Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9294-9300.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.031
Previous Articles Next Articles
MicroRNAs regulate self-renewal and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Chen Xue-bin, Xu Yin-sheng, Zhang Fang, Sheng Wang
- Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
-
Received:2012-01-08Revised:2012-03-19Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
Contact:Sheng Wang, Professor, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China shengwang@bjut.edu.cn -
About author:Chen Xue-bin☆, Studying for doctorate, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China chenxuebin116@163.com -
Supported by:Academic Human Resources Development in Institutions of Higher Learning Under the Jurisdiction of Beijing Municipality, No.01500054RA001*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xue-bin, Xu Yin-sheng, Zhang Fang, Sheng Wang. MicroRNAs regulate self-renewal and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9294-9300.
share this article
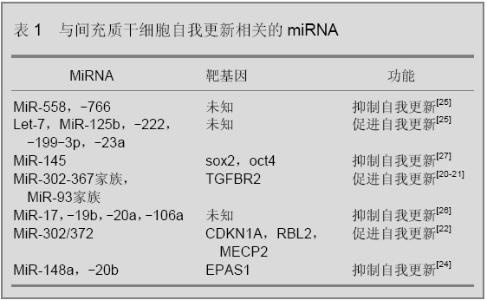
2.1 miRNA在间充质干细胞自我更新中的功能 miRNA可以调控干细胞自我更新,见表1。Xu等[19]的报道中,过表达miR-145会导致胚胎干细胞自我更新能力降低,miR-145可以通过抑制干细胞重组的重要因子sox2、oct4、klf-4的表达而降低胚胎干细胞干性。研究表明在鼠纤维细胞中过表达miR-302-367家族miRNA可以提高由Sox2、Klf4和Oct4诱导形成诱导全能干细胞的能力[20],类似的研究表明miR-93和miR-106通过靶向调控转化生长因子β受体Ⅱ的表达[21],miR-302/372通过抑制靶基因CDKN1A、RBL2、MECP2的表达提高了细胞向诱导全能干细胞的转化效率[22],miR-34通过调控靶基因nanog、sox2、mycn的表达抑制了干细胞自我更新和重组[23]。 Giraud-Triboult等[24]比较了间充质干细胞和胚胎干细胞miRNA和mRNA的表达谱差异,发现在间充质干细胞中miR-148a和miR-20b表达下降,其靶基因EPAS1转录因子的表达增高,从而提高间充质干细胞形态特异性蛋白的表达,维持间充质干细胞的形态特征。Yu等[25]比较了年老猴子和年轻猴子骨髓间充质干细胞活性和miRNA表达的差异。与年轻猴子相比年老猴子骨髓间充质干细胞中端粒酶的表达下降了约65%,miRNA芯片分析结果显示在年老猴子的间充质干细胞中,miR-766和miR-558表达升高,miR-125b、let-7、miR-222、miR-199-3p、miR-23a和miR-221表达下降。类似的研究中Hackl等[26]发现miR-17、miR-19b、miR-20a和miR-106a在细胞老化模型中表达降低,这些miRNA对于间充质干细胞的自我更新具有重要作用。Riggi等[27]的研究发现EWS-FLI-1在胚胎干细胞中可以激活Oct4、Nanog、Sox2的表达,在间充质干细胞中过表达EWS-FLI-1能够提高Sox2的表达,同时降低miR-145的表达,而miR-145的一个靶基因就是Sox2,EWS-FLI-1和miR-145通过形成抑制性的反馈调节调控Sox2表达来调节干细胞的干性。Nie等[28]分析了miRNA与间充质干细胞凋亡之间的关系,作者发现在间充质干细胞中过表达miR-21、miR-23a和miR-210可以增强干细胞在低氧环境中的生存率,降低这些miRNA的表达会加快细胞凋亡。总之miRNA在间充质干细胞的自我更新过程中发挥着重要作用,随着人们对间充质干细胞自我更新认识的加深,miRNA在其过程中的作用也会越来越重要。 2.2 miRNA在间充质干细胞分化中的功能 间充质干细胞在适当的条件下可以诱导分化为骨细胞、软骨细胞、肌肉细胞、神经细胞和脂肪细胞等,在间充质干细胞分化过程中伴有miRNA表达的变化,特异性miRNA在间充质干细胞分化过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。 2.2.1 miRNA对间充质干细胞成骨分化过程的调控 间充质干细胞在向骨分化的过程中会受到血小板衍生生长因子、wnt、骨形态发生蛋白等多种信号途径的调节。Goff等[29]研究发现血小板衍生生长因子信号途径可以通过控制miRNA的表达来促使间充质干细胞向骨方向分化。Wnt途径的激活可以促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化,研究表明,miR-27通过调控靶基因APC的表达激活wnt信号途径[30],miR-29通过抑制wnt信号途径的反向调控因子Dkk1、Kremen2、sFRP2激活wnt信号途径[31],从而促使细胞向骨细胞方向分化。Runx2是成骨过程中一个重要的细胞因子,它可以激活与成骨相关基因的表达,其表达受到骨形态发生蛋白信号途径的调节,间充质干细胞中过表达miR-204和miR-335会抑制RUNX2的表达[13,32],从而降低间充质干细胞向骨方向分化的能力。Mizuno等[33]研究表明miR-125b可以调控骨形态发生蛋白诱导的成骨过程,当miR-125的表达被抑制时,由骨形态发生蛋白诱导的碱性磷酸酶表达增多,会促进细胞成骨分化。Zhang等[34]研究发现miR-20a的靶基因是骨形态发生蛋白信号途径的反向调控因子PPARγ、Bambi和CRim1,在成骨过程中miR-20a表达增加,miR-20a通过调控骨形态发生蛋白-RUNX2信号途径而促使细胞向骨方向分化。 