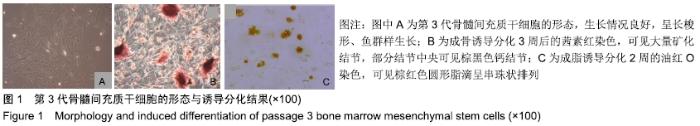
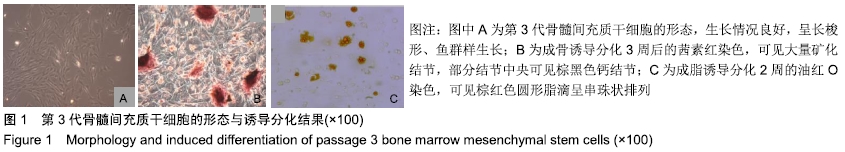
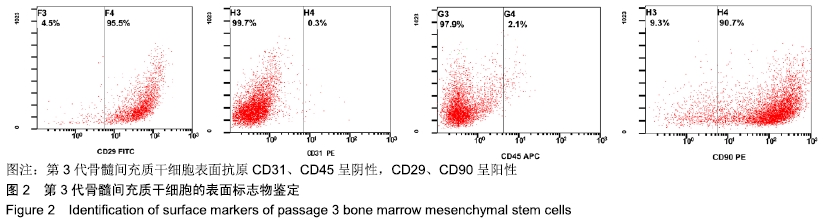
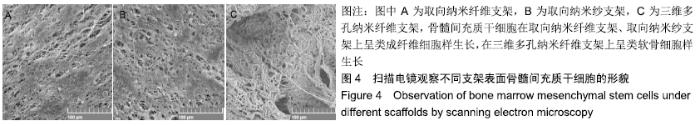
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1540-1546.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1886
Previous Articles Next Articles
P38/Akt pathway regulates the oriented differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in nanofiber annulus fibrosus scaffolds with different spatial structures
He Yunfei1, 2, Wang Shuang1, Ma Jun3, Yu Lei1, Wen Jiankun1, Ye Xiaojian1
- 1Department of Spinal Minimally Invasive Surgery, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the 940 Hospital of People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, General Hospital of Central Theater Command, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2019-05-15Revised:2019-06-03Accepted:2019-06-27Online:2020-04-08Published:2020-02-15 -
Contact:Ye Xiaojian, Chief physician, Department of Spinal Minimally Invasive Surgery, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China -
About author:He Yunfei, MD, Attending physician, Department of Spinal Minimally Invasive Surgery, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China; Department of Orthopedics, the 940 Hospital of People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China Wang Shuang, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Spinal Minimally Invasive Surgery, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China Both He Yunfei and Wang Shuang contributed equally to this paper. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81772445
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Yunfei, Wang Shuang, Ma Jun, Yu Lei, Wen Jiankun, Ye Xiaojian. P38/Akt pathway regulates the oriented differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in nanofiber annulus fibrosus scaffolds with different spatial structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1540-1546.
share this article
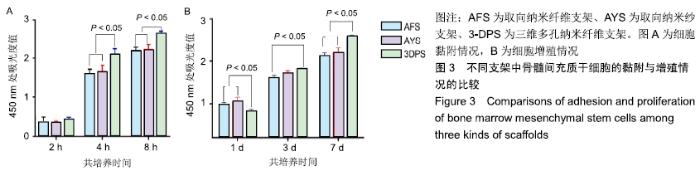
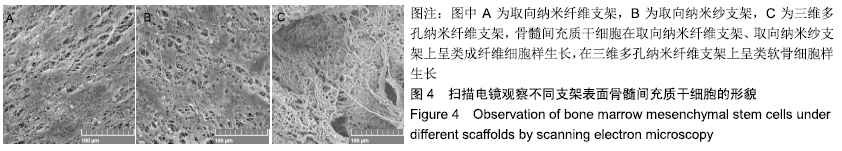
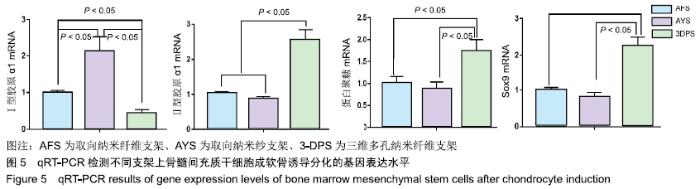
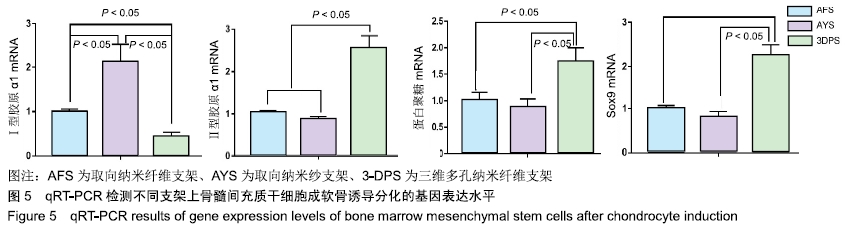
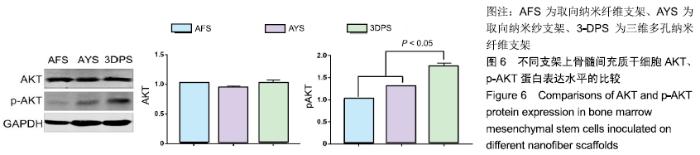
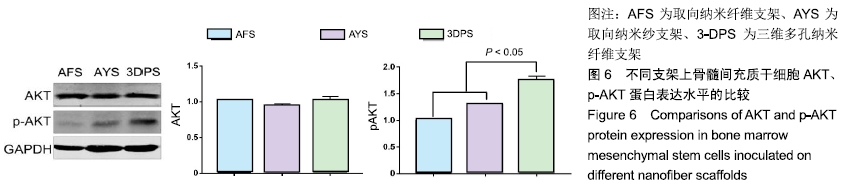
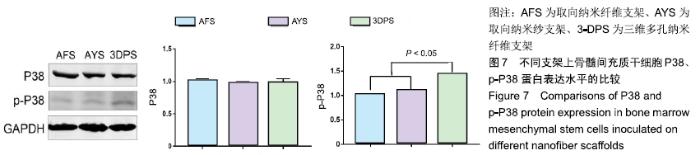
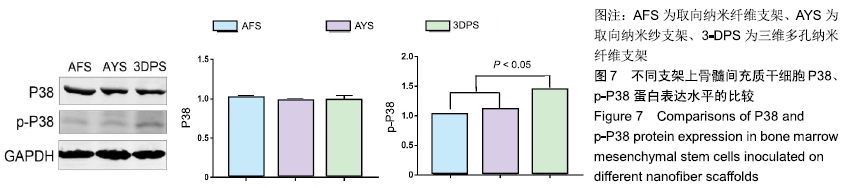
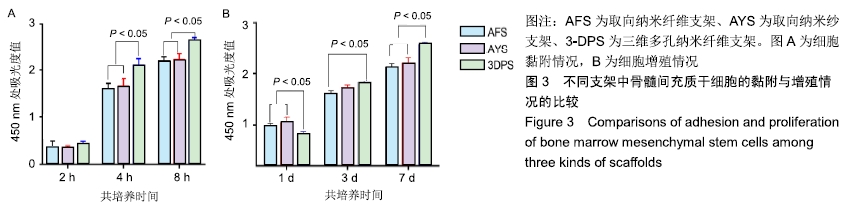
2.2 细胞黏附、增殖行为的检测 骨髓间充质干细胞在3种支架中培养后,在2 h时三者细胞黏附情况无显著差异,随时间延长,细胞的黏附效率均增加,4,8 h后AFS、AYS组细胞黏附效率仍无显著差异,而3-DPS组黏附率更高,可以认为3种材料中骨髓间充质干细胞均可良好黏附,但随时间延长,3-DPS的黏附效率高于其余两组,见图3A。继续延长培养时间,在1,3,7 d时以CCK-8法评估细胞在3种支架中的增殖情况,可以看出骨髓间充质干细胞在3种支架中均可良好增殖,在1 d时3-DPS组增殖情况差于另外两组,而在7 d时则明显优于其他两组,而AFS、AYS组在1,3,7 d时增殖情况均无明显差异,见图3B。 "
