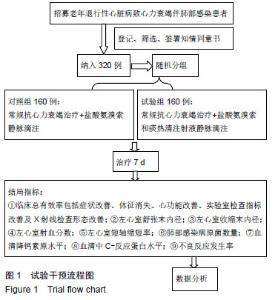
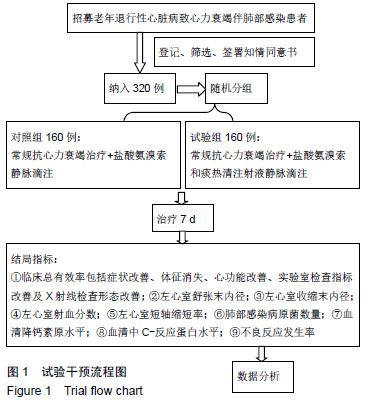
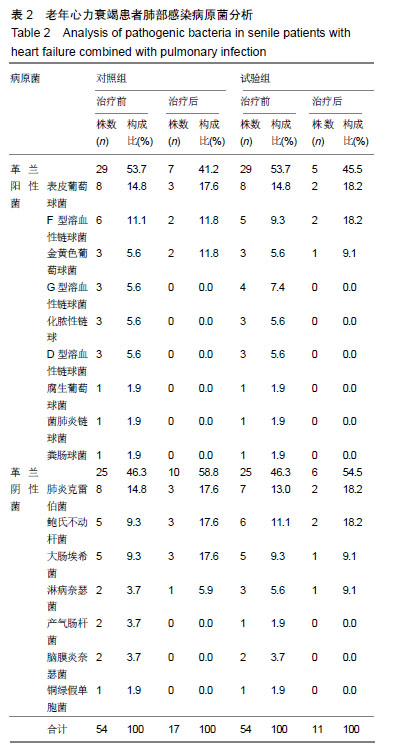
| [1]Gastelurrutia P, Lupón J, Moliner P, et al. Comorbidities, fragility, and quality of life in heart failure patients with midrange ejection fraction. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018;2(2):176-185. [2]Wu JR, Song EK, Moser DK, et al. Dietary vitamin c deficiency is associated with health-related quality of life and cardiac event-free survival in adults with heart failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2019;34(1):29-35.[3]Di Mauro M, Petroni R, Clemente D, et al. Clinical profile of patients with heart failure can predict rehospitalization and quality of life. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2018;19(3): 98-104. [4]Cherian TS, Shrader P, Fonarow GC, et al. Effect of atrial fibrillation on mortality, stroke risk, and quality-of-life scores in patients with heart failure (from the outcomes registry for better informed treatment of atrial fibrillation [ORBIT-AF]). Am J Cardiol. 2017;119(11):1763-1769.[5]Cosentino ER, Landolfo M, Bentivenga C, et al. Morbidity and mortality in a population of patients affected by heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an observational study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019;19(1):20. [6]Zhao Q, Wang L, Kurlansky PA, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes among elderly patients with heart failure and coronary artery disease and without atrial fibrillation: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019; 19(1):19.[7]Molyneaux PL, Cox MJ, Willis-Owen SA, et al. The role of bacteria in the pathogenesis and progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190(8): 906-913. [8]Kokhan EP, Aleksandrov AS, Shandurenko IN, et al. Postoperative wound complications in cardiosurgery. Angiol Sosud Khir. 2014;20(1):148-153.[9]Teng X, Wang Y, Lin N, et al. Evaluation of serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as biomarkers of Henoch-Schönlein purpura in pediatric patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35(3):667-671.[10]Li YM, Liu XY. Serum levels of procalcitonin and high sensitivity C-reactive protein are associated with long-term mortality in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 352(1-2):68-73.[11]Clinical Research Coordination Group of Guaifenesin Compound Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Oral Solution, Lu Q. A prospective multicenter randomized controlled clinical study on the efficacy and safety of Guaifenesin compound pseudoephedrine hydrochloride oral solution. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010;48(3):204-207. [12]Dai HS. Effect of large volume lavage of ambroxol hydrochloride on patients with pneumoconiosis combined with chronic bronchitis. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2007;25(9):565-566.[13]Wang X, Wang L, Wang H, et al. Perioperative lung protection provided by high-dose ambroxol in patients with lung cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;73(2):281-284. [14]Gao Y, Cheng Y, Dong S, et al. Effect of perioperative treatment with ambroxol on lung cancer patients after video-assisted thoracic surgery lobectomy. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2014;39(8):849-854. [15]Li Q, Yao G, Zhu X. High-dose ambroxol reduces pulmonary complications in patients with acute cervical spinal cord injury after surgery. Neurocrit Care. 2012;16(2):267-72. [16]余吉西,陈荣兴,李伟兴.痰热清注射液治疗心力衰竭患者合并肺部感染的临床研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2013,23(18): 4386-4388.[17]孙润锋,陈云,杨华,等.痰热清注射液对心力衰竭伴肺部感染患者血清胆碱酯酶及免疫功能的影响研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2017,27(22):5087-5090.[18]吴秀锋.头孢哌酮-舒巴坦与痰热清注射液联用对老年慢性心力衰竭患者合并肺部感染的临床疗效评价[J].抗感染药学, 2018, 15(7):1221-1223. |