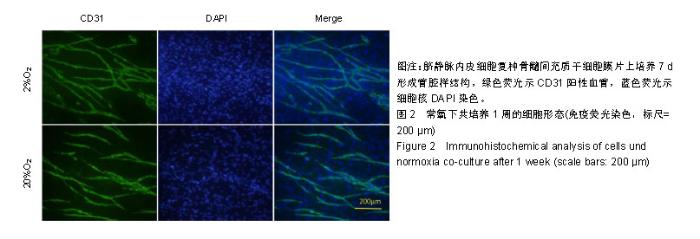
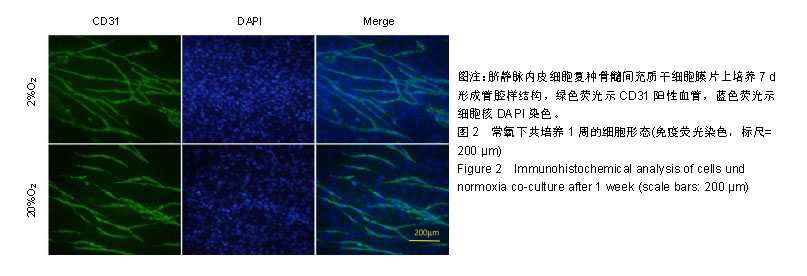
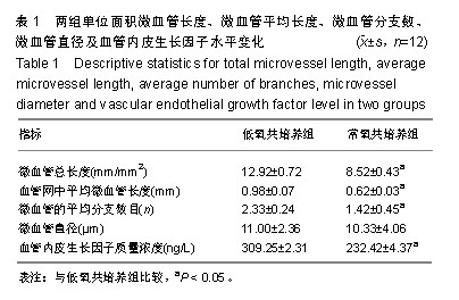
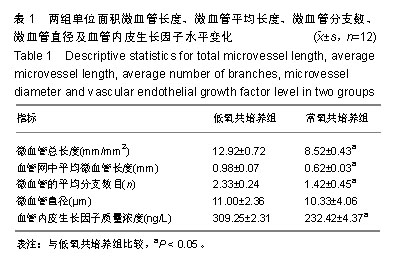
| [1]李欣,金作林,吴琼,等.应用牙周膜干细胞-牙囊干细胞复合细胞膜片同种异体移植修复比格犬牙周组织缺损的研究[J].口腔疾病防治,2016,24(4):204-210.[2]Iwata T, Yamato M, Tsuchioka H, et al. Periodontal regeneration with multi-layered periodontal ligament-derived cell sheets in a canine model. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14): 2716-2723.[3]文艺,杨鸿旭,刘倩,等.骨髓间充质干细胞联合血管内皮祖细胞修复骨质疏松性牙槽骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(19): 2748-2755.[4]Yang J, Yamato M, Kohno C, et al. Cell sheet engineering: recreating tissues without biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2005;26(33):6415-6422.[5]Haraguchi Y, Shimizu T, Sasagawa T, et al. Fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues by stacking cell sheets in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2012;7(5):850-858.[6]Asakawa N, Shimizu T, Tsuda Y, et al. Pre-vascularization of in vitro three-dimensional tissues created by cell sheet engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):3903-3909.[7]Novosel EC, Kleinhans C, Kluger PJ. Vascularization is the key challenge in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(4-5):300-311.[8]Mascarenhas S, Avalos B, Ardoin SP. An update on stem cell transplantation in autoimmune rheumatologic disorders. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012;12(6):530-540.[9]Yuan X, Tsai AC, Farrance I, et al. Aggregation of culture expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in microcarrier-based bioreactor. Biochem Eng J. 2018;131: 39-46.[10]Liu Y, Ming L, Luo H, et al. Integration of a calcined bovine bone and BMSC-sheet 3D scaffold and the promotion of bone regeneration in large defects. Biomaterials. 2013;34(38): 9998-10006.[11]Stoppato M, Stevens HY, Carletti E, et al. Influence of scaffold properties on the inter-relationship between human bone marrow derived stromal cells and endothelial cells in pro-osteogenic conditions. Acta Biomater. 2015;25:16-23.[12]Pedersen TO, Blois AL, Xue Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce endothelial cell quiescence and promote capillary formation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):23.[13]Huang CC, Pan WY, Tseng MT, et al. Enhancement of cell adhesion, retention, and survival of HUVEC/cbMSC aggregates that are transplanted in ischemic tissues by concurrent delivery of an antioxidant for therapeutic angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2016;74;53-63.[14]Gurel PG, Torun KG, Hasirci V. Influence of co-culture on osteogenesis and angiogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and aortic endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 2016;108:1-9.[15]梁源,隋珂,尚冯青,等.血管内皮祖细胞/骨髓间充质干细胞复合细胞膜片的构建[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(41): 6561-6566.[16]Zhilai Z, Biling M, Sujun Q, et al. Preconditioning in lowered oxygen enhances the therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2016;1642;426-435.[17]Kobayashi J, Kikuchi A, Aoyagi T, et al. Cell sheet tissue engineering: Cell sheet preparation, harvesting/manipulation, and transplantation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(5): 955-967.[18]孟文霞,郭薇,李志强,等.血管生成相关因子在口腔扁平苔藓中的表达[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(11):712-717.[19]Xu R, Sun Y, Chen Z, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning inhibits hypoxia-induced apoptosis of cardiac progenitor cells via the PI3K/Akt-DNMT1-p53 pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30922.[20]Mohyeldin A, Garzon-Muvdi T, Quinones-Hinojosa A. Oxygen in stem cell biology: a critical component of the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(2):150-161.[21]Grayson WL, Zhao F, Bunnell B, et al. Hypoxia enhances proliferation and tissue formation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358(3): 948-953.[22]Basciano L, Nemos C, Foliguet B, et al. Long term culture of mesenchymal stem cells in hypoxia promotes a genetic program maintaining their undifferentiated and multipotent status. BMC Cell Biol. 2011;12:12.[23]Teixeira FG, Panchalingam KM, Anjo SI, et al. Do hypoxia/normoxia culturing conditions change the neuroregulatory profile of Wharton Jelly mesenchymal stem cell secretome? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6;133.[24]Habib R, Haneef K, Naeem N, et al. Hypoxic stress and IL-7 gene overexpression enhance the fusion potential of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with bovine renal epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;403(1-2):125-137.[25]Chen J, Zhang D, Li Q, et al. Effect of different cell sheet ECM microenvironment on the formation of vascular network. Tissue Cell. 2016;48(5):442-451.[26]Amiri F, Jahanian-Najafabadi A, Roudkenar MH. In vitro augmentation of mesenchymal stem cells viability in stressful microenvironments: in vitro augmentation of mesenchymal stem cells viability. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015;20(2): 237-251.[27]Qin HH, Filippi C, Sun S, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning potentiates the trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells on co-cultured human primary hepatocytes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6;237.[28]Fan L, Zhang C, Yu Z, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances angiogenesis and osteogenesis in rabbit femoral head osteonecrosis. Bone. 2015;81:544-553.[29]Denu RA, Hematti P. Effects of oxidative stress on mesenchymal stem cell biology. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016:2989076. |