Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3584-3590.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1302
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advantages and application prospects of microfluidic chip technology in cell adhesion research
- 1大连大学医学院,辽宁省大连市 116622;2大连大学环境与化学工程学院,辽宁省大连市 116622
-
Received:2019-03-27 -
Contact:Wang Yunhua, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Medicine, Dalian University, Dalian 116622, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhuan Hang, Master candidate, School of Medicine, Dalian University, Dalian 116622, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81471807 (to WYH), No. 41476085 (to ZGX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhuan Hang, Zheng Guoxia, Wang Yunhua. Advantages and application prospects of microfluidic chip technology in cell adhesion research[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3584-3590.
share this article
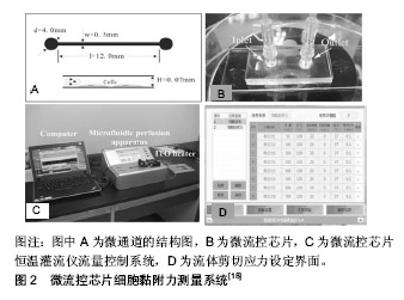
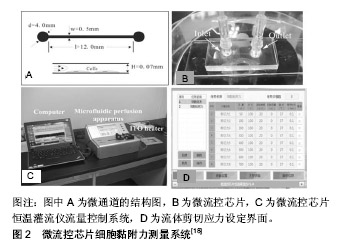
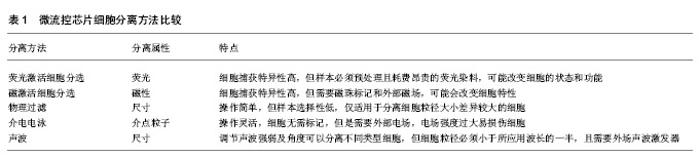
2.1 微流控芯片技术在基础研究中的应用 2.1.1 微流控芯片技术在动态监测细胞黏附过程中的应用 细胞黏附是一种复杂、动态且高度调节的过程,多数研究工具仅能分析实验前后细胞的黏附状态变化,难以获得细胞黏附过程的实时信息。借助于微流控芯片技术和多种物理、生物化学和光学传感器,可自动化和持续性监测细胞铺展面积、黏着斑数量、大小、分布等情况,为直接观察细胞黏附动力学提供了一种更为直观、可行的方法。Honarmandi等[9]将微流控技术与荧光成像技术结合实现了黏着斑中蛋白质组装或募集过程的可视化。Thompson等[10]根据细胞运动速度特征量化了癌细胞在基质表面的黏附行为,即无黏附、滚动黏附、瞬时黏附、牢固黏附等。Tu等[11]利用微流控芯片技术和纳米等离子体构造了基于光学异常透射的微纳米传感器,在单细胞水平上无标记、无损、实时监测单个小鼠胚胎干细胞系C3H10细胞和人宫颈癌细胞HeLa细胞在基质上附着和扩散过程中的光谱位移变化,证实了细胞的异质性,不同的细胞个体的黏附性存在着较大差异,在黏附过程中具有不同的动力学参数,为研究单细胞黏附动力学提供了新的途径。 2.1.2 微流控芯片技术在定量检测细胞黏附力中的应用 细胞黏附力是细胞生物力学特性之一,其实质是细胞与细胞间或细胞与基质间的相互作用力。定量检测细胞黏附力,有助于从力学角度解释细胞黏附机制和评价细胞生物学功能。对细胞黏附力的定量测量也有助于生物材料的筛选,特别是医用植入材料的性能评价。目前测量细胞黏附力的方法有离心法[12]、原子力显微镜 法[13]、微管吸吮法[14]、光镊法等[15]。但是这些方法检测机制各不相同,也缺乏统一的评价标准,实验数据很难量化比较。