Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 125-131.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1501
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mesenchymal stem cells for acute liver injury: homing to the liver and directed differentiation
Sun Ting, Li Fan, Du Lianfang
- Department of Ultrasound, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai 200080, China
-
Revised:2018-09-06Online:2019-01-08Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Du Lianfang, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Ultrasound, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai 200080, China -
About author:Sun Ting, Doctorate candidate, Department of Ultrasound, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai 200080, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81471666 (to LF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Ting, Li Fan, Du Lianfang. Mesenchymal stem cells for acute liver injury: homing to the liver and directed differentiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 125-131.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
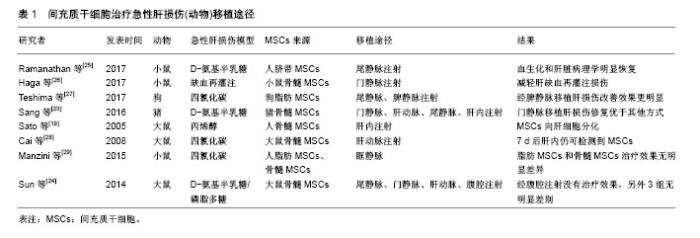
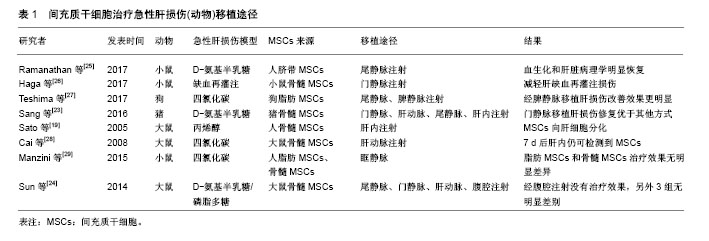
2.1 MSCs概述 MSCs是来源于中胚层的一类具有多向分化潜能的干细胞,主要存在于全身结缔组织和器官间质中[8]。MSCs最初是在骨髓中被发现,由Friedenstein和Petrakova在1976年首先报道,他们通过贴壁培养的方式从兔骨髓组织中分离出一种非造血功能的干细胞,形态为纺锤形,在体外贴壁生长且易于增殖[9]。1991年Caplan把骨髓中提取的这类细胞群命名为“间充质干细胞”[10]。随后在脂肪、外周血、脐带、各种胎儿组织中也发现MSCs的存在。根据来源不同,MSCs可以命名为骨髓间充质干细胞、脂肪间充质干细胞、脐带间充质干细胞等。尽管不同来源的MSCs在分化能力和增殖速度方面有差异,它们表达的细胞膜表面抗原却基本一致。MSCs具有自我更新和多向分化潜能,不仅可以分化为造血基质细胞,还可以分化成造血以外的细胞,如成骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞、内皮细胞、神经元细胞等[11-12]。MSCs具有强大的增殖能力,在体内和体外均可以实现三系的分化-成脂、成骨、成软骨,这也是鉴定MSCs的必要条件[13-14]。MSCs的主要特征之一是移徙能力,植入体内后可以在受损部位释放的归巢信号作用下特异性迁移至炎症和组织损伤处[15]。此外,MSCs具有显著的免疫调节特性,在体内能够逃避免疫系统的识别并能调节宿主的某些防御机制[16]。同时,由于MSCs的低免疫原性,在外周血中不易被白细胞不相容抗原识别,因而在治疗中能够显著降低移植排斥,提高干细胞移植的存活率[17]。 2.2 MSCs治疗急性肝损伤的移植途径 MSCs用于治疗急性肝损伤时有多种移植途径,每种途径都有各自的优缺点。 2.2.1 尾静脉移植 经尾静脉注射移植MSCs是最简便易行也是最常用的方法,操作简单,损伤小,不需特殊实验设备。大鼠急性肝损伤动物模型研究中最常用的就是尾静脉注射。Di Bonzo等[18]研究了急性和慢性肝损伤小鼠经尾静脉注射人源MSCs后肝内细胞的分布情况,结果发现慢性肝损伤组的细胞归巢率高于急性肝损伤组,机制可能是短时间内干细胞经外周静脉血归巢至肝脏的数量有限。 2.2.2 肝内移植 肝内注射MSCs是一种局部移植方式。Sato等[19]采用26 G穿刺针将1×106人源MSCs直接注射至肝左外叶内,一段时间后可以观察到肝内有大量干细胞的沉积,并且有向肝细胞分化的特征。肝内注射有利于干细胞的肝内归巢,但是该操作过程复杂、损伤较大,注射的干细胞有通过肝静脉进入肺毛细血管造成栓塞的风险,因此并不是干细胞治疗的推荐方式。 2.2.3 门静脉注射 与腹腔内注射比较,经门静脉注射的干细胞归巢肝脏速率高。Popp等[20]在研究中发现,门静脉注射2 h后在肝实质内可以检测到MSCs的存在,但2 d后肝内MSCs数量却显著较少,推测门静脉注射后大部分MSCs可能在早期即被肝脏清除。门静脉注射干细胞同样操作过程复杂,且有造成门静脉高压的危险,另外,移植的细胞可能进入体循环造成脑、肺等器官的栓塞。 2.2.4 肝动脉移植 经肝动脉注射MSCs也是向肝脏移植干细胞的一种途径,可以使得干细胞以较高浓度在肝内存在。但此方法侵入性大,操作复杂,因此临床实用性较小,仅在少量动物实验中应用。 2.2.5 脾内注射 脾内注射时需开腹暴露脾脏,用30号针在脾下极缓慢注射MSCs悬液。Deng等[21]对急性肝衰竭小鼠通过脾静脉和尾静脉注射脂肪MSCs后观察小鼠生存率、肝功能、肝组织病理结构的改变,结果发现两种移植途径在肝功能改善、MSCs归巢数量方面无明显差异,仅脾静脉移植时小鼠生存率稍高。由于脾静脉血流直接汇入肝脏,因而脾内注射的干细胞会经门静脉进入肝脏,有致门静脉栓塞的风险。 2.2.6 腹腔内注射 腹腔内注射的优势是可以一次性移植大量细胞,操作简单,损伤性小,不存在器官栓塞的风险。Zhao等[22]比较了尾静脉、肝内和腹腔3种途径移植骨髓MSCs对四氯化碳诱导的肝损伤的治疗效果,结果却发现腹腔注射并不能有效改善肝功能和纤维化。