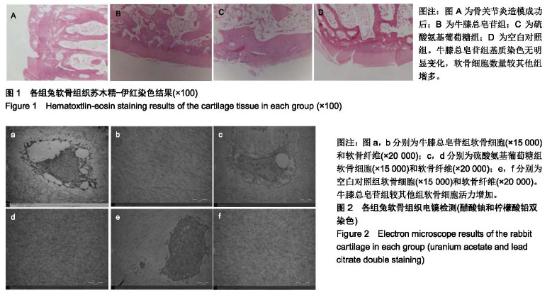
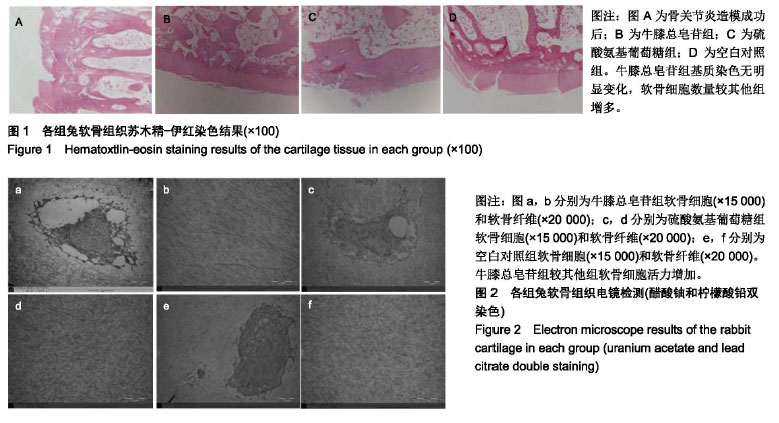
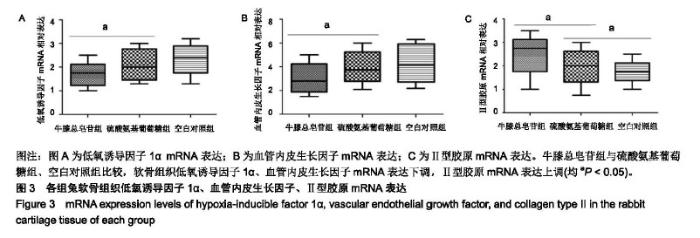
| [1]骆帝,许波,李刚,等.骨碎补治疗骨关节炎的网络药理学研究[J].中草药,2018,49(15): 3516-3521.[2]彭力平,马笃军,林栋栋,等.牛膝醇提物体内诱导兔骨关节炎模型软骨修复的病理学观察[J].湖南中医杂志,2013,29(2):126-129.[3]刘渊,孙雪莲,周红海,等.牛膝总皂苷含药血清对兔膝软骨细胞增殖与凋亡的实验研究[J].时珍国医国药,2015,26(10):2382-2385[4]张爽,刘石,汪宇峰,等.间充质干细胞修复骨关节炎软骨损伤的临床应用意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(33):5379-5385.[5]Makris EA, Gomoll AH, Malizos KN, et al. Repair and tissue engineering techniques for articular cartilage. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):21-34. [6]Ackerman IN,Bohensky MA,de Steiger R, et al. Substantial rise in the lifetime risk of primary total knee replacement surgery for osteoarthritis from 2003 to 2013: an international, population-level analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2017; 25(4): 455-461.[7]董政权,陈崇伟,卫小春,等. 骨关节炎常用治疗药物的研究现状及展望[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2018,4(4)252-255.[8]郭达,张斌山,刘金文.骨关节炎的古代方药规律研究[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30 (9):2194-2195.[9]姚共和,刘向前,李建斌,等.中医期刊治疗膝关节骨关节炎方剂用药特点分析[J].湖南中医学院学报,2005,25(6):54 -56.[10]张磊,王彦志,赵会丽,等.牛膝化学成分及其对细胞增殖影响[J].中成药,2018,40(6):1320-1325.[11]郭婕,李季平,刘中华,等.怀牛膝多糖的微波提取工艺研究[J].中国果菜,2017,37(4):14-18.[12]张小鸿.牛膝总皂苷保护软骨细胞作用及其机制研究[D].福州:华侨大学,2014.[13]余阗,彭力平,马笃军,等.牛膝总皂苷对实验兔骨关节炎滑膜组织的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2017,25(6) :1-5.[14]孙雪莲,刘渊,周红海.牛膝总皂苷对兔膝骨关节炎软骨组织形态变化及关节液中IL-1β、TGF-β1含量的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2016,27(3):321-326.[15]那莎,段陈方圆,王璐,等.牛膝总皂苷对大鼠急性痛风性关节炎的防治作用及机制研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2017, 22(9): 966-971.[16]陶益,杜映姗,黄苏润,等.牛膝不同炮制品中化学成分的UPLC-Q- TOF/MS分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(12):1-5.[17]肖伟,马笃军,彭力平,等.牛膝醇提物对兔骨关节炎软骨细胞体外增殖及糖胺聚糖的干预作用[J].中国医药导报, 2017,14(5): 20-24.[18]谢获.牛膝总皂苷对兔早期骨关节炎及P13K/AKT通路的影响[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2011.[19]曾俊华,马笃军,彭力平,等.实验兔膝骨关节炎模型的建立及鉴定[J].中国临床研究,2016,29(5):679-682.[20]徐涛涛,劳杨骏,廖菲,等.HIF-1α信号通路与激素性股骨头坏死相关性研究进展[J].世界中西医结合杂志, 2015,10(5):730-733.[21]邵进,张岩,王治,等.低氧诱导因子-1α参与骨发育及骨代谢调控的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(3):349-355.[22]田大川,李海乐,肖大伟,等.联合应用软骨再生支架与突变型HIF-1α修饰BMSCs分泌的外泌体对晚期软骨缺损修复的促进作用[J].吉林大学学报,2018,44(2):216-222[23]黄慧萍,李晶,于大海,等.低氧对大鼠髁突软骨细胞 HIF-1α和VEGF表达的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2011,27(6):773-776[24]Wang V,Davis DA,Hague M,et al.Differential gene up-regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and hypoxiainducible factor -2alpha in HEK293T cells. Cancer Res.2005;65(8):3299-3306.[25]翁金清,彭昊,周建林,等.HIF-1α、VEGF及 CD34 在大鼠骨关节炎模型软骨中的表达及意义[J].生物医学工程与临床,2015, 19(4):407-411.[26]Allerstorfer D,Longato S,Schwarzer C,et al.VEGF and its role in the early development of the long bone epiphysis.J Anat. 2010;216(5):611-624.[27]Hayami T,Funaki H,Yaoeda K,et al.Expression of the cartilage derived anti-angiogenic factor chondromodulin-Ⅰdecreases in the early stage of experimental osteoarthritis.J Rheumatol. 2003;30(10):2207-2217.[28]Pfander D,Cramer T,Deuerling D,et al.Expression of thrombospondin-1 and its receptor CD36 in human osteoarthritic cartilage.Ann Rheum Dis.2000;59(6):448-454. |