微流控芯片因其微米尺度与细胞尺寸匹配,装置简便易操作、实验通量高、能够提供平行可控、稳定的细胞内环境和流体力场环境,可实现细胞黏附力学信息的实时、原位、动态探测和操控,逐渐成为定量研究细胞黏附强度的有力工具之一[16]。Kim等[17]测定了小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞系NIH3T3细胞在玻璃表面上的黏附力为28 nN,远低于Gallant等测得NIH3T3细胞在涂覆纤维蛋白的玻璃表面上的黏附力200 nN,表明纤维蛋白能够提供更多的整联蛋白结合位点,促进细胞与基质的黏附。Li等[18]利用微流控芯片细胞黏附力测量系统动态监测了上皮-间质转化的过程,发现经转化生长因子β诱导后人非小细胞肺癌细胞A549细胞的黏附强度显著降低,迁移能力增强,细胞黏附强度可潜在用于估计肿瘤细胞的迁移能力,见图2。课题组Lu等[19]利用集成微流控芯片系统通过计算50%细胞脱离的临界剪切力定量,表征了蓝氏贾第鞭毛虫滋养体在不同基底表面上的黏附力,有助于解释滋养体附着在肠上皮表面的生物学机制。"
微流控芯片也被应用于单细胞检测层面。Kevin 等[20]对单个NIH3T3黏附强度进行了定量研究,发现细胞黏附强度与细胞面积和圆形度正相关。但是另一研究发现细胞的黏附力主要取决于细胞表面受体与基质表面配体键的数量和结合力,与细胞的铺展面积无关。Mao等[21]开发了一种基于微流控芯片技术的“单细胞提取器”,实现了对贴壁细胞样品中任意单细胞原位、无损地提取,并揭示了细胞黏附强度与细胞活力的关系,黏附强度较大的细胞通常具有较高的细胞活力。Mao等[22]还首次测量单个循环肿瘤细胞与内皮细胞的黏附强度及评估了药物对细胞与细胞间黏附强度的影响。结果表明不同类型的循环肿瘤细胞与内皮细胞的黏附强度明显不同,使用替莫唑胺可以剂量依赖的方式抑制循环肿瘤细胞与内皮细胞的黏附,能够有效预防肿瘤转移。 这些黏附力的定量研究,尤其是在生理条件下单细胞黏附力的定量检测,是传统研究方法所难以实现的。微流控技术为开发抗肿瘤药物及其他生物材料研究提供了新的方法和定量评价指标。 2.2 微流控芯片技术在临床研究中的应用 2.2.1 微流控芯片技术在稀有细胞的分离和富集中的应用 对不同细胞类型进行分类或从异质细胞群体中分离出特定的细胞类型,是生物学研究和疾病诊断中的一个重要环节。常用的微流控芯片细胞分离方法包括荧光激活细胞分选[23]、磁激活细胞分选[24]、物理过滤[25]、介电电泳及声波细胞分选等[26-27],但这些方法都有各自的优点和局限性,见表1。虽然荧光激活细胞分选和磁激活细胞分选是目前细胞分选的金标准,但这2种方法需要对细胞表面进行荧光抗体或磁珠标记,可能改变细胞的功能,影响细胞的后续培养和分析。细胞黏附可作为分离和检测目标细胞的物理标记之一。基于黏附的微流体细胞分选是少数无标记分选技术之一,其不依赖于颗粒的大小,使其成为细胞分选的合适选择。在新的微流控芯片技术中,用功能化的表面捕获靶细胞,据细胞与基质的黏附结合强度来分离细胞,然后在微流体驱动下快速、无损地释放被捕获的靶细胞,实验所需样本量少,无需标记或预处理,分离后的细胞仍具有生物活性,可用于体外培养和后续的研究。多个研究小组证实了这种分离技术在稀有细胞类型分选和富集的实用性。Singh等[28]利用人多功能干细胞与分化细胞之间黏附强度的差异,快速、有效、选择性地分离出完全重编程人多功能干细胞。分离无需标记,存活率大于80%,而荧光激活细胞分选过程中由于流体压力和电场作用的影响,细胞存活率仅为40%。桑维维等[29]构建的MUC1黏蛋白抗体修饰微流控芯片,能有效捕获乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231,捕获率达(80±3)%,释放率约98%,细胞释放后存活率高,可实现再培养。Zhang等[30]设计了一种高通量细胞黏附芯片,根据细胞与基质黏附能力的高低,从癌症干细胞中分离和富集2种异质性乳腺癌细胞系SUM-149细胞和SUM-159细胞。Chen等[31]根据正常血细胞和癌细胞对纳米粗化蚀刻玻璃基底的黏附差异,用微流控芯片从全血样本中捕获循环肿瘤细胞的效率高达80%。