Gao等[35]通过生物芯片技术分析了骨髓间充质干细胞成骨诱导前后miRNA表达谱的变化,得到4个表达下降的miRNA(miR-31、miR-106a、miR-148a和miR-424)和3个表达升高的miRNA(miR-30c、miR-15b和miR-130b),通过靶基因预测作者认为4个显著下降的miRNA靶基因可能是Runx2、CBFB、骨形态发生蛋白,而表达升高的miRNA靶基因可能是间充质干细胞特异性标记蛋白CD44、ITGB1、FLT1和间充质干细胞干性维持因子成纤维细胞生长因子2和CXCL12,这些miRNA共同作用促使了细胞向骨方向分化。类似研究中Schoolmeesters等[36]分析了间充质干细胞向骨分化前后miRNA表达谱的变化,发现miR-27a,miR-489在分化以后表达下调,miR-148b在成骨分化后表达下调,实验表明通过改变这3个miRNA在间充质干细胞中的表达,可以促使细胞在不加诱导剂的情况下向成骨方向分化。Eskildsen等[37]的研究表明在体外成骨过程中抑制miR-138的表达可以促进成骨特异性基因碱性磷酸酶的表达,促进间充质干细胞成骨分化,体内研究证实抑制miR-138的表达可以使成骨能力提高60%。在Kim等[38]的研究中,miR-196通过降低靶基因HOXC8的表达促使间充质干细胞向骨方向分化,在间充质干细胞中过表达miR-196a可以增强干细胞向骨分化的能力。总之,miRNA在间充质干细胞的成骨分化过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。 2.2.2 miRNA对间充质干细胞成软骨分化中的调控 间充质干细胞向软骨分化过程也受到了miRNA的调控,在软骨分化过程中,早期细胞聚集是软骨细胞形成的一个必须步骤,Song等[39]发现miR-488在细胞聚集的早期高表达,在软骨分化以后表达降低,研究发现miR-488通过调节靶基因基质金属蛋白酶3的表达水平调控了软骨分化早期细胞聚集过程,促进了软骨分化的发生。 Miyaki等[40]分析了人骨髓来源的间充质干细胞和正常软骨细胞miRNA表达谱差异,结果显示miR-140在两种细胞中表达差异最显著。研究表明miR-140与正常软骨细胞基因表达有密切联系,在骨关节炎软骨或白细胞介素6诱导的条件下,软骨细胞中miR-140表达下降,miR-140表达降低会造成正常软骨细胞特异性蛋白表达失调。Yan等[6]利用生物芯片技术比较了大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨诱导后和正常软骨细胞的miRNA表达谱,在44个表达差异显著的miRNA中,检测了miR-29a和miR-29b在成软骨诱导过程中的调控作用,这两个miRNA的靶基因都是软骨特异性的蛋白collagenⅡ,过表达miR-29a和miR-29b会导致间充质干细胞软骨分化能力降低。 在细胞成软骨诱导过程中,转化生长因子β信号通路起着非常重要的作用,Lin等[41]研究发现,miR-199a*通过抑制骨形态发生蛋白Ⅱ信号途径smad1蛋白的表达抑制了其下游sox9,collagenⅡ,COMP的表达,过表达miR-199a*减弱了间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化的能力。Yang等[42]分析了鼠骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化前后miRNA的表达谱变化。研究发现,过表达miR-145可以降低转化生长因子β信号途径下游与软骨分化相关的重要转录因子sox9的表达,抑制了间充质干细胞向软骨细胞的分化[14]。本实验室利用芯片检测人脐带间充质干细胞成软骨分化前后miRNA的表达情况,研究发现miR-485和miR-889可以通过调节sox9的表达来调控间充质干细胞成软骨分化的能力(数据未发表)。 2.2.3 miRNA对间充质干细胞成脂肪分化的调控 近些年来,肥胖已成为困扰人类健康的一大问题,与脂肪相关的研究越来越多,miRNA对脂肪形成过程的调控也引起了人们的注意。Bengestrate等[43]分析人脂肪来源间充质干细胞成脂肪分化前后miRNA表达谱的变化,得到了4个表达明显调高的miRNA(miR-26a、miR-99a、miR-143和miR-455)以及3个表达明显下降的miRNA(miR-7、miR-130b、miR-92),研究发现这些miRNA的表达与脂肪特性基因的表达密切相关。Nakanishi等[44]利用生物芯片和生物信息学手段分析了肥胖症大鼠肝脏脂肪细胞的miRNA表达谱,研究表明当细胞向脂肪细胞分化时miR-335表达增加,miR-335的表达与肪细胞特异性蛋白PPARγ、Ap2、FAS的表达密切相关,作者认为肝脏中miR-335表达水平可以作为检测肥胖症的一个标记。类似的研究中Ortega等[45]分析了成熟脂肪细胞和早期脂肪母细胞miRNA表达水平的差异,得到了50个表达差异明显的miRNA,这些在脂肪分化前后表达差异显著的miRNA可能会成为肥胖症或与肥胖症相关一些疾病的特异性标记物或治疗靶点。 转化生长因子β信号途径可以抑制间充质干细胞向脂肪分化,Kim等[46]研究发现在间充质干细胞中过表达miR-21会抵消转化生长因子β引起成脂分化抑制的现象,研究表明miR-21的一个靶基因是转化生长因子β信号通路的受体转化生长因子β受体Ⅱ,而且miR-21的表达还会调控到smad3的磷酸化水平,miR-21通过转化生长因子β信号通路的抑制促进了间充质干细胞向脂肪分化。在Sun等[47]的研究中,let-7可以通过部分抑制细胞克隆形成和增殖相关转录因子HMGA2的表达来促进3T3L1细胞成脂肪分化,miR-143通过抑制Erk5蛋白的表达促进了细胞成脂肪分化[48]。Kim等[49]报道miR-27a在成脂诱导中表达降低,过表达miR-27a可以通过抑制PPARγ的表达调控细胞成脂分化能力。Wang等[50]的研究表明,在3T3L1细胞中稳定转染miR-17-92家族miRNA可以增加细胞成脂肪分化过程中三酰甘油的积累,实验证实miR-17-92通过靶向抑制Rb2/p130的表达增强了细胞成脂分化能力。研究表明miR-369-5p、miR-371、miR-138、miRNA-378/378*和miR-210等在干细胞成脂肪分化过程中都发挥着重要的调控作用[51-54]。 2.2.4 miRNA对间充质干细胞成肌肉分化的调控 间充质干细胞在向肌肉分化的过程也受到miRNA的调控。Danielson等[55]研究表明miRNA的表达是间充质干细胞向肌肉细胞分化所必需的,实验比较了正常骨髓间充质干细胞和缺失Drosha和Dicer的间充质干细胞成肌肉分化的能力,发现突变的间充质干细胞不能分化为肌肉细胞。在Shan等[56]的研究中,作者检测了与肌肉细胞不接触共培养的间充质干细胞和用5-氮胞苷成肌肉诱导间充质干细胞中miRNA的表达变化,作者发现此过程中在肌肉细胞特异性蛋白开始表达的同时miR-143,miR-181,miR-206,miR-208表达增高,作者认为这些miRNA与肌肉分化密切相关。