因而,腹腔内注射干细胞的治疗效果有待于进一步实验证实。 Sang等[23]比较了尾静脉、肝动脉、门静脉、肝内4种途径移植猪骨髓MSCs对急性损伤猪肝脏的修复作用,研究发现肝内移植和尾静脉移植在生存率改善方面无明显差异,均低于肝动脉和门静脉移植组,在肝功能、肝脏组织结构改善和肝细胞凋亡率方面,门静脉移植均优于肝动脉移植。 Sun等[24]在研究中对比分析了急性肝损伤大鼠经尾静脉、肝动脉、门静脉、腹腔内4种途径移植骨髓MSCs的治疗效果,发现尾静脉、肝动脉和门静脉移植在肝脏组织病理和生化指标恢复方面无统计学差异,而腹腔内注射在动物实验中并没有显示出明显的治疗效果,说明只有进入血液循环的肝干细胞才能发挥治疗作用。 各研究中不同移植途径的治疗效果有所不同,可能与实验动物种属、造模方式、MSCs来源以及检测时间点不同有关,见表1[19,23-29]。总体来看,不管采用哪种移植途径,干细胞均能够改善肝功能,只是在MSCs归巢、定植数量方面,门静脉移植要优于尾静脉移植。同时根据MSCs在肝内出现时间和维持时间也推测归巢至肝脏的MSCs可能只起到一个刺激肝细胞活化的作用,MSCs的归巢数量与肝脏合成能力的改善并不完全一致。"
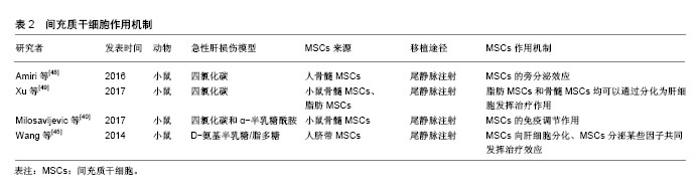
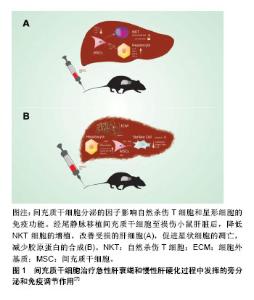
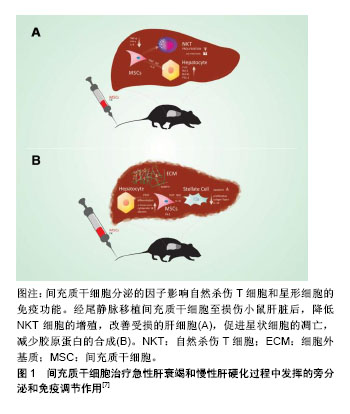
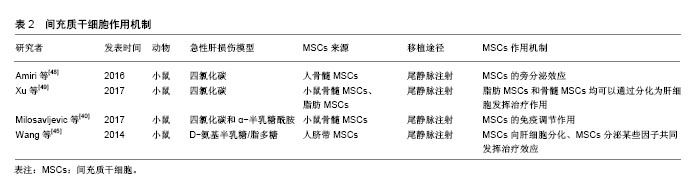
2.3 MSCs治疗急性肝损伤的机制 文献对MSCs治疗急性肝脏疾病机制的探索主要集中在3个方面:肝细胞分化或与肝细胞融合、旁分泌效应以及免疫调节作用。 2.3.1 肝细胞分化或与肝细胞融合 MSCs可能是通过细胞融合或直接转化方式具备肝细胞的某些性能。研究证明在细胞因子、生长因子作用下人源、鼠源MSCs均可以发生表型的改变,表达某些肝细胞的基因型,因而推测MSCs具有分化成肝细胞的能力[30-31]。 Lange等[32]将大鼠骨髓MSCs与大鼠肝细胞在含肝细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子的培养皿中共培养3周后分选细胞,发现MSCs表达白蛋白、细胞角蛋白18、细胞角蛋白19和甲胎蛋白基因。在Luk等[33]学者的实验中,只是将大鼠骨髓MSCs与正常或受损的肝细胞共培养,并不添特定的生长因子,结果同样发现MSCs向肝细胞分化,说明可能是肝细胞分泌的某些因子调节MSCs向肝细胞转化。Zheng等[34]比较了人源脂肪MSCs和骨髓MSCs分化为肝细胞的能力,发现脂肪MSCs具有更高的肝分化潜能。值得注意的是,发生干细胞转化的MSCs仍然表达CD90等某些干细胞的标记,表明MSCs的分化并不完全。Sato等[35]在烯丙醇处理的急性肝损伤大鼠肝脏内观察到Y染色体标记的人MSCs,说明MSCs异种移植后也会发生肝细胞分化。此外,与肝细胞相互融合也是MSCs发挥治疗作用的一种方式,因为在急性肝损伤大鼠中可以检测到四倍体、六倍体和非整倍体肝细胞的存在[36]。但是,研究数据显示归巢至肝脏的MSCs仅有很少一部分发生肝细胞样分化(7%-12%),而且仅为低功能转化(8%-23%),并不能完全替代正常肝细胞的功能[37]。 2.3.2 MSCs的免疫调节作用 MSCs可通过一系列分子启动免疫调节修复受损组织,包括细胞间直接作用或是通过旁分泌触发远程效应。发生急性损伤的肝脏通常伴随着炎症反应和T细胞、B细胞和单核细胞的浸润,MSCs的免疫抑制和免疫调节作用在肝脏疾病中可降低炎症因子水平。Aggarwal等[38]证明MSCs可以通过分泌前列腺素E2增加白细胞介素10的分泌以及减少肿瘤坏死因子α,干扰素γ和白细胞介素4的分泌,发挥树突状细胞的免疫调节作用。此外,MSCs还通过增加程序性死亡受体与配体的结合以及下调抗原呈递细胞表面共刺激分子CD80和CD86的表达来诱导细胞凋亡,从而抑制T细胞增殖[39]。 研究发现扁桃体来源的MSCs通过分泌半乳糖凝集素1显著减弱刀豆素A诱导的急性肝损伤毒性并有效抑制了T细胞炎性因子分泌[40]。除此之外,MSCs对自然杀伤细胞有很强的抑制功能,并能产生可溶性细胞因子IDO和前列腺素E2发挥更强的免疫抑制作用[41]。因此,MSCs在免疫疗法方面有可观的应用前景。 2.3.3 MSCs的旁分泌效应 多篇文献显示在急性肝损伤中,归巢至肝脏的MSCs可以产生一系列细胞因子和信号分子,能够有效减轻肝脏炎症、抑制肝细胞凋亡。Lotfinia等[42]对硫代乙酰胺诱导的急性肝损伤小鼠利用人胚胎干细胞来源培养基治疗,发现实验组动物生存率明显高于模型组,机制可能是其分泌的血管内皮生长因子、白细胞介素10等能促进肝细胞增殖、抑制肝细胞凋亡。在Ma等[43]研究中也发现MSCs是通过肝细胞生长因子、血管内皮生长等促进肝细胞增殖。然而,MSCs旁分泌效应的确切分子机制仍在研究中,而且MSCs分泌的一些细胞因子可能在某些情况下有促炎作用。 事实上,更多学者趋向支持MSCs发挥治疗效果的分子机制并非完全独立,而是多方面因素共同作用的结果,即可能是旁分泌和免疫效应的协同作用,或是肝细胞分化、旁分泌效应、免疫效应三者共同发挥协同作用[44-45]。特别是在体内实验中,受损的肝脏自身会释放一些炎症因子和细胞因子,在不同因子的刺激下,MSCs可以发生不同的“命运”转归,如在肝细胞生长因子的作用下可能分化为肝细胞,而在白细胞介素6的影响下可能促进其旁分泌效应,而白细胞介素6又是参与炎症反应免疫调节的一个重要保护性因子,可以通过调节抗凋亡蛋白水平使肝细胞免于Fas介导的死亡。 MSCs的哪种机制发挥主导作用,似乎与肝损伤模型的建立方式有关系,像刀豆素A诱导的急性肝损伤,MSCs主要发挥免疫调节作用,而对于四氯化碳造成的肝损伤,MSCs则主要通过其旁分泌效应对肝细胞起保护作用[46-47]。目前认为MSCs在急性肝损伤中通过分化为肝细胞、分泌营养和免疫调节因子这几个过程促进肝细胞再生,见表2[40,45,48-49]。但每个过程发挥作用程度和时间有差异,转分化肝细胞可能在后期起主要作用,体外实验证明MSCs转化为肝细胞大约需21 d。MSCs分泌的细胞因子则可以在移植后发挥抑制肝细胞凋亡,促进肝细胞增殖和血管生成等作用。 图1是MSCs在治疗急性和慢性肝脏疾病时发挥旁分泌和免疫调节作用的示意图。"