这种基于黏附的捕获方式,与循环肿瘤细胞表面标志物的表达情况和转移倾向无关,具有收集整个循环肿瘤细胞群体的潜力。Dasanna等[32]根据疟疾感染的红细胞的黏附特性,在微流控芯片内进行细胞黏附动力学模拟,表明可通过优化流体剪切速率和通道的倾斜角度,从受感染患者的血液中分离出疟疾感染的红细胞。 基于黏附的微流体分选,提供了一种高通量和无标记的细胞分离技术。然而由于血液样本的复杂性,细胞与细胞、细胞与基质间的相互作用不易控制,当处理细胞浓度较高的样品时,芯片内易发生堵塞,造成细胞分选效率降低。此外在靶细胞释放过程中,存在流速过小细胞释放速度慢、流速过大形成的流体剪切应力对细胞造成机械损伤等问题。因此在现有技术的基础上,充分结合不同细胞分离技术的优势,提高对靶细胞的捕获和释放能力,完成高效、精准及低成本的细胞分离,是改进基于黏附微流体细胞分离技术的研究重点。 2.2.2 微流控芯片技术在生物医学材料中的应用 在组织工程中,细胞与细胞外基质或材料表面的黏附,是大多数细胞存活的先决条件,在生物材料和植入物与组织的整合中起着至关重要的作用。细胞与基质的黏附既取决于材料本身又受基质表面性质、表面修饰、表面形貌、净电荷、孔隙率及降解速率等众多因素的影响[33-35]。在细胞与材料的黏附性能研究中,传统的方法主要考察细胞在特定材料表面的黏附数量和形态,对细胞黏附性能做出直观分析和判断。而新的分析方法中,通过对细胞施加剪切力来定量测定细胞的黏附力,可为细胞在特定材料表面的黏附强度和材料性能做出更准确的评 价[36]。微流控芯片易于构建组织微环境并进行细胞黏附力定量检测的特点,为细胞-材料相互作用研究、植入性材料研究提供了更具有优势的性能评价平台。 Tang等[37]根据聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺材料表面亲疏水性随温度变化发生可逆转变的特性,通过改变温度快速调控细胞在聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺表面的黏附和解离,可替代酶类物质或细胞刮刀实现细胞片的完整分离和回收,有效避免酶解和机械损伤。利用微流控芯片将聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺材料降温脱附与干细胞的体外培养相结合,可无损地收获干细胞,有望为组织工程提供优良的种子细胞。Hampe等[38]定量评价了纳米多孔金孔隙率对星形胶质细胞黏附强度的影响,结果显示孔隙率影响细胞黏附结构域的形成和细胞骨架的发育。随着孔隙率减小,纳米金表面的细胞黏附强度显著降低,产生抗细胞黏附的作用。利用微流控技术对材料结构与细胞黏附强度之间的关系进行定量表征,有助于解决植入性电极材料与组织器官发生异常黏附的问题。Li等[39]以三维水凝胶网络作为生物支架,以微流控芯片作为生物反应器,在芯片内培养小鼠成纤维细胞系L929细胞,发现支架的网状结构调节细胞的空间排列,细胞主要以其丝状伪足在支架上扩散并锚定在水凝胶表面支撑细胞生长。水凝胶的宽度影响细胞的黏附数量,较宽的水凝胶能够提供足够的表面积,更利于细胞的黏附、扩散和增殖。Stamp等[40]将钛材料作为细胞培养基质构建了微流体装置,筛选出人成骨肉瘤细胞系SaOs-2细胞在钛基质表面黏附、成骨分化的最适温度和pH值、粗糙度。这种细胞与材料表面直接接触培养的方式,能更直观地反映材料与细胞的相互作用,为评价细胞与材料的黏附特性和筛选出适于细胞发挥生理功能的胞外基质材料提供了新的手段。 在正常生理条件下,诸多细胞如血管内皮细胞、成骨细胞、平滑肌细胞等通常处于复杂的力学环境中,细胞的生长过程受动态机械力学刺激的调控。植入性人工血管、人工心脏瓣膜等在体内也往往受到血流动力学影响,因此在评估细胞与材料的黏附性能时,不能忽视机械力学刺激在细胞黏附中的作用。经过微阀、微泵等微加工技术的处理,在微流控芯片内可精确控制流体流速、压力、方向等参数及模拟血流剪切力、压力、牵张力对细胞进行静态的或者周期性的应力刺激,这些机械刺激能够诱导体外细胞更加接近生理状态的体内生物过程行为的产生,对细胞的生理行为和黏附特性有很大影响。 