在Chen等[57]的研究中,miR-1和miR-133可以分别通过抑制靶基因HDAC4和SRF的表达来调控胚胎发育中骨骼肌相关基因的表达。Naguibneva等[58]的研究表明miR-181在肌肉细胞中高表达,实验证实miR-181的高表达可以抑制肌肉细胞分化的一个抑制因子Hox-A11的表达,从而促进细胞向肌肉细胞分化。 2.2.5 miRNA对间充质干细胞成神经分化的调控 在间充质干细胞成神经分化过程中Notch信号途径起反向调节作用,Jing等[59]的研究发现,miR-9在神经诱导过程中表达增高,实验表明miR-9的靶基因是notch1蛋白,miR-9通过调节Notch信号途径增强了间充质干细胞向神经分化的能力。研究表明miR-206和miR-130a可以通过对靶基因TacI的调节来调控神经细胞中SP的合成与释放[60]。Maisel等[15]分析了间充质干细胞向神经分化前后mRNA和miRNA表达谱变化,研究显示HIF-1和miR-124a通过调节与氧相关的信号通路促进间充质干细胞向神经细胞的分化。Crobu等[61]分析了骨髓间充质干细胞成神经分化前后的miRNA表达谱差异,发现miR-31和miR-138在间充质干细胞中表达较高,而miR-21、miR-143、miR-23b在成神经诱导后表达升高。类似的研究中,miR-373、miR-584、miR-149、miR-91、miR-30c等在成神经诱导后的表达增高,这些神经诱导前后发生变化的miRNA与神经细胞分化有着密切的关系[62]。 综上所述,miRNA在间充质干细胞向骨、软骨、脂肪、肌肉、神经等分化过程中起到重要的调控作用。 2.3 miRNA在间充质干细胞中的其他调控作用 最近研究发现细胞来源的微泡(microvesicle)是细胞与细胞之间信息传导的一种新机制,这些微泡通过与靶细胞的融合来传递其中含有的基因信息。研究表明胚胎干细胞分泌的微泡中所含mRNA对造血干细胞的重编有调控作用[63]。在人体中,间充质干细胞可以通过释放一些细胞因子、激酶和细胞基质蛋白分子而修复受损组织。Collino等[64]从间充质干细胞分泌的微泡中检测到了多种miRNA,通过芯片分析发现有些miRNA在微泡中富集,间充质干细胞对其他组织细胞的调节和修复,有一部分是通过微泡中的miRNA发挥作用的。"
| [1] Gregory RI, Chendrimada TP, Cooch N, et al. Human RISC couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell. 2005;123(4):631-640.[2] Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, et al. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature. 2004; 432(7014):231-235.[3] Kim DH, Behlke MA, Rose SD, et al. Synthetic dsRNA Dicer substrates enhance RNAi potency and efficacy. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(2):222-226.[4] Ketting RF, Fischer SE, Bernstein E, et al. Dicer functions in RNA interference and in synthesis of small RNA involved in developmental timing in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2001;15(20): 2654-2659.[5] Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, et al. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature. 2004; 432(7014):231-235.[6] Yan C, Wang Y, Shen XY, et al. MicroRNA regulation associated chondrogenesis of mouse MSCs grown on polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biomaterials. 2011;32(27):6435-6444.[7] Guo L, Zhao RC, Wu Y. The Role of microRNAs in self-Renewal and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2011;39(6):608-616.[8] Afanasyev BV, Elstner EE, Zander AR, et al. founder of the mesenchymal stem cell concept. Cellular Therapy and Transplantation (CTT). 2009;1:35-38.[9] Mauck RL, Yuan X, Tuan RS. Chondrogenic differentiation and functional maturation of bovine mesenchymal stem cells in long-term agarose culture. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(2):179-189.[10] Wakitani S, Imoto K, Yamamoto T, et al. Human autologous culture expanded bone marrow mesenchymal cell transplantation for repair of cartilage defects in osteoarthritic knees. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(3):199-206.[11] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E, et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):319-331.