| [1] Krawitz S, Lingiah V, Pyrsopoulos NT.Acute Liver Failure: Mechanisms of Disease and Multisystemic Involvement.Clin Liver Dis. 2018;22(2):243-256. [2] D'souza N, Rossignoli F, Golinelli G, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells as a delivery platform in cell and gene therapies.BMC Med. 2015;13:186. [3] Abbasi-Malati Z, Roushandeh AM, Kuwahara Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Horizon: A New Arsenal of Therapeutic Agents.Stem Cell Rev. 2018;14(4):484-499. [4] Tan CY, Lai RC, Wong W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote hepatic regeneration in drug-induced liver injury models.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(3):76. [5] Wang Y, Yu X, Chen E, et al. Liver-derived human mesenchymal stem cells: a novel therapeutic source for liver diseases.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):71. [6] 李培杰,王佳,李伟之,等.人脐血间充质干细胞在大鼠急性肝损伤修复中的作用[J].陕西医学杂志,2017,46(6):702-705.[7] Volarevic V, Nurkovic J, Arsenijevic N, et al. Concise review: Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of acute liver failure and cirrhosis.Stem Cells. 2014; 32(11):2818-2823. [8] Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues.Transplantation. 1968; 6(2):230-247. [9] Friedenstein AJ, Gorskaja JF, Kulagina NN.Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse hematopoietic organs.Exp Hematol. 1976;4(5):267-274. [10] Caplan AI.Mesenchymal stem cells.J Orthop Res. 1991; 9(5): 641-650. [11] Zhao L, Chen S, Shi X, et al. A pooled analysis of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for liver disease.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):72. [12] Vizoso FJ, Eiro N, Cid S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):E1852. [13] Kang ES, Kim DS, Suhito IR, et al. Two-dimensional material-based bionano platforms to control mesenchymal stem cell differentiation.Biomater Res. 2018;22:10. [14] Roushandeh AM, Bahadori M, Roudkenar MH.Mesenchymal Stem Cell-based Therapy as a New Horizon for Kidney Injuries.Arch Med Res. 2017;48(2):133-146. [15] Liepelt A, Tacke F.Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) as a target in liver diseases.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016;311(2):G203-209. [16] Lukáš Z, Ba?enkováD, Soltys J, et al. Bioactive mediators Associated with Mesenchymal Stem Cells -Mediated Immunomodulation.J J Bone Stem Res. 2005;1(2):006. [17] Wang M, Yuan Q, Xie L.Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Immunomodulation: Properties and Clinical Application.Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:3057624. [18] Di Bonzo LV, Ferrero I, Cravanzola C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells as a two-edged sword in hepatic regenerative medicine: engraftment and hepatocyte differentiation versus profibrogenic potential.Gut. 2008;57(2): 223-231. [19] Sato Y, Araki H, Kato J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells xenografted directly to rat liver are differentiated into human hepatocytes without fusion.Blood. 