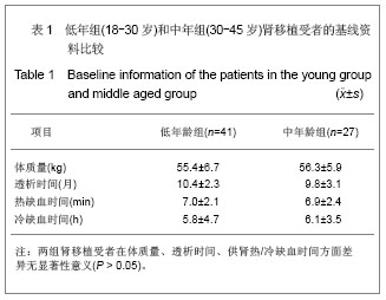
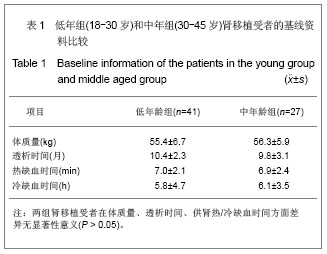
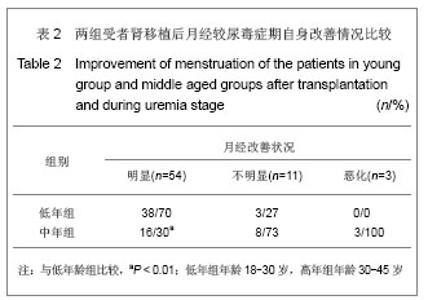
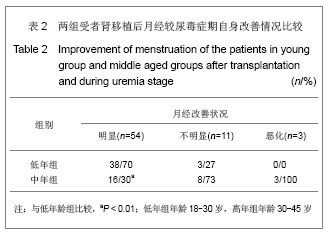
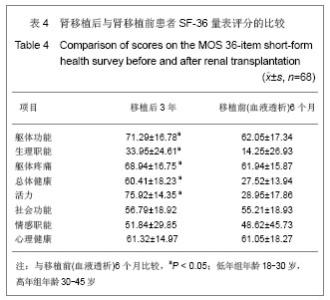
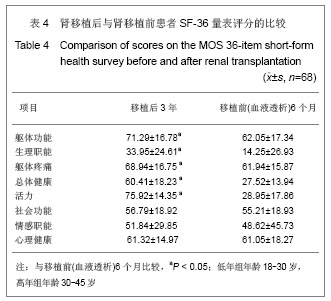
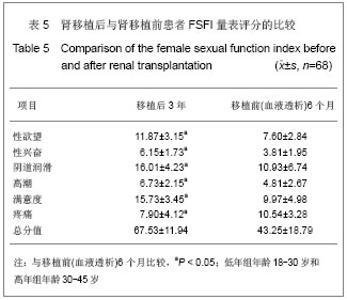
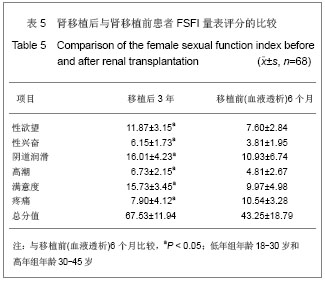
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 797-804.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.05.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Investigation in women of childbearing age after renal transplantation: Menstruation, sexual life and birth condition
Zuo Fu-jie1, Han Shu2, Wang Li-ming2, Min Min1, Feng Xiao-fang1, Zhou Mei-sheng2, Li Qun1
- 1 Department of Kidney Transplant Rehabilitation, Zhabei District Central Hospital, Shanghai 200070, China
2 Department of Renal Transplantation, Changzheng Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China
-
Received:2012-08-10Revised:2012-11-15Online:2013-01-29Published:2013-01-29 -
Contact:Wang Li-ming, Doctor, Chief physician, Department of Renal Transplantation, Changzheng Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China -
About author:Zuo Fu-jie, Attending physician, Department of Kidney Transplant Rehabilitation, Zhabei District Central Hospital, Shanghai 200070, China zfj716824@yahoo.com.cn Han Shu, Doctor, Attending physician, Department of Renal Transplantation, Changzheng Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China hanshu73@163.com.cn Zuo Fu-jie and Han Shu contributed equally to this paper.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zuo Fu-jie, Han Shu, Wang Li-ming, Min Min, Feng Xiao-fang, Zhou Mei-sheng, Li Qun. Investigation in women of childbearing age after renal transplantation: Menstruation, sexual life and birth condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(5): 797-804.
