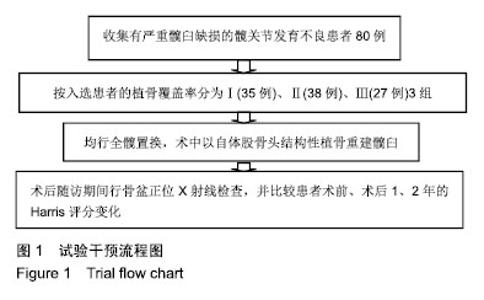
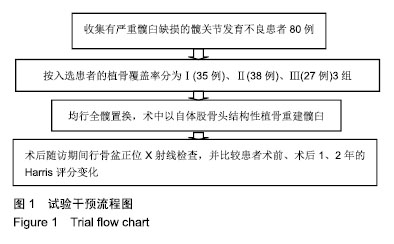
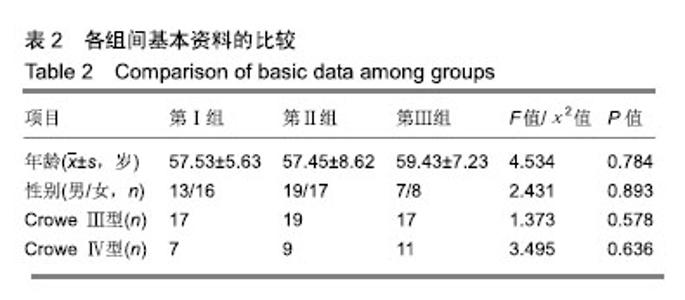
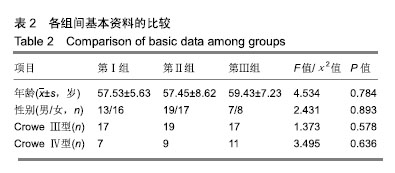
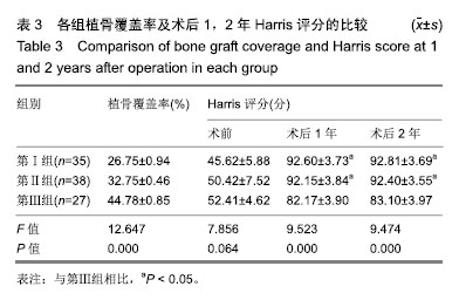
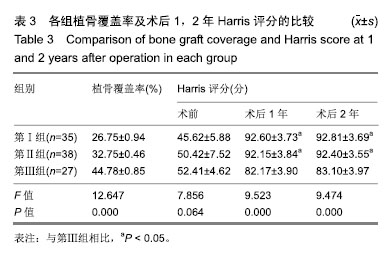
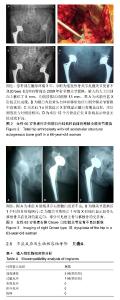
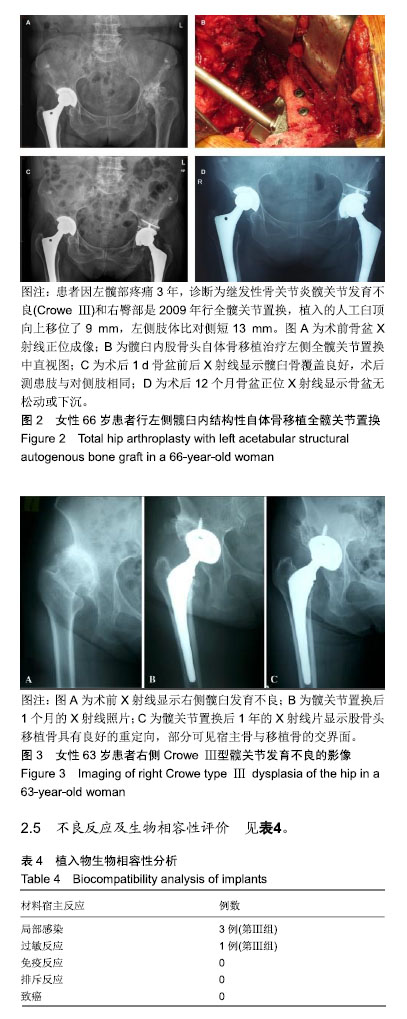
| [1]程亮亮,赵德伟.成人发育性髋关节发育不良的诊治现状[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(7):516-520.[2]Clohisy JC, Barrett SE, Gordon JE, et al. Periacetabular osteotomy for the treatment of severe acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(2):254-259. [3]孙西虎,赵建军,张圣军.成人髋臼发育不良的诊断及治疗进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2015,17(2):185-187.[4]Dorrell JH, Catterall A. The torn acetabular labrum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(3):400-403.[5]卢群山,张元凯.全髋关节置换后假体松动1例报道[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(3):219-221.[6]吕科,雷文黎,姜猛,等.自体骨移植小臼杯全髋关节置换治疗成人髋臼发育不良[J].临床医学研究与实践,2016,1(14):15-17.[7]常再平,王林,李龙,等.髋关节置换对股骨头坏死患者髋关节Harris评分及运动功能的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2017, 17(11):2116-2118.[8]Ishidou Y, Matsuyama K, Sakuma D, et al. Osteoarthritis of the hip joint in elderly patients is most commonly atrophic, with low parameters of acetabular dysplasia and possibleinvolvement of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2017;12(1):30.[9]Hitz OF, Flecher X, Parratte S, et al. Minimum 10-year outcome of one-stage total hip arthroplasty without subtrochanteric osteotomy using a cementless custom stem for crowe III and IV hip dislocation. J Arthroplasty. 2018; 33(7):2197-2202.[10]尚小斌,杨卿,鲁锐,等.人工全髋关节置换联合自体股骨头结构性植骨及转子下截骨治疗CroweⅣ型髋关节发育不良的短期随访[J].骨科,2017,8(1):39-43.[11]卢群山,张元凯.全髋关节置换后假体松动1例报道[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(3):219-221.[12]Hickman JM, Peters CL. Hip pain in the young adult: diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the acetabular labrum and acetabular dysplasia. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2001;30(6):459-467.[13]Hinman RS, Dobson F, Takla A. Patient-reportedoutcome in femoroacetabular impingement? Test-retest reliability of six questionnaires. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(6):458-463. [14]Hodges PW, Tucker K. Moving differently in pain: a new theory to explain the adaptation to pain. Pain. 2011;152 (3 Suppl):S90-S98. [15]Horii M, Kubo T, Inoue S, et al. Coverage of the femoral head by the acetabular labrum in dysplastic hips: quantitative analysis with radial MR imaging. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003; 74(3):287-292. [16]Kemp JL, Collins NJ, Roos EM, et al. Psychometric properties of patient-reported outcome measures for hip arthroscopic surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(9):2065-2073.[17]孙祥燚,张雷,周利武,等.全髋关节置换治疗成年双侧髋关节发育不良的短期疗效[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,12(8):139-142.[18]具紫明.浅析人工全髋关节置换治疗髋关节创伤性骨关节炎的临床疗效[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2017,34(6):39.[19]Chegini S, Beck M, Ferguson SJ. The effects of impingement and dysplasia on stress distributions in the hip joint during sitting and walking: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(2):195-201.[20]Clohisy JC, Ackerman J, Baca G, et al. Patient-reported outcomes of periacetabular osteotomy from the prospective ANCHOR cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(1): 33-41.[21]Dai M, Sakai Y, Ibuchi S, et al. Sex- and age-specific differences in femoral head coverage and acetabular morphology among healthy subjects-derivation of normal ranges and thresholds for abnormality. Skeletal Radiol. 2017;46(4):523-531.[22]Sankar WN, Duncan ST, Baca GR, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of acetabular dysplasia: the academic network of conservational hip outcomes research (ANCHOR) periacetabular osteotomy. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017; 25(2):150-159.[23]Downie WW, Leatham PA, Rhind VM, et al. Studies with pain rating scales. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978;37(4):378-381.[24]Ganz R, Klaue K, Vinh TS, et al. A new periacetabular osteotomy for the treatment of hip dysplasias. Technique and preliminary results. Clin Orthop Relat R. 1988;(232):26-36.[25]林传松,杨爱勇,关钦强,等.全髋关节置换治疗髋臼发育不良继发骨性关节炎的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(2): 145-146.[26]Kim M, Kadowaki T. High long-term survival of bulk femoral head autograft for acetabular reconstruction in cementless THA for developmental hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;46(6):1611-1620.[27]Nunley RM, Prather H, Hunt D, et al. Clinical presentation of symptomatic acetabular dysplasia in skeletally mature patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(Suppl 2):17-21. [28]Peters CL, Erickson J. The etiology and treatment of hip pain in the young adult. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(Suppl 4): 20-26. [29]Register B, Pennock AT, Ho CP, et al. Prevalence of abnormal hip findings in asymptomatic participants: a prospective, blinded study. Am J Sport Med. 2012;40(12):2720-2724.[30]Schubert AG, Kempf J, Heiderscheit BC. Influence of stride frequency and length on running mechanics: a systematic review. Sports Health. 2014;6(3):210-217. |