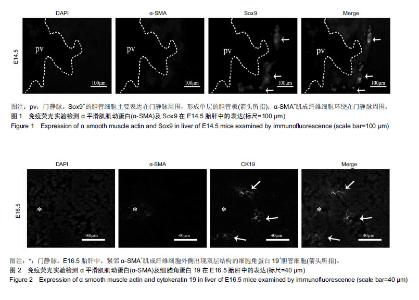
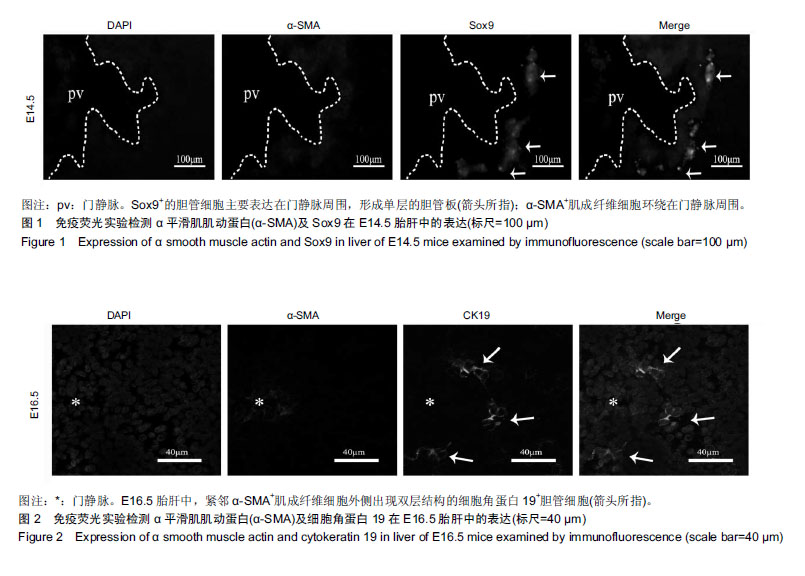
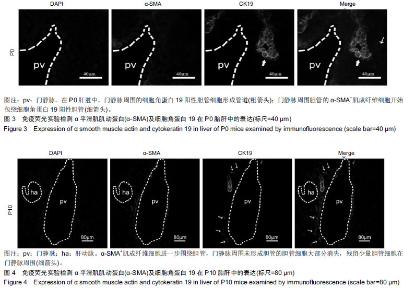
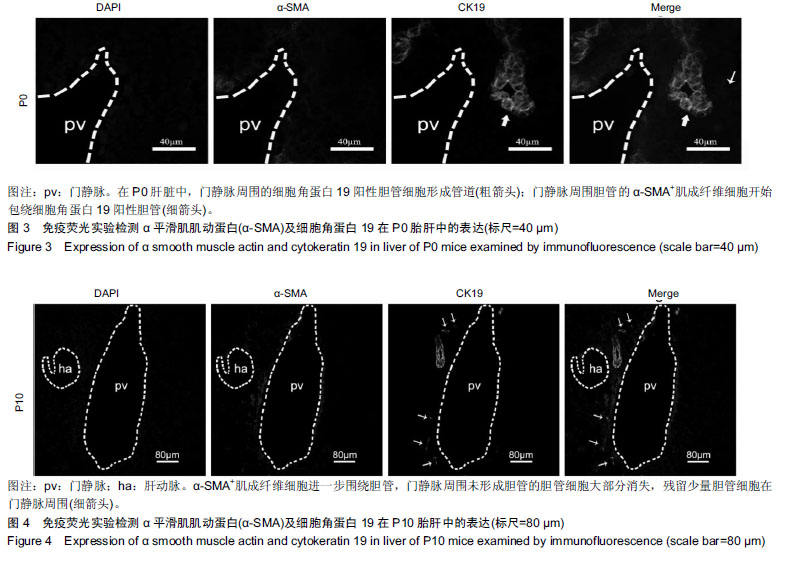
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3705-3709.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1317
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of myofibroblasts in the development of mouse intrahepatic bile ducts
Yang Junjun1, Li Dewei2, Wang Wei2, Feng Yuan1
- (1Department of Infections, the Second Clinical College of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong Central Hospital, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China)