2005;106(2): 756-763. [20] Popp FC, Slowik P, Eggenhofer E, et al. No contribution of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to liver regeneration in a rat model of prolonged hepatic injury.Stem Cells.2007; 25(3): 639-645. [21] Deng L, Kong X, Liu G, et al. Transplantation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Efficiently Rescues Thioacetamide-Induced Acute Liver Failure in Mice. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(6):2208-2215. [22] Zhao X, Shi XL, Zhang ZH, et al. Role of neutrophils in treatment of rats with D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016;24(8):601-607. [23] Sang JF, Shi XL, Han B, et al. Intraportal mesenchymal stem cell transplantation prevents acute liver failure through promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2016;15(6):602-611. [24] Sun L, Fan X, Zhang L, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation via four routes for the treatment of acute liver failure in rats.Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):987-996. [25] Ramanathan R, Rupert S, Selvaraj S, et al. Role of Human Wharton's Jelly Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (WJ-MSCs) for Rescue of d-Galactosamine Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017;7(3):205-214. [26] Haga H, Yan IK, Borrelli DA, et al. Extracellular vesicles from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against murine hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury.Liver Transpl. 2017;23(6):791-803. [27] Teshima T, Matsumoto H, Michishita M, et al. Allogenic Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Acute Hepatic Injury in Dogs.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3892514. [28] Cai J, Zhang X, Wang X, et al. In vivo MR imaging of magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells transplanted into rat liver through hepatic arterial injection.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2008;3(2):61-66. [29] Manzini BM, da Silva Santos Duarte A, Sankaramanivel S, et al. Useful properties of undifferentiated mesenchymal stromal cells and adipose tissue as the source in liver-regenerative therapy studied in an animal model of severe acute fulminant hepatitis.Cytotherapy. 2015;17(8):1052-1065. [30] Manzini BM, da Silva Santos Duarte A, Sankaramanivel S, et al. Useful properties of undifferentiated mesenchymal stromal cells and adipose tissue as the source in liver-regenerative therapy studied in an animal model of severe acute fulminant hepatitis.Cytotherapy. 2015;17(8):1052-1065. [31] Song HL, Shen ZY, Zheng WP, et al. Differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells and their regulatory effects on activated lymphocytes and liver graft regeneration and rejection. J Hepatology. 