminergic neuroblasts. Neurosci Lett.2004 ;359(1-2):124-126.[10] Czyzyk-Krzeska MF, Furnari BA, Lawson EE, et al.Hypoxia increases rate of transcription and stability of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA in pheochromocytoma (PC12)cells. J Biol Chem.1994;269(1):760-764. |