share this article
| [1] Park KS, Hwang YJ, Cho MH, et al. Quality of life in children with end-stage renal disease based on a PedsQL ESRD module. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27(12):2293-2300.[2] Perl J, Zhang J, Gillespie B,et al. Reduced survival and quality of life following return to dialysis after transplant failure: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][3] Molnar-Varga M, Molnar MZ, Szeifert L,et al. Health-related quality of life and clinical outcomes in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;58 (3): 444-452.[4] Sha GZ,Zhang ZY,Ji SM,et al. Yixue Yanjiusheng Xuebao. 2010; 23(7):738-742.沙国柱,张卓玉,季曙明,等.肾移植女性受者移植后续用含铜宫内节育器对月经模式的影响[J]. 医学研究生学报,2010, 23(7): 738-742.[5] Xu LG,Qi XP,Song QZ,et al. Xiandai Miniao Waike Zazhi. 2004; 9(1):17-19.许龙根,戚晓平,宋启哲,等.肾移植患者性生活质量的影响因素[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志,2004,9(1):17-19.[6] Xu LG,Han S,Liu Y,et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2009; 30(1):40-42.许龙根,韩澍,刘永,等.女性肾移植受者术后生育22例报告[J].中华器官移植杂志,2009,30(1):40-42.[7] Jenkinson C, Wright L, Coulter A. Criterion validity and reliability of the SF-36 in a population sample. Qual Life Res. 1994;3(1):7-12.[8] Campolina AG, Ciconelli RM.SF-36 and the development of new assessment tools for quality of life. Acta Reumatol Port. 2008;33(2):127-133.[9] Molnar-Varga M, Molnar MZ, Szeifert L, et al. Health-related quality of life and clinical outcomes in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;58(3):444-452.[10] Fujisawa M, Ichikawa Y, Yoshiya K,et al. Assessment of health-related quality of life in renal transplant and hemodialysis patients using the SF-36 health survey. Urology. 2000;56(2):201-206.[11] Jie L,Liu Q,Wang XL,et al. Zhongguo Neijing Zazhi. 2011; 17(9):913-916.颉丽,刘青,王晓黎,等.腹腔镜下两种阴道成形术治疗MRKH综合征的临床研究[J].中国内镜杂志,2011,17(9):913-916.[12] Li JY. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao. 2012;7(15):108-110.李晶燕.聚焦超声治疗外阴上皮内非瘤样变及术后对性生活质量的评价[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(15):108-110.[13] Han XP,Yu LX,Yan P,et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 1997;18(2): 105.韩献萍,于立新,严萍,等. 肾移植前后妇女的生育力和相关激素研究[J]. 中华器官移植杂志, 1997,18(2): 105.[14] Jin JS,Lin QY,Qiu XP,et al. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi. 2002;12(8):57-58.金建生,林庆友,邱晓萍,等.尿毒症患者的性激素变化及其临床意义探讨[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2002,12(8):57-58.[15] Saha MT, Saha HH, Niskanen LK,et al. Time course of serum prolactin and sex hormones following successful renal transplantation. Nephron. 2002;92(3):735-737.[16] Blumenkrantz MJ, Gallagher N, Bashore RA,et al. Retrograde menstruationin women undergoing chronic peritoneal dialysis. Obstet Gynecol .1981;57 (5): 667-670.[17] Zhou MS,Zhu YH,Min ZL,et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2005;26 (1):25-27.周梅生,朱有华,闵志廉,等.女性患者肾移植前后性相关激素、微量元素以及生育能力的研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,2005,26(1): 25-27. [18] Pezeshki M, Taherian AA, Gharavy M,et al. Menstrual characteristics and pregnancy in women after renal transplantation. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2004;85(2):119-125. [19] Wang L,Qian YS. Zhejiang Yufang Yixue. 2001;13(6):11,27.王良,钱元淑.妇女肾移植后月经过多的性激素水平及治疗[J].浙江预防医学,2001,13(6):11,27.[20] Ghazizadeh S, Lessan-Pezeshki M, Mahdavi M,et al. Menstrual problems among kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2003;35(7): 2720-2721.[21] Zhu XQ,Dong Y,Shi YF,et al. Yixue Yanjiu Zazhi. 2011;40(8): 14-16.朱雪琼,董煜,石一复,等.子宫肌瘤患者绝经后的激素替代疗法[J]. 医学研究杂志,2011,40(8):14-16.[22] Wu RJ,Jiang QY. Zhonghua Quanke Yishi Zazhi. 2011;10(12): 856-858.吴瑞瑾,江桥英. 月经过多的诊治分析[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2011,10(12):856-858.[23] Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Knoll G, et al. Systematic review: kidney transplantation compared with dialysis in clinically relevant outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(10):2093-2109.[24] Yuan H. Disi Junyi Daxue Xuebao.2009;30(8):700.袁红. 米非司酮联合甲基睾丸素治疗围绝经期子宫肌瘤85例[J]. 第四军医大学学报, 2009,30(8):700.[25] Macdonald JH, Kirkman D, Jibani M. Kidney transplantation: a systematic review of interventional and observational studies of physical activity on intermediate outcomes. