Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (21): 3281-3288.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1742
Roles of ROCK signaling in proliferation and paracrine action of hypoxia-induced c-Kit+ bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Shao Zhongming, Wang Keke, Liao Xiaomin, Ha Yanping, Li Rujia, Shen Zhihua, Jie Wei
- Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2019-01-21Online:2019-07-28Published:2019-07-28 -
Contact:Jie Wei, PhD, Professor, Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Shao Zhongming, Master candidate, Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China. Wang Keke, Doctorate candidate, Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China. Shao Zhongming and Wang Keke contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81670254 (to JW); the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2016A020214016 (to JW); and the YangFan Plan of Guangdong Province, No. 4YF16007G (to JW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shao Zhongming, Wang Keke, Liao Xiaomin, Ha Yanping, Li Rujia, Shen Zhihua, Jie Wei. Roles of ROCK signaling in proliferation and paracrine action of hypoxia-induced c-Kit+ bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3281-3288.
share this article

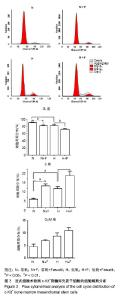
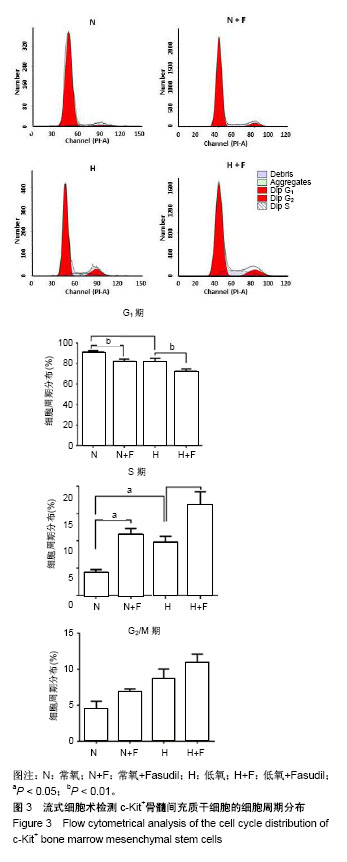
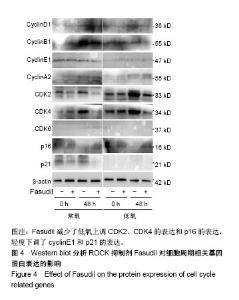
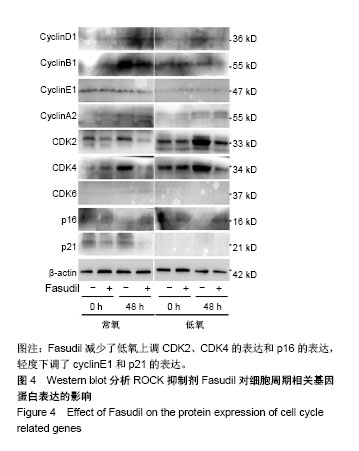
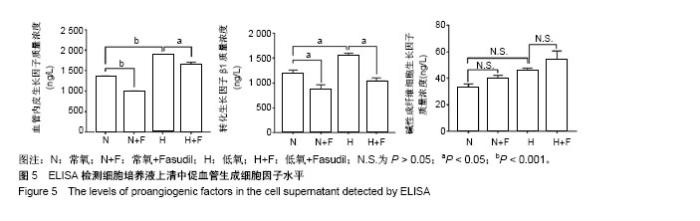
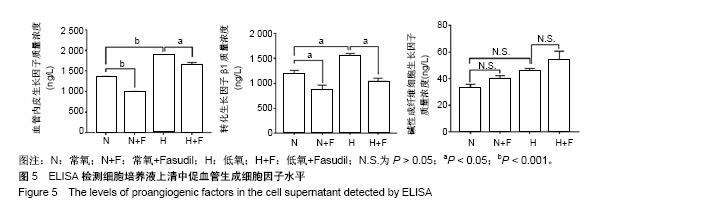
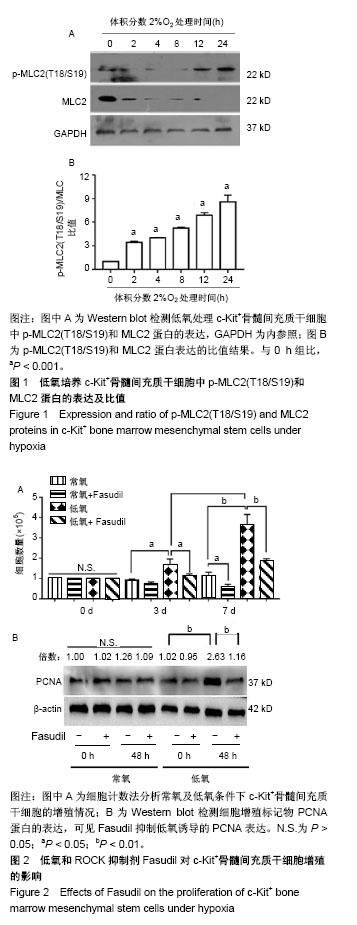
2.1 c-Kit+ BMSCs的鉴定结果 MACS法成功分选出c-Kit+细胞亚群,流式细胞术测得c-Kit阳性率为91.6%,免疫荧光显示c-Kit呈胞质/胞膜阳性;生长汇合状态的c-Kit+ BMSCs大多呈梭形,纤维状。 2.2 低氧刺激活化c-Kit+ BMSCs中ROCK信号 将c-Kit+ BMSCs置于含体积分数2%O2的培养箱中培养,于培养0,2,4,8,12及24 h收获细胞总蛋白,Western blot检测p-MLC2(T18/S12)和MLC2蛋白表达。结果显示,随低氧时间的延长,MLC2蛋白表达水平逐渐下降,而p-MLC2 (T18/S12)表达水平逐渐上升,见图1A。作为ROCK下游靶基因,MLC2的磷酸化程度可作为判断ROCK信号活化的指标[32]。本文以p-MLC2(T18/S12)/MLC2比值的变化反映内源性ROCK信号的活化情况,结果证实低氧刺激的c-Kit+ BMSCs中p-MLC2(T18/S12)/MLC2的比值逐渐上升(均P < 0.001),见图1B,提示低氧刺激促进了c-Kit+ BMSCs中ROCK信号的活化。 2.3 ROCK抑制剂Fasudil减弱了低氧诱导的c-Kit+ BMSCs增殖 应用细胞计数法分析常氧及低氧条件下c-Kit+ BMSCs的增殖情况。与预期结果一致,低氧培养显著诱导c-Kit+ BMSCs的数量增加。无论是常氧条件还是低氧状态下给予Fasudil均显著抑制了细胞的增殖,以培养7 d时尤为显著,见图2A。进一步采用Western blot检测细胞增殖标记物PCNA蛋白的表达,发现常氧条件下培养48 h时PCNA增加不明显,而低氧48 h即可显著诱导PCNA表达,Fasudil抑制低氧诱导的PCNA表达(P < 0.01),见图2B。"
| [1] Satija NK, Singh VK, Verma YK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: a new paradigm in regenerative medicine. J Cell Mol Med.2009;13(11-12):4385-4402.[2] Sipp D, Robey PG, Turner L. Clear up this stem-cell mess. Nature.2018; 561(7724):455-457.[3] Mushahary D, Spittler A, Kasper C, et al. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A.2018; 93(1):19-31.[4] Zhou B, Wu SM. Reassessment of c-Kit in cardiac cells: a complex interplay between expression, fate, and function. Circ Res.2018; 123(1):9-11.[5] Ding R, Jiang X, Ha Y, et al. Activation of Notch1 signalling promotes multi-lineage differentiation of c-Kit(POS)/NKX2.5(POS) bone marrow stem cells: implication in stem cell translational medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:91.