| [1] URBAN JP, ROBERTS S.Degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther.2003;5(3):120-130. [2] YASUMA T, KOH S, OKAMURA T, et al.Histological changes in aging lumbar intervertebral discs. Their role in protrusions and prolapses.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1990;72(2):220-229. [3] BOOS N, WEISSBACH S, ROHRBACH H, et al.Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(23):2631-2644. [4] HOY D, BAIN C, WILLIAMS G, et al.A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain. Arthritis Rheum.2012;64(6):2028-2037. [5] PIRVU T, BLANQUER SB, BENNEKER LM, et al.A combined biomaterial and cellular approach for annulus fibrosus rupture repair. Biomaterials. 2015;42:11-19. [6] GLUAIS M, CLOUET J, FUSELLIER M, et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of an electrospun-aligned microfibrous implant for annulus fibrosus repair. Biomaterials.2019;205:81-93. [7] HUDSON KD, ALIMI M, GRUNERT P, et al.Recent advances in biological therapies for disc degeneration: tissue engineering of the annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus and whole intervertebral discs.Curr opin Biotechnol.2013;24(5):872-879. [8] CHU G, SHI C, WANG H, et al.Strategies for Annulus Fibrosus Regeneration: From Biological Therapies to Tissue Engineering.Front Bioeng Biotechnol.2018;6:90. [9] VAN UDEN S, SILVA-CORREIA J, OLIVEIRA JM, et al.Current strategies for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: substitution and regeneration possibilities.Biomater Res. 2017;21:22. [10] GUTERL CC, SEE EY, BLANQUER SB, et al.Challenges and strategies in the repair of ruptured annulus fibrosus.Eur Cell Mater.2013;25:1-21. [11] MA J, HE Y, LIU X, et al.A novel electrospun-aligned nanoyarn/three- dimensional porous nanofibrous hybrid scaffold for annulus fibrosus tissue engineering.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:1553-1567. [12] LI X, ZHANG Y, QI G. Evaluation of isolation methods and culture conditions for rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology. 2013;65(3):323-334. [13] LI J, LIU C, GUO Q, et al. Regional variations in the cellular, biochemical, and biomechanical characteristics of rabbit annulus fibrosus.PloS One. 2014;9(3):e91799. [14] VERGARI C, MANSFIELD J, MEAKIN JR, et al.Lamellar and fibre bundle mechanics of the annulus fibrosus in bovine intervertebral disc.Acta Biomater.2016;37:14-20. [15] WISMER N, GRAD S, FORTUNATO G, et al. Biodegradable electrospun scaffolds for annulus fibrosus tissue engineering: effect of scaffold structure and composition on annulus fibrosus cells in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A.2014;20(3-4):672-682. [16] YIN Z, CHEN X, SONG HX, et al. Electrospun scaffolds for multiple tissues regeneration in vivo through topography dependent induction of lineage specific differentiation.Biomaterials.2015;44:173-185. [17] TIAN F, HOSSEINKHANI H, HOSSEINKHANI M, et al.Quantitative analysis of cell adhesion on aligned micro- and nanofibers.J Biomed Mater Res A.2008;84(2):291-299. [18] WOO KM, CHEN VJ, MA PX. Nano-fibrous scaffolding architecture selectively enhances protein adsorption contributing to cell attachment. J Biomed Mater Res A.2003;67(2):531-537. [19] AHMED I, PONERY AS, NUR-E-KAMAL A, et al.Morphology, cytoskeletal organization, and myosin dynamics of mouse embryonic fibroblasts cultured on nanofibrillar surfaces. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;301(1-2): 241-249. [20] LI WJ, JIANG YJ, TUAN RS.Chondrocyte phenotype in engineered fibrous matrix is regulated by fiber size.Tissue Eng.2006;12(7):1775-1785. [21] DAVIES JE, AJAMI E, MOINEDDIN R, et al. The roles of different scale ranges of surface implant topography on the stability of the bone/implant interface. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(14):3535-3546. [22] SEO CH, JEONG H, FENG Y, et al.Micropit surfaces designed for accelerating osteogenic differentiation of murine mesenchymal stem cells via enhancing focal adhesion and actin polymerization. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2245-2252. [23] HUANG H, KAMM RD, LEE RT. Cell mechanics and mechanotransduction: pathways, probes, and physiology.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2004;287(1):C1-11. [24] IQBAL J, ZAIDI M. Molecular regulation of mechanotransduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(3):751-755. [25] GIANCOTTI FG, RUOSLAHTI E.Integrin signaling.Science. 1999;285 (5430):1028-1032. [26] BIGGS MJ, RICHARDS RG, GADEGAARD N, et al.The use of nanoscale topography to modulate the dynamics of adhesion formation in primary osteoblasts and ERK/MAPK signalling in STRO-1+ enriched skeletal stem cells.Biomaterials. 2009;30(28):5094-5103. [27] ZHANG Y, PIZZUTE T, PEI M.A review of crosstalk between MAPK and Wnt signals and its impact on cartilage regeneration.Cell Tissue Res. 2014;358(3):633-649. [28] WANG Y, YAO M, ZHOU J, et al.The promotion of neural progenitor cells proliferation by aligned and randomly oriented collagen nanofibers through β1 integrin/MAPK signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 2011;32(28):6737-6744. [29] CHEN YC, LEE DC, TSAI TY, et al.Induction and regulation of differentiation in neural stem cells on ultra-nanocrystalline diamond films.Biomaterials.2010;31(21):5575-5587. [30] LI J, ZHAO Z, LIU J, et al.MEK/ERK and p38 MAPK regulate chondrogenesis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through delicate interaction with TGF-beta1/Smads pathway.Cell Prolif. 2010; 43(4):333-343. [31] LI J, ZHAO Z, YANG J, et al.p38 MAPK mediated in compressive stress-induced chondrogenesis of rat bone marrow MSCs in 3D alginate scaffolds.J Cell Physiol.2009;221(3):609-617. [32] CHUN JS. Expression, activity, and regulation of MAP kinases in cultured chondrocytes. Methods Mol Med.2004;100:291-306. [33] STANTON LA, SABARI S, SAMPAIO AV, et al.p38 MAP kinase signalling is required for hypertrophic chondrocyte differentiation. Biochem J. 2004; 378(Pt 1):53-62. [34] TULI R, TULI S, NANDI S, et al.Transforming growth