[12] Koh W, Sheng CT, Tan B, et al. Analysis of deep sequencing microRNA expression profile from human embryonic stem cells derived mesenchymal stem cells Reveals possible Role of let-7 microRNA family in downstream targeting of Hepatic Nuclear Factor 4 Alpha. BMC Genomics. 2010;11 Suppl 1:S6.[13] Huang J, Zhao L, Xing L. MicroRNA-204 regulates Runx2 protein expression and mesenchymal progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cells. 2010;28(2):357-364.[14] Yang B, Guo H, Zhang Y, et al. MicroRNA-145 regulates chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by targeting Sox9. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21679.[15] Maisel M, Habisch HJ, Royer L. Genome-wide expression profiling and functional network analysis upon neuroectodermal conversion of human mesenchymal stem cells suggest HIF-1 and miR-124a as important regulators. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(17):2760-2778.[16] Anderson C, Catoe H, Werner R. MIR-206 Regulates connexin43 expression during skeletal muscle development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(20):5863-5871.[17] Kim YJ, Hwang SJ, Bae YC, et al. MiR-21 Regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2009;27(12):3093-3102.[18] 张芳,陈学斌,盛望.人脐带与骨髓来源间充质干细胞miRNA的差异表达[J].北京工业大学学报,2011,37(10):1560-1564. [19] Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, et al. MicroRNA-145 Regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2009; 137(4):647-658.[20] Liao B, Bao X, Liu L, et al. MicroRNA cluster 302-367 enhances somatic cell Reprogramming by accelerating a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(19):17359-17364.[21] Li Z, Yang CS, Nakashima K, et al. Small RNA-mediated regulation of iPS cell generation. EMBO J. 2011;30(5): 823-834. [22] Subramanyam D, Lamouille S, Judson RL, et al. Multiple targets of miR-302 and miR-372 promote reprogramming of human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(5):443-448.[23] Choi YJ, Lin CP, Ho JJ, et al. miR-34 miRNAs provide a barrier for somatic cell Reproramming. Nat Cell Biol. 2011; 13(11):1353-1360.[24] Giraud-Triboult K, Rochon-Beaucourt C, Nissan X, et al. Combined mRNA and microRNA profiling Reveals that miR-148a and miR-20b control human mesenchymal stem cell phenotype via EPAS1. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43(2): 77-86.[25] Yu JM, Wu X, Gimble JM, et al. Age-related changes in mesenchymal stem cells derived from rhesus macaque bone marrow. Aging Cell. 2011;10(1):66-79.[26] Hackl M, Brunner S, Fortschegger K, et al. miR-17, miR-19b, miR-20a, and miR-106a aRe down-regulated in human aging. Aging Cell. 2010;9(2):291-296.[27] Riggi N, Suvà ML, De Vito C, et al. EWS-FLI-1 modulates miRNA145 and SOX2 expression to initiate mesenchymal stem cell reprogramming toward Ewing sarcoma cancer stem cells. Genes Dev. 2010;24(9):916-932.[28] Nie Y, Han BM, Liu XB, et al. Identification of MicroRNAs involved in hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7(6):762-768.