[6] Anam K, Davis TA. Comparative analysis of gene transcripts for cell signaling receptors in bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell and mesenchymal stromal cell populations. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013; 4(5):112.[7] 哈艳平,王振良,雷洪,等. 过表达Notch1胞内域对c-Kit+骨髓间充质干细胞分化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(6): 785-792.[8] Zhang GW, Gu TX, Guan XY, et al. Delayed enrichment for c-kit and inducing cardiac differentiation attenuated protective effects of BMSCs' transplantation in pig model of acute myocardial ischemia. Cardiovasc Ther. 2015; 33(4):184-92.[9] Wang YL, Zhang G, Wang HJ, et al. Preinduction with bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhances cardiomyogenic differentiation of c-Kit+ mesenchymal stem cells and repair of infarcted myocardium. Int J Cardiol. 2018; 265:173-180.[10] Taghavi S, Sharp TE 3rd, Duran JM, et al. Autologous c-Kit+ mesenchymal stem cell injections provide superior therapeutic benefit as compared to c-Kit+ cardiac-derived stem cells in a feline model of isoproterenol-induced cardiomyopathy. Clin Transl Sci. 2015; 8(5):425-431.[11] Hao ZC, Lu J, Wang SZ, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: A promising strategy for fracture healing. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(5). doi: 10.1111/cpr.12359. [12] Phinney DG, Pittenger MF. Concise Review: MSC-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4): 851-858.[13] Lazar E, Benedek T, Korodi S, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes-an emerging tool for myocardial regeneration. World J Stem Cells.2018; 10(8):106-115.[14] Cunnane EM, Weinbaum JS, O'Brien FJ, et al. Future Perspectives on the Role of Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles in Vascular Tissue Regeneration. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018; 5:86.[15] Antebi B, Rodriguez LA 2nd, Walker KP 3rd, et al. Short-term physiological hypoxia potentiates the therapeutic function of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.2018;9(1):265. [16] Tong C, Hao H, Xia L, et al. Hypoxia pretreatment of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded in a collagen-chitosan sponge scaffold promotes skin wound healing in diabetic rats with hindlimb ischemia. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(1):45-56.[17] Julian L, Olson MF. Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): structure, regulation, and functions. Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29846.[18] Schofield AV, Bernard O. Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) signaling and disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;48(4):301-316.[19] Fu PC, Tang RH, Yu ZY, et al. The Rho-associated kinase inhibitors Y27632 and fasudil promote microglial migration in the spinal cord via the ERK signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res.2018;13(4):677-683.[20] Zhang C, Wu JM, Liao M, et al. The ROCK/GGTase Pathway Are Essential to the Proliferation and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells Mediated by Simvastatin. J Mol Neurosci. 2016; 60(4):474-485.[21] Wang T, Kang W, Du L, et al. Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 facilitates the proliferation, migration and pluripotency of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J Cell Mol Med.2017; 21(11):3100-3112. [22] 彭志明,赵晓阳,朱凯,等. Lingo-1介导Rho-ROCK通路调控神经干细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(29): 4669-4674.[23] 徐亮,陶树清,文刚,等. RhoA/ROCK信号通路在骨质疏松大鼠BMSCs成骨分化中的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017, 23(11): 1415-1419.[24] Zhang L, Jiang G, Zhao X, et al. Dimethyloxalylglycine Promotes Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenesis via Rho/ROCK Signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(4):1391-403. [25] Chen Z, Wang X, Shao Y, et al. Synthetic osteogenic growth peptide promotes differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts via RhoA/ROCK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011; 358(1-2):221-227.[26] Li Z, Han S, Wang X, et al. Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 promotes the differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into keratinocyte-like cells in xeno-free conditioned medium. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:17.[27] Liu X, Zhang Z, Yan X, et al. The Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 facilitates the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Histol. 2014; 45(6):707-714.[28] Chiba Y, Kuroda S, Shichinohe H, et al. Synergistic effects of bone marrow stromal cells and a Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, fasudil on axon regeneration in rat spinal cord injury. Neuropathology. 2010;30(3):241-50.[29] Wang X, Tang P, Guo F, et al. RhoA regulates Activin B-induced stress fiber formation and migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell through distinct signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017; 1861(1 Pt A):3011-3018.[30] Li JR, Zhao YS, Chang Y, et al. Fasudil improves endothelial dysfunction in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia through RhoA/ROCK/NFATc3 pathway. PLoS One. 2018; 13(4):e0195604.[31] 高艳,谢敏,石俊青. Rho/Rho激酶信号通路在低氧致肺纤维化中的作用及法舒地尔的干预效应[J].第三军医大学学报, 2010, 32(22):2378-2382.[32] Patel RA, Liu Y, Wang B, et al. Identification of novel ROCK inhibitors with anti-migratory and anti-invasive activities. Oncogene. 2014;33(5):550-555.[33] Das R, Jahr H, van Osch GJ, et al. The role of hypoxia in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: considerations for regenerative medicine approaches. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(2):159-168.[34] Johnson C, Huynh V, Hargrove L, et al. Inhibition of Mast Cell-Derived Histamine Decreases Human Cholangiocarcinoma Growth and Differentiation via c-Kit/Stem Cell Factor-Dependent Signaling. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(1):123-133. [35] Gude NA, Firouzi F, Broughton KM, et al. Cardiac c-Kit Biology Revealed by Inducible Transgenesis. Circ Res. 2018; 123(1):57-72.[36] Ashman LK, Griffith R. Therapeutic targeting of c-KIT in cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013; 22(1):103-115.[37] Lennartsson J, Rönnstrand L. Stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit: from basic science to clinical implications. Physiol Rev. 2012; 92(4):1619-1649.