factor-beta- mediated chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal progenitor cells involves N-cadherin and mitogen-activated protein kinase and Wnt signaling cross-talk.J Biol Chem.2003;278(42): 41227-41236. [35] OH CD, CHANG SH, YOON YM, et al.Opposing role of mitogen-activated protein kinase subtypes, erk-1/2 and p38, in the regulation of chondrogenesis of mesenchymes.J Biol Chem. 2000; 275(8): 5613-5619. [36] CHEN L, QANIE D, JAFARI A, et al. Delta-like 1/fetal antigen-1 (Dlk1/FA1) is a novel regulator of chondrogenic cell differentiation via inhibition of the Akt kinase-dependent pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011; 286(37): 32140-32149. [37] DOWNWARD J.Mechanisms and consequences of activation of protein kinase B/Akt. Curr Opin Cell Biol.1998;10(2):262-267. [38] LAWLOR MA, ALESSI DR.PKB/Akt: a key mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses.J Cell Sci.2001;114(Pt 16):2903-2910. [39] BRAZIL DP, HEMMINGS BA.Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci.2001;26(11):657-664. [40] DURONIO V, SCHEID MP, ETTINGER S.Downstream signalling events regulated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity.Cell Signal. 1998;10(4):233-239. [41] LI W, WU X, QU R, et al.Ghrelin protects against nucleus pulposus degeneration through inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway and activation of Akt signaling pathway.Oncotarget.2017; 8(54): 91887-91901. [42] PRATSINIS H, KLETSAS D.PDGF, bFGF and IGF-I stimulate the proliferation of intervertebral disc cells in vitro via the activation of the ERK and Akt signaling pathways.Eur Spine J.2007;16(11):1858-1866. [43] BAKER BM, HANDORF AM, IONESCU LC, et al.New directions in nanofibrous scaffolds for soft tissue engineering and regeneration. Expert Rev Med Devices.2009;6(5):515-532. |
| [1] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [4] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [5] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [6] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [7] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [8] | Li Wenjing, Li Haobo, Liu Congna, Cheng Dongmei, Chen Huizhen, Zhang Zhiyong. Comparison of different bioactive scaffolds in the treatment of regenerative pulp of young permanent teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 499-503. |
| [9] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [10] | Xie Zhifeng, Liu Qing, Liu Bing, Zhang Tao, Li Kun, Zhang Chunqiu, Sun Yanfang. Biomechanical characteristics of the lumbar disc after fatigue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 339-343. |
| [11] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [12] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [13] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [14] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [15] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||