Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 47-54.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1525
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dopamine-induced biomimetic hydroxyapatite coating: preparation and biological effect on bone marrow mesenchym stem cells
Xu Yanan1, Yang Qiming1, Li Hong2, Jiang Dianming3, Qiao Bo1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China; 2College of Physical Science and Technology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610015, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 401120, China
-
Revised:2018-07-17Online:2019-01-08Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Qiao Bo, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China -
About author:Xu Yanan, Doctorate candidate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (for the Youth), No. 81501876 (to QB); the Science and Technology Project of Chongqing Education Committee, No. KJ1702031 (to QB); the Achievement Transformation Project of Chongqing Education Committee, No. KJZH17110 (to JDM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Yanan, Yang Qiming, Li Hong, Jiang Dianming, Qiao Bo. Dopamine-induced biomimetic hydroxyapatite coating: preparation and biological effect on bone marrow mesenchym stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 47-54.
share this article
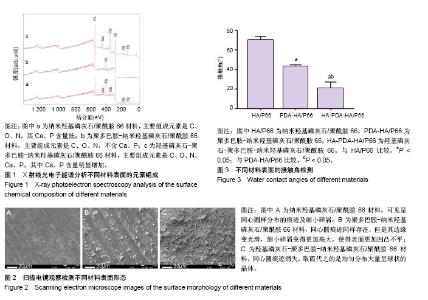
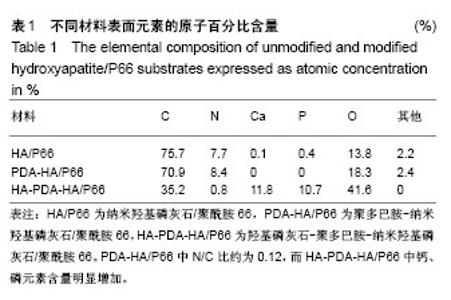
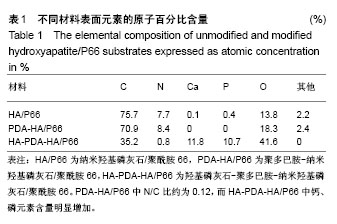
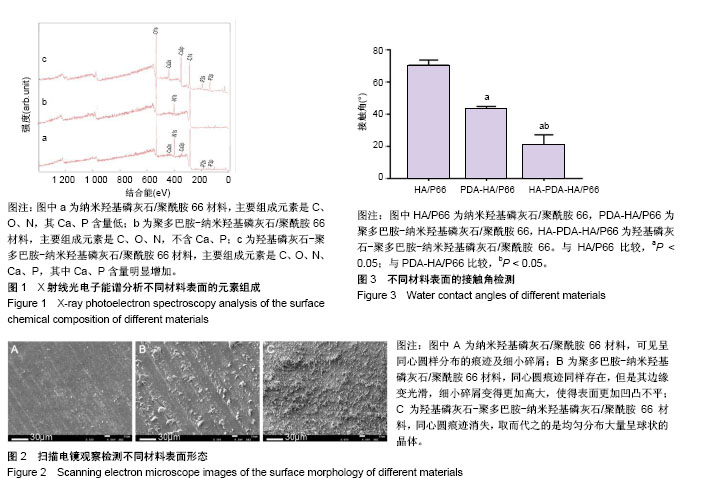
图2所示为扫描电镜检测3种材料的表面形态,其中纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料表面可见车床加工所留下的呈同心圆样分布的痕迹及细小的碎屑;聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料表面同心圆痕迹同样存在,但是其边缘变光滑,细小碎屑变得更加高大,使得表面更加凹凸不平;HA-PDA-HA/P66材料表面的同心圆痕迹消失,取而代之的是均匀分布大量呈球状的晶体。 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66、聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66与HA-PDA-HA/P66材料的表面粗糙度分别为(0.410±0.065),(0.623±0.059),(0.996±0.138) μm,3组间表面粗糙度两两比较差异均有显著性意义。 图3所示为3种材料的接触角,结果表明HA-PDA-HA/ P66、聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66、纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料的接触角依次增大,说明其亲水性逐渐降低。"

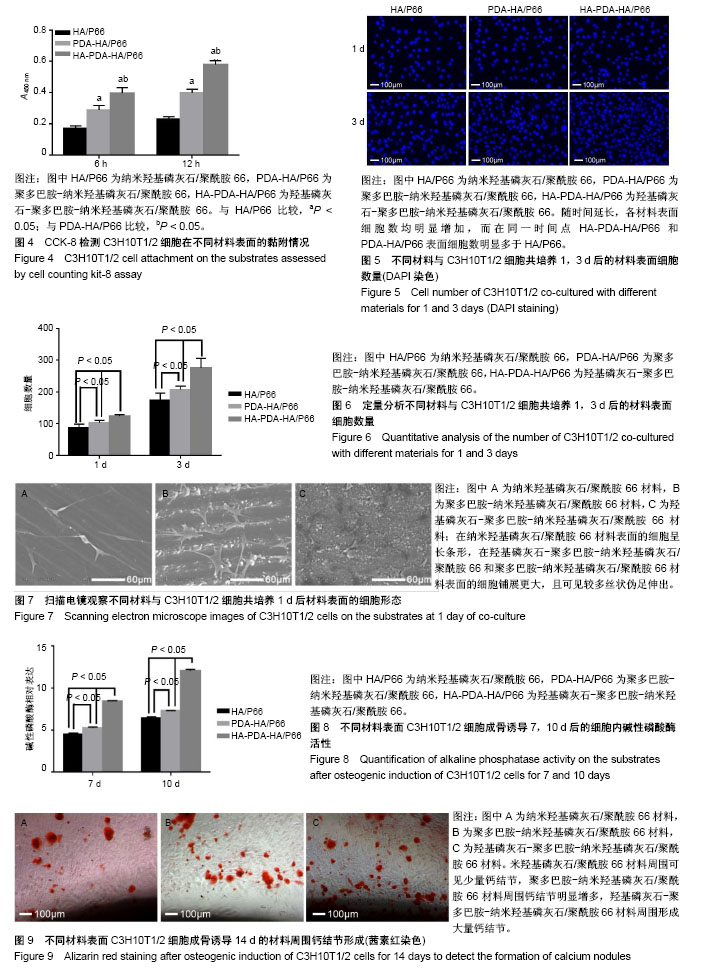
2.2 不同材料表面细胞黏附和增殖 图4所示为细胞与材料共培养6,12 h的细胞黏附情况,共培养6,12 h后,材料表面的细胞数量均为HA-PDA-HA/P66 > 聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66 > 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66,说明羟基磷灰石及聚多巴胺涂层均有利于细胞黏附。 图5所示为共培养1,3 d后通过DAPI染色观察材料表面细胞增殖情况,随时间延长,各个样本表面的细胞数均明显增加,HA-PDA-HA/P66和聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料同一时间点表面的细胞数明显多于纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66。