Gong等[41]在微流控芯片内用微图案和流体加载方向的不同组合方式模拟了体内基底膜表面形貌和血流引起的机械负荷(压力和剪切应力)对人脐静脉内皮细胞在基质表面黏附的影响,研究发现有序的材料结构引导细胞微丝、微管、局部黏着斑定向生长,流体压力相对于剪切力对细胞在材料上的脱附作用更显著,通过调控微图案排列方向和流体加载方向可增强或抑制细胞黏附对血流机械负荷的抗性。 Vanessa等[42]开发的微流体血管支架系统,将多孔聚碳酸酯弯曲形成管腔结构并培养内皮细胞以重建血管化组织,支架多孔的结构易于气体和营养物质或生长因子等交换,半圆形通道具有类似天然血管的曲率,其产生的剪切力更接近于人体血管中生理剪切应力水平,研究显示这种支架具有良好的生物相容性,利于内皮细胞黏附,培养的细胞形态更接近于体内生理状态,并且能产生更可靠的血管屏障功能。 Sharmistha等[43]利用微流控芯片研究了基质特性和剪切力对人间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响,发现纳米羟基磷灰石相对于多壁碳纳米管显示出更好的生物相容性,更适于细胞成骨分化。相比于静态培养,在1 Pa的生理剪切力水平刺激下更适宜人间充质干细胞分化为成骨样细胞。生物物理和生物力学的协同作用能刺激人间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞样细胞,可用于骨再生应用。 理想的生物医学材料应具有无毒、良好的生物相容性和生物稳定性及特定的机械力学性能和易加工等特征。虽然微流控芯片技术为筛选适合细胞生长的胞外材料提供了新的手段,但细胞与材料的黏附性能只是反映生物材料与细胞相互作用的一个方面,尚不能完整评价细胞与材料的相互作用。其次,多数实验仅研究了短期(<2周)内细胞在黏附界面的保留情况,缺乏调查细胞与材料的长期反应,实验结果并不能完全预估生物材料在体内的长期安全性和有效性。由于现有技术的限制,微流控芯片尚不能植入到人体内,无法反映生物材料植入体内后与周围环境产生的不良后果,如炎症、血栓形成等。因此,未来将微流控芯片与天然或合成的生物材料相结合,开发和构建具有生物活性、可植入的仿生微流控芯片,直接在人体内进行精准的细胞操纵和预分析,有望更真实、更贴切、更全面地评价细胞与材料相互作用。 2.2.3 微流控芯片技术在细胞黏附相关疾病研究中的应用 细胞黏附特性的改变与众多疾病的发生发展密切相关,如心血管疾病、肿瘤转移、炎症等,然而缺乏与人体真实生理和病理条件相同的体外组织或器官模型,限制了疾病研究和药物筛选。随着器官集成芯片和器官仿生技术逐步成熟,微流控芯片技术可在体外构建和模拟包含有多种活体细胞、功能组织界面、生物流体和机械力刺激等复杂因素的组织器官微环境[44],更精确地反映人体组织器官的主要结构和功能特征。现有的微流控芯片技术已成功在体外构建心[45]、肝[46]、肺[47]、肾[48]、肠等器官模型[49],通过管道连接、流体灌注或层层组装技术将芯片的多个功能单元相互连接,在单个芯片内实现了多种细胞共培养和多个器官系统的相互作用。此外,根据细胞或组织的病理特征,在微流控芯片内构建体外特异性疾病病理、药理微环境模型,弥合了传统细胞培养和动物实验的差距,对于药物毒性和药效的预测比常规体外模型更有潜力,微流控芯片为临床疾病研究和药理学筛选提供了一种新型有用的体外平台。 非黏附性和可变形性是正常红细胞的生物力学特征。而镰状红细胞病患者的红细胞变形性差且具有黏附性,与血管内皮的异常黏附会阻碍微循环甚至造成血管闭塞。Kucukal等[50]利用一种微流体系统模拟了微循环血流的生理剪切力梯度,发现红细胞的黏附性在微流体模型中分布不均匀,镰状红细胞病患者的红细胞呈剪切依赖性黏附,健康受试者的红细胞呈非黏附性,并揭示了镰状红细胞的黏附数量和强度与镰状红细胞病患者炎症和铁超负荷等重要临床表型之间存在显著关联。Kim等[51]在微流控芯片内通过控制氧张力、流体流速评估了在正常氧含量和缺氧状态下35例纯合子镰状细胞病患者的红细胞黏附情况,研究表明缺氧会显著增加红细胞对血管内皮的黏附,加重微循环闭塞。 选择素与细胞表面糖复合物的相互作用是介导肿瘤细胞在血管内皮上黏附关键步骤,并涉及肿瘤细胞的转移和侵袭。