2015;62(1):S295. [32] Lange C, Bassler P, Lioznov MV, et al. Liver-specific gene expression in mesenchymal stem cells is induced by liver cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(29):4497-4504. [33] Luk JM, Wang PP, Lee CK, et al. Hepatic potential of bone marrow stromal cells: Development of in vitro co-culture and intra-portal transplantation models. J Immunol Methods. 2005; 305(1):39-47. [34] Zheng YB, Gao ZL, Xie C, et al. Characterization and hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human amniotic fluid and human bone marrow: a comparative study.Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(11):1439-1448. [35] Sato Y, Araki H, Kato J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells xenografted directly to rat liver are differentiated into human hepatocytes without fusion.Blood. 2005;106(2):756-763. [36] Camargo FD, Finegold M, Goodell MA.Hematopoietic myelomonocytic cells are the major source of hepatocyte fusion partners.J Clin Invest. 2004;113(9):1266-1270. [37] Liu WH, Song FQ, Ren LN, et al. The multiple functional roles of mesenchymal stem cells in participating in treating liver diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(3):511-520. [38] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF.Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses.Blood. 2005; 105(4):1815-1822. [39] Simovic Markovic B, Nikolic A, Gazdic M, et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Gal-3 in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhances Their Capacity to Promote Alternative Activation of Macrophages in Dextran Sulphate Sodium-Induced Colitis.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2640746. [40] Milosavljevic N, Gazdic M, Simovic Markovic B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate acute liver injury by altering ratio between interleukin 17 producing and regulatory natural killer T cells.Liver Transpl. 2017;23(8):1040-1050. [41] Moll G, Alm JJ, Davies LC, et al. Do cryopreserved mesenchymal stromal cells display impaired immunomodulatory and therapeutic properties. Stem Cells. 2014;32(9):2430-2442. [42] Lotfinia M, Kadivar M, Piryaei A, et al. Effect of Secreted Molecules of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Acute Hepatic Failure Model. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(24):1898-1908. [43] Ma HC, Shi XL, Ren HZ, et al. Targeted migration of mesenchymal stem cells modified with CXCR4 to acute failing liver improves liver regeneration.World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20(40):14884-14894. [44] Heymann F, Hamesch K, Weiskirchen R, et al. The concanavalin A model of acute hepatitis in mice.Lab Anim. 2015;49(1 Suppl):12-20. [45] Wang H, Zhao T, Xu F, et al. How important is differentiation in the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stromal cells in liver disease. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(3):309-318. [46] Dhawan A, Puppi J, Hughes RD, et al. Human hepatocyte transplantation: current experience and future challenges.