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2009;16(6):482-500.[26] van der Mei SF, Kuiper D, Groothoff JW,et al. Long-term health and work outcomes of renal transplantation and patterns of work status during the end-stage renal disease trajectory. J Occup Rehabil. 2011;21(3):325-334.[27] Landreneau K, Lee K, Landreneau MD. Quality of life in patients undergoing hemodialysis and renal transplantation--a meta-analytic review. Nephrol Nurs J. 2010;37(1):37-44.[28] Maglakelidze N, Pantsulaia T, Tchokhonelidze I,et al. Assessment of health-related quality of life in renal transplant recipients and dialysis patients.Transplant Proc. 2011;43(1): 376-379.[29] Rambod M, Shabani M, Shokrpour N, et al. Quality of life of hemodialysis and renal transplantation patients. Health Care Manag (Frederick). 2011;30(1):23-28.[30] Balaska A, Moustafellos P, Gourgiotis S, et al. Changes in health-related quality of life in Greek adult patients 1 year after successful renal transplantation. Exp Clin Transplant. 2006;4(2):521-524.[31] Liem YS, Bosch JL, Hunink MG. Preference-based quality of life of patients on renal replacement therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Value Health. 2008; 11(4):733-741. [32] Pollice R, Di Mauro S, Bernardini M, et al. Psychopathology, quality of life and social functioning in dialysis treatment and kidney transplantation patients. Clin Ter. 2010;161(4): 329-333.[33] Germin-Petrovi? D, Mesaros-Devci? I, Lesac A,et al. Health-related quality of life in the patients on maintenance hemodialysis: the analysis of demographic and clinical factors. Coll Antropol. 2011;35(3):687-693. [34] Zheng JH,Min ZL,Zhu YH,et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 1996;17(3):120-122.郑军华,闵志廉,朱有华,等. 肾移植患者血清垂体-性腺激素、微量元素的测定及其性功能的研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,1996, 17(3): 120-122.[35] Shan YX,Yan CH. Suzhou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 1999;19(7): 784-785.单玉喜,颜纯海.肾移植患者性激素检测及性功能变化研究[J]. 苏州医学院学报,1999,19(7):784-785.[36] Zheng JH,Min ZL,Zhu YH,et al. Zhongguo Xinli Weisheng Zazhi. 1996;10(1) :28.郑军华,闵志廉,朱有华,等. 肾移植患者及家属性心理和性行为调查[J] . 中国心理卫生杂志, 1996,10(1) :28.[37] Filocamo MT, Zanazzi M, Li Marzi V,et al. Sexual dysfunction in women during dialysis and after renal transplantation. J Sex Med. 2009;6 (11): 3125-3131.[38] Ma XN.Beijing: People's Military Medical Press. 1995:171- 194.马晓年.年龄对性功能的影响[A] .见:薛兆英,许又新,马晓年主编.现代性医学[M] .北京:人民军医出版社,1995:171-194.[39] Sun Y,Li J,Liu YY. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(5):921-924.孙颖, 李静, 刘雅英. 肾移植患者的心理状态及其干预措施[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(5):921-924.[40] Murray JE, Reid DE, Harrison JH,et al. Successful pregnancies after human renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1963;269:341-343.[41] Tao X,Cao MZ,Zhang B,et al. Zhongguo Nankexue Zazhi. 2009; 23(11):19-22.陶欣,曹明珠,张滨,等.广州地区不同年龄成年女性性行为方式调查[J].中国男科学杂志,2009,23(11):19-22.[42] Jin LM,Xu LG,Zheng SS. Guoji Miniao Xitong Zazhi. 2008; 28(4): 535-539.金丽明,许龙根,郑树森. 肾移植受者术后生育问题[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志,2008,28(4):535-539.[43] Chang Y,Zhang LJ. Zhongguo Fuchanke Linchuang Zazhi. 2007;8(2):156-157.常玥,张丽江. 肾移植术后妊娠及分娩[J].中国妇产科临床杂志, 2007,8(2):156-157.[44] Xu LG, Wang HW, Peng WL, et al. Marital status and fertility of 185 male renal transplant recipients in China. J Androl. 2008;29(6):618-621.[45] Lessan-Pezeshki M. Pregnancy after renal transplantation: points to consider. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17(5): 703-707.[46] Yu LX,Miao Y,Han XP,et al. Zhonghua Miniao Waike Zazhi. 2011;32(11):758-761.于立新,苗芸,韩献萍,等.女性肾移植受者妊娠结果及子代健康状况随访[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2011,32(11):758-761.[47] Al-Khader AA, Basri N, Al-Ghamdi, et al. Pregnancies in renal transplant recipients--with a focus on babies. Ann Transplant. 2004;9(3):65-67.[48] Armenti VT, Constantinescu S, Moritz MJ,et al. Pregnancy after transplantation.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2008;22(4): 223-240.