通过定量分析进一步证实材料表面细胞的增殖能力:HA-PDA-HA/P66 >聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66 >纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66,见图6,说明羟基磷灰石及聚多巴胺涂层均能促进细胞增殖。 2.3 不同材料表面细胞形态 图7所示为材料与细胞共培养1 d后使用扫描电镜观察材料表面的细胞形态,纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料表面细胞呈长条形;在羟基磷灰石-聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66和聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料表面可见细胞铺展的更大,且可见较多丝状伪足伸出,这说明相比于纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料,此两种材料更有利于C3H10T1/2细胞的伸展。 2.4 不同材料表面细胞成骨分化结果 碱性磷酸酶活性检测:图8所示为成骨诱导培养7,10 d后不同材料表面细胞内碱性磷酸酶活性,HA-PDA-HA/P66材料表面细胞内碱性磷酸酶活性明显高于聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66和纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料(P < 0.05),而聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料表面的细胞内碱性磷酸酶活性高于纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料。 茜素红染色:图9所示为成骨诱导培养14 d后使用不同材料表面细胞内钙结节形成情况,HA-PDA-HA/P66材料周围的钙结节明显多于其他组,聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料周围的钙结节又多于纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66材料。"
| [1] Manam NS, Harun W, Shri D, et al. Study of corrosion in biocompatible metals for implants: A review. J Alloys Compd. 2017;701:698-715. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Wu Dandan, Liu Qi. Epigenetic mechanisms in periodontal disease, periodontal cell osteogenesis and bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5716-5722. |
| [11] | Li Yuwei, Wang Haijiao, Cui Wei, Zhou Peng, Li Cheng, Xiao Wei, Hu Bingtao, Li Fan. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with mesh-hold in the treatment of spinal metastases with extensive destruction of cortical bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5490-5494. |
| [12] | Wang Pei. Application of polycaprolactone-based biopolymer scaffolds in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5506-5510. |
| [13] | Li Jun, Zuo Xinhui, Liu Xiaoyuan, Zhang Kai, Han Xiangzhen, He Huiyu, . Effect of over expression of miR-378a on osteogenic and vascular differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4939-4944. |
| [14] | Shi Qin, Sun Baolan, Yang Xiaoqing, Zhang Yuquan . Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miRNAs in tissue repair and treatment of related diseases: application and advantages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 5040-5045. |
| [15] | Wang Xinwei, Zhao Yingjie, Chang Yan, Wei Wei. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of cartilage damage in osteoarthritis: role, application, and problem [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 5053-5058. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 351
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 399
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||