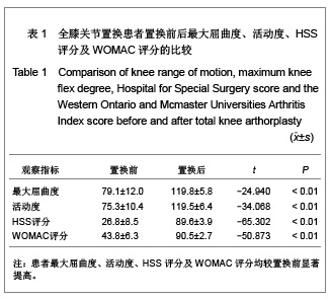
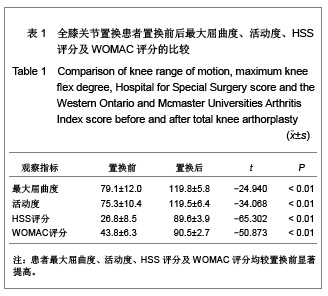
| [1] Lv HS, Yuan YL, Kou BL, et al. Beijing Daxue Xuebao (Yixueban). 2002;34(5):618-622. 吕厚山,袁燕林,寇伯龙,等. 1336 个人工膝关节置换术的临床特点分析[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2002,34(5):618-622.[2] Zhou YX. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2006;26(9):646-648. 周一新.人工膝关节假体设计对全膝关节置换术后髌股关节功能的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(9):646-648.[3] Zhang X, Wang ZW. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(13):2421-2424. 张欣,王志伟.人工全膝关节表面置换中髌骨的处理[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复. 2011,15(13):2421-2424.[4] Li S, Chen Y, Su W, et al. Systematic review of patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011;35(3): 305-316.[5] Radcliff KE, Orozco FR, Quinones D, et al. Preoperative risk stratification reduces the incidence of perioperative complications after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27(8 Suppl):77-80.e8.[6] Chen HS, Jin W, Xu F, et al. Shiyong Guke Zazhi. 2009;15(7): 540-541. 陈焕诗,金伟,许峰.人工全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节骨关节炎[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2009,15(7):540-541.[7] Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, et al. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(248):13-14.[8] Li BW. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(17):3313-3316. 李宝文. 全膝人工关节置换涉及的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(17):3313-3316.[9] Zhou YX. ZHonghua Guke Zazhi. 2006;26(9):646-648. 周一新.人工膝关节假体设计对全膝关节置换术后髌股关节功能的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(9):646-648.[10] Havet E, Gabrion A, Leiber-Wackenheim F, et al. Radiological study of the knee joint line position measured from the fibular head and proximal tibial landmarks. Surg Radiol Anat. 2007; 29(4):285-289.[11] Lv HS. Zhonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi. 2007;1(4):193-195. 吕厚山.当前膝关节置换存在的问题与思考[J].中华关节外科杂志, 2007,1(4):193-195.[12] Zhang HM, Sun G, Zhao TJ, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2006; 19(7):389-391. 张洪美,孙钢,赵铁军.全膝人工关节股骨假体屈曲原因分析及其对疗效影响[J].中国骨伤,2006,19(7):389-391.[13] Lu H, Mow CS, Lin J. tal knee arthroplasty in the presence of severe flexion contracture: a report of 37 cases. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(7):775-780.[14] Lv HS, Kou BL, Yuan YL,et al. ZHonghua Waike Zazhi. 1997, 7:424-427. 吕厚山,寇伯龙,袁燕林,等.高度屈膝畸形的人工全膝关节置换术[J].中华外科杂志,1997,7:424-427.[15] Lv HS, Guan ZP, Zhou DG, et al. ZHonghua Waike Zazhi. 2005; 43(20):1305-1308. 吕厚山,关振鹏,周殿阁,等. 膝关节外翻畸形的人工全膝关节置换术[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(20):1305-1308.[16] Zeng W, Wei YZ, Gao X, et al. Zhonghua Sunshang yu Xiufu Zazhi(dianziban). 2009;4(2):212-215. 曾伟,魏艳珍,高曦,等.软组织平衡在膝外翻畸形全膝关节置换中的意义[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2009,4(2):212-215.[17] Xu MT, Zha ZG, Liu N, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoixng Waike Zazhi. 2011;19(2):109-122. 徐美涛,查振刚,刘宁,等.人工全膝关节置换术在外翻膝的临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(2):109-122.[18] Lädermann A, Saudan M, Riand N, et al. Fixed-bearing versus mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized clinical and radiological study. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2008;94(3):247-251.[19] Shi FJ, Zhang JH, Wang F, et al. Shiyong Guke Zazhi. 2011; 17(8):701-703. 史法见,张锦洪,王芳,等.全膝关节置换术治疗膝外翻畸形疗效观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(8):701-703. [20] Zhou SG, Lv HS. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2001;21(12):714- 717. 周殿阁,吕厚山. 软组织平衡在膝内翻全关节置换术中的效果[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2001,21(12):714-717.[21] Liu XY, Li XS, Liu XD, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2010;23 (2): 139-142. 刘兴炎,李旭升,刘旭东,等.重度畸形膝关节病全膝关节置换的疗效分析[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(2):139-142.[22] Seon JK, Park SJ, Lee KB, et al. Range of motion in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective comparison of high-flexion and standard cruciate-retaining designs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(3):672-679.[23] Kim YH, Choi Y, Kwon OR, et al. Functional outcome and range of motion of high-flexion posterior cruciate-retaining and high-flexion posterior cruciate-substituting total knee prostheses. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(4):753-760.[24] Li J, Zheng K, Hu PX, et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2010;24(3):278-281. 李瑾,郑慷,胡培兴.高屈曲度与普通后稳定假体的人工全膝关节置换术近期疗效比较[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(3): 278-281.[25] Ranawat CS. Design may be counterproductive for optimizing flexion after TKR. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(416):174-176.[26] Lv SJ, Li WQ. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(9):1715-1718. 吕尚军,李文强.膝关节置换治疗膝内翻畸形的力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(9):1715-1718.[27] Robertsson O, Dunbar M, Pehrsson T, et al. Patient satisfaction after knee arthroplasty: a report on 27,372 knees operated on between 1981 and 1995 in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(3):262-267.[28] Sun YB, Liu J, Tian ZW, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2011;19(13):1073-1076. 孙云波,刘军,田峥巍,等.全膝关节置换股骨切迹发生因素分析及远期随访研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(13):1073-1076.[29] Khatod M, Codsi M, Bierbaum B. Results of resurfacing a native patella in patients with a painful total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2004;17(3):151-155.[30] Hsu RW. The management of the patella in total knee arthroplasty. Chang Gung Med J. 2006;29(5):448-457.[31] Zou YG, Chen ZW, Feng ZQ, et al. Nanfang Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2011;31(8):1428-1430. 邹勇根,陈志维,冯宗权,等. 影响膝关节置换术术后膝前痛的相关因素[J].南方医科大学学报,2011,31(8):1428-1430.[32] Epinette JA, Manley MT. Outcomes of patellar resurfacing versus nonresurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a 9-year experience based on a case series of scorpio PS knees. J Knee Surg. 2008;21(4):293-298.[33] Oztürk A, Bilgen S, Atici T, et al. The evaluation of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty with or without patellar resurfacing. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2006;40(1):29-37.[34] Yim SJ, Jang MS, Kim WJ,et al. The Effect of Electrocautery around the Patellar Rim in Patellar Non-Resurfacing Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012;24(2): 104-107.[35] Zhou YX, Zhang H, Huang DY, et al. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2003;23(2):82-85. 周一新,张洪,黄德勇,等.股骨假体设计对保留髌骨全膝关节置换术后膝前痛的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(2):82-85. |