[49] EBPG Expert Group on Renal Transplantation. European best practice guidelines for renal transplantation. Section IV: Long-term management of the transplant recipient. IV.10. Pregnancy in renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17 Suppl 4:50-55.[50] Han ZY,Wu ZQ,Wu YB,et al. Qiguan Yizhi. 2011;2(4):201-204.韩志友,吴振起,吴雅冰,等.肾移植术后妊娠4例次报告并文献复习[J].器官移植,2011,2(4):201-204.[51] Wilson GA, Coscia LA, McGrory CH, et al. National transplantation pregnancy registry: postpregnancy graft loss among female pancreas-kidney recipients.Transplant Proc. 2001;33(1-2):1667-1669.[52] Jackson P, Paquette L, Watiker V, et al. Intrauterine exposure to mycophenolate mofetil and multiple congenital anomalies in a newborn: possible teratogenic effect. Am J Med Genet A. 2009;149A(6):1231-1236. [53] He WJ. Guoji Yaoxue Yanjiu Zazhi. 2008;35(3):226.何文俊.吗替麦考酚酯和麦考酚酸缓释片可能导致流产和先天性畸形[J].国际药学研究杂志,2008,35(3):226.[54] Fernando ON. Pregnancy in transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2002;34(6):2403-2404. |
| [1] | Fan Jiabing, Zhang Junmei. Morphological measurement and analysis of the mandible in adult females with different vertical skeletal types [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1177-1183. |
| [2] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [3] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [4] | Li Dao, Xiao Guanqing, Zhang Yu, Xie Chao, Ye Peiyi, Li Xiaolei, He Hanchang, Chen Youyuan, Kong Yaozhong. Effects of the new type Palindrome H-heparin-coated dialysis catheter on the systemic coagulation function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1570-1573. |
| [5] | Zhong Yanping, Zou Hongyan, Quan Zhanrou, Deng Zhihui, Hong Wenxu. Analysis of full-length sequence and 18 point mutations of HLA-B in a leukemia patient and her family [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 77-82. |
| [6] | Cai Qiucheng, Fan Hongkai, Xiong Rihui, Jiang Yi. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects liver function following fatty liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2625-2629. |
| [7] | Jiang Shanshan, Wang Feng, Yu Limei. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their application in organ transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 103-109. |
| [8] | Zhou Yi-fei, Zheng Qian, Mao Jie, Lv Jia-ling, Wu Xiao-ling, Xu Xiao-mei. Combined oral contraceptives facilitate periodontium remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 542-547. |
| [9] | Luo Wei. Correlation of volleyball exercise with bone mineral density in females at different ages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(24): 3780-3785. |
| [10] |
Zhang Jin-zhe, Zhou Qun-hua, Yang Li-qun, Zhang Wei, Li Jian-xin, Jin Ying, Yi Dong-xu.
Non-biodegradable and biodegradable long-term subdermal contraceptive implants: advances in theoretical research and application
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(22): 3595-3601.
|
| [11] | Liu Teng-fei, Zhou Jian-kang, Huang Tuan-jie, Xing Qu, Cheng Kang, Li Peng, Li Dong-peng, Yang Bo, Ma Shan-shan, Guan Fang-xia . MG53 protein protects against multiorgan ischemia/reperfusion injury: present and future [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(20): 3248-3254. |
| [12] |
Wang Shi-ying, Zhao Xin-xin, Shi Jun, Yang Su-xia, Sun Zhi-qiang .
Preparation, transfer property and biocompatibility of the hollow fiber dialysis membrane
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(2): 268-272.
|
| [13] | Li Ling, Li Ning, Ai Zi-ye, Yao Ya-jun, Wei Wan-hui, He Wei-yang, Wang Yan-feng, Ye Qi-fa. Intra-patient variability of tacrolimus concentration in transplant recipients: a prognostic predictor post transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7437-7422. |
| [14] | Tang Feng, Xie Ning, Wu Tao, Liu Jun, Wang Bin-bin, Wang Yang, Xu Li-zhang. A scoliosis model of bipedal female mouse induced by high-concentration osteopontin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7301-7306. |
| [15] | Yan Hong-guang. Walking gait characteristics of adult women with different body mass indexes wearing different height heels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7349-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||