[29] Goff LA, Boucher S, Ricupero CL, et al. Differentiating human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells regulate microRNAs: prediction of microRNA regulation by PDGF during osteogenesis. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(10):1354-1369.[30] Wang T, Xu Z. miR-27 promotes osteoblast differentiation by modulating Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;402(2):186-189.[31] Kapinas K, Kessler C, Ricks T, et al. miR-29 modulates Wnt signaling in human osteoblasts through a positive feedback loop. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(33):25221-25231.[32] Tomé M, López-Romero P, Albo C, et al. miR-335 orchestrates cell proliferation, migration and differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18(6): 985-995.[33] Mizuno Y, Yagi K, Tokuzawa Y, et al. miR-125b inhibits osteoblastic differentiation by down-regulation of cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368(2): 267-272.[34] Zhang JF, Fu WM, He ML, et al. MiRNA-20a promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by co-regulating BMP signaling. 2011;8(5):829-838.[35] Gao J, Yang T, Han J, et al. MicroRNA expression during osteogenic differentiation of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(7): 1844-1856.[36] Schoolmeesters A, Eklund T, Leake D, et al. Functional profiling reveals critical role for miRNA in differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5605.[37] Eskildsen T, Taipaleenmäki H, Stenvang J, et al. MicroRNA-138 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(15):6139-6144. [38] Kim YJ, Bae SW, Yu SS, et al. miR-196a regulates proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(5):816-825.[39] Song J, Kim D, Jin EJ. MicroRNA-488 suppresses cell migration through modulation of the focal adhesion activity during chondrogenic differentiation of chick limb mesenchymal cells. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35(2):179-185.[40] Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, et al. MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60(9):2723-2730.[41] Lin EA, Kong L, Bai XH, et al. miR-199a, a bone morphogenic protein 2-responsive MicroRNA, regulates chondrogenesis via direct targeting to Smad1. Biol Chem. 2009;284(17): 11326-11335.[42] Yang B, Guo H, Zhang Y, et al. The microRNA expression profiles of mouse mesenchymal stem cell during chondrogenic differentiation. BMB Rep. 2011;44(1):28-33.[43] Bengestrate L, Virtue S, Campbell M, et al. Genome-wide profiling of microRNAs in adipose mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and mouse models of obesity. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21305.[44] Nakanishi N, Nakagawa Y, Tokushige N, et al. The up-regulation of microRNA-335 is associated with lipid metabolism in liver and white adipose tissue of genetically obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;385(4): 492-496.[45] Ortega FJ, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Pardo G, et al. MiRNA expression profile of human subcutaneous adipose and during adipocyte differentiation. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9022.[46] Kim YJ, Hwang SJ, Bae YC, et al. Mir-21 Regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2009;27(12):3093-3102.[47] Sun T, Fu M, Bookout AL, et al. MicroRNA let-7 regulates 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 2009;23(6):925-931.[48] Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, et al. MicroRNA-143 regulates adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(50): 52361-52365.[49] Kim SY, Kim AY, Lee HW, et al. miR-27a is a negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation via suppressing PPARgamma expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;392(3):323-328.[50] Wang Q, Li YC, Wang J, et al. miR-17-92 cluster accelerates adipocyte differentiation by negatively regulating tumor-suppressoR Rb2/p130. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(8):2889-2894.[51] Bork S, Horn P, Castoldi M, et al. Adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells is down-regulated by microRNA-369-5p and up-regulated by microRNA-371. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(9):2226-2234.[52] Yang Z, Bian C, Zhou H, et al. MicroRNA hsa-miR-138 inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells through adenovirus EID-1. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(2):259-267.[53] Gerin I, Bommer GT, McCoin CS, et al. Roles for miRNA-378/378* in adipocyte gene expression and lipogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;299(2): E198-E206.[54] Qin L, Chen Y, Niu Y, et al. A deep investigation into the adipogenesis mechanism: profile of microRNAs regulating adipogenesis by modulating the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:320.[55] Danielson LS, Menendez S, Attolini CS, et al. A differentiation-based microRNA signature identifies leiomyosarcoma as a mesenchymal stem cell-related malignancy. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(2):908-917.[56] Shan ZX, Lin QX, Yu XY, et al. MicRoRNAs can be expRessed in caRdiomyocyte-like cells diffeRentiated fRom human mesenchymal stem cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007;27(12):1813-1816.[57] Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet. 2006;38(2):228-233.[58] Naguibneva I, Ameyar-Zazoua M, Polesskaya A, et al. The microRNA miR-181 targets the homeobox protein Hox-A11 during mammalian myoblast differentiation. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(3):278-284.[59] Jing L, Jia Y, Lu J, et al. MicroRNA-9 promotes differentiation of mouse bone mesenchymal stem cells into neurons by Notch signaling. Neuroreport. 2011;22(5):206-211.[60] Castillo MD, Trzaska KA, Greco SJ, et al. Immunostimulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived neurons: implications for stem cell therapy in allogeneic transplantations. Clin Transl Sci. 2008;1(1):27-34.[61] Crobu F, Latini V, Marongiu MF, et al. Differentiation of single cell derived human mesenchymal stem cells into cells with a neuronal phenotype: RNA and microRNA expression profile. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(4):3995-4007.[62] Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in neurogenesis of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. J Genet. 2011;90(1):81-93.[63] Guo L, Zhao RC, Wu Y. The role of microRNAs in self-renewal and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2011;39(6):608-616.[64] Collino F, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, et al. Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11803. |
| [1] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [2] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [3] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [4] | Jiang Xinghai, Song Yulin, Li Dejin, Shao Jianmin, Xu Junzhi, Liu Huakai, Wu Yingguo, Shen Yuehui, Feng Sicheng. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 genes transfected into bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct a vascularized amphiphilic peptide gel module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [5] | Gao Yanguo, Guo Xu, Li Xiaohan, Chen Shiqi, Zhu Haitao, Huang Liangyong, Ye Fang, Lu Wei Wang Qibin, Zheng Tao, Chen Li. Optimization of prescription ratio of “Honghuangbai” gel by orthogonal test in diabetic skin wound mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [6] | Min Changqin, Huang Ying. Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [7] | Shao Ziyu, Li Qian, Qumanguli·Abudukelimu, Han Youjun, Hu Yang. Preparation and characterization properties of three different ratios of biphasic calcium phosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1952-1961. |
| [8] | Xu Chang, Jiang Mingzhu, Liu Xin, Yan Weijun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of implant anchorage combined with torque auxiliary arch to lower anterior teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1971-1978. |
| [9] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [10] | Zhou Hongli, Wang Xiaolong, Guo Rui, Yao Xuanxuan, Guo Ru, Zhou Xiongtao, He Xiangyi. Fabrication and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite/sodium alginate/polycaprolactone/alendronate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [11] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [12] | Yang Lixia, Diao Liqin, Li Hua, Feng Yachan, Liu Xin, Yu Yuexin, Dou Xixi, Gu Huifeng, Xu Lanju. Regulatory mechanism of recombinant type III humanized collagen protein improving photoaging skin in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1988-2000. |
| [13] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [14] | Tan Jing, Li Li, Wang Liangliang, Qin Xiangyu. Bionic functional coating improves the integration of titanium implants and skin tissue interface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2014-2022. |
| [15] | Pan Zhiyi, Huang Jiawen, Xue Wenjun, Xu Jianda. Advantages of MXene-based flexible electronic sensors and their application in monitoring diabetic foot wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||