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(5):288-298. [47] Sun K, Xie X, Xie J, et al. Cell-based therapy for acute and chronic liver failures: distinct diseases, different choices.Sci Rep. 2014;4:6494. [48] Amiri F, Molaei S, Bahadori M, et al. Autophagy-Modulated Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Liver Restoration in Mouse Models of Acute Liver Failure. Iran Biomed J. 2016;20(3):135-144. [49] Xu LJ, Wang SF, Wang DQ, et al. Adipose-derived stromal cells resemble bone marrow stromal cells in hepatocyte differentiation potential in vitro and in vivo.World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(38):6973-6982.[50] Zhu X, He B, Zhou X, et al. Effects of transplanted bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in animal models of acute hepatitis.Cell Tissue Res. 2013;351(3): 477-486. [51] Zhang Y, Yang P, Sun T, et al. miR-126 and miR-126* repress recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells and inflammatory monocytes to inhibit breast cancer metastasis.Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(3):284-294. [52] Li GC, Zhang HW, Zhao QC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor angiogenesis via the action of transforming growth factor β1.Oncol Lett. 2016;11(2):1089-1094. [53] Mi F, Gong L.Secretion of interleukin-6 by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2017;37(4): BSR20170181. [54] Lacina L, Plzak J, Kodet O, et al. Cancer Microenvironment: What Can We Learn from the Stem Cell Niche.Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(10):24094-24110. [55] Park JS, Suryaprakash S, Lao YH, et al. Engineering mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine and drug delivery. Methods. 2015;84:3-16. [56] Alfaifi M, Eom YW, Newsome PN, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for liver diseases.J Hepatol. 2018;68(6):1272- 1285. [57] Tsolaki E, Yannaki E.Stem cell-based regenerative opportunities for the liver: State of the art and beyond.World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(43):12334-12350. [58] Cheng L, Zhang K, Wu S, et al. Focus on Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Opportunities and Challenges in Cell-Free Therapy.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:6305295. [59] Visweswaran M, Pohl S, Arfuso F, et al. Multi-lineage differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells - To Wnt, or not Wnt.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;68:139-147. [60] Sawitza I, Kordes C, Götze S, et al. Bile acids induce hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Sci Rep. 2015; 5: 13320. [61] Heo J, Ahn EK, Jeong HG, et al. Transcriptional characterization of Wnt pathway during sequential hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and adipose tissue-derived stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;434(2):235-240. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||