[38] Sheng L, Mao X, Yu Q, et al. Effect of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway on hypoxia-induced proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med, 2017;13(1):55-62.[39] Wang ZH, Zhu D, Xie S, et al. Inhibition of Rho-kinase Attenuates Left Ventricular Remodeling Caused by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Rats via Suppressing Myocardial Inflammation and Apoptosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2017; 70(2):102-109.[40] Qiao F, Zou Z, Liu C, et al. ROCK2 mediates the proliferation of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells induced by hypoxia in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Exp Ther Med. 2016; 11(6):2567-2572.[41] 曹美霞,屈长青. Rho-ROCK 信号通路功能及其活性调节[J]. 生物学杂志, 2015,32(6): 81-85.[42] Xu N, Chen SH, Qu GY, et al. Fasudil inhibits proliferation and collagen synthesis and induces apoptosis of human fibroblasts derived from urethral scar via the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res.2017; 9(3):1317-1325.[43] Golias CH, Charalabopoulos A, Charalabopoulos K. Cell proliferation and cell cycle control: a mini review. Int J Clin Pract.2004; 58(12):1134-1141.[44] Tang L, Dai F, Liu Y, et al. RhoA/ROCK signaling regulates smooth muscle phenotypic modulation and vascular remodeling via the JNK pathway and vimentin cytoskeleton. Pharmacol Res.2018; 133:201-212.[45] Polymeri A, Giannobile WV, Kaigler D. Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Horm Metab Res.2016; 48(11):700-713.[46] 陈珂玲,周总光,周斌,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞旁分泌因子治疗重症急性胰腺炎的潜能[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2015, 32(1): 245-248.[47] Dai Y, Xu M, Wang Y, et al, HIF-1alpha induced-VEGF overexpression in bone marrow stem cells protects cardiomyocytes against ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol.2007; 42(6):1036-1044.[48] Chen J, Yang Y, Shen L, et al., Hypoxic Preconditioning Augments the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells in a Rat Ischemic Stroke Model. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 37(6): 1115-1119.[49] Jin J, Peng C, Wu SZ, et al. Blocking VEGF/Caveolin-1 signaling contributes to renal protection of fasudil in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015; 36(7):831-840. [50] Gu L, Gao Q, Ni L,et al. Fasudil inhibits epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation of human renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells induced by high glucose. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).2013; 61(7):688-694. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [6] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [7] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [8] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [9] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [10] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [11] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [12] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [13] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [14] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [15] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||