Shea等[52]利用微流控芯片技术研究了在生理剪切力作用下,E-选择素如何介导胰腺癌细胞滚动并黏附到血管内皮上的机制,通过构建微流控细胞相互作用模型,施加不同大小的剪切力,对胰腺癌细胞在血管壁上的黏附行为进行观察,并对黏附作用进行了定量检测,确定了E-选择素、CD44、透明质酸、足糖萼和黏蛋白MUC-16等因子在黏附中的作用。 中性粒细胞的黏附和浸润参与炎症的发生。Antoniellis Silveira等[53]使用微流体黏附测定了辛伐他汀对剪切应力条件下肿瘤坏死因子诱导人嗜中性粒细胞与纤连蛋白配体黏附能力的影响,并研究了辛伐他汀对RhoA和NFκB转录因子活性及细胞形态的影响。研究数据表明,辛伐他汀可能通过干扰肿瘤坏死因子诱导的细胞骨架重排及抑制Rho A活性、NFκB易位抑制β2整合素活性,来抑制中性粒细胞黏附而响应炎症刺激。 "
| [1]Khalili AA,Ahmad MR.A Review of Cell Adhesion Studies for Biomedical and Biological Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16(8):18149-18184.[2]Kunutsor SK,Bakker SJ,Dullaart RP.Soluble Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecules May be Protective of Future Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Findings from the PREVEND Prospective Cohort Study. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017; 24(8): 804-818.[3]Garrido-Urbani S, Vonlaufen A, Stalin J,et al. Junctional adhesion molecule C (JAM-C) dimerization aids cancer cell migration and metastasis.Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. 2018;1865(4):638-649.[4]Dimitriadis GK,Kaur J,Adya R,et al.Chemerin induces endothelial cell inflammation: activation of nuclear factor-kappa beta and monocyte-endothelial adhesion. Oncotarget.2018;9(24):16678-16690.[5]Guevara-Pantoja PE,Jimã©Nez-Valdã©S RJ, GarcãA-Cordero JL, et al. Pressure-actuated monolithic acrylic microfluidic valves and pumps.Lab Chip. 2018;18(4): 662-669.[6]Cui X,Liu Y,Hu D,et al.A fluorescent microbead-based microfluidic immunoassay chip for immune cell cytokine secretion quantification.Lab Chip.2018;18(3);522-531.[7]Chen C, Townsend AD, Hayter EA, et al. Insert-based microfluidics for 3D cell culture with analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem.2018;410(22):1-11.[8]Wang W,Li L,Ding M,et al.A Microfluidic Hydrogel Chip with Orthogonal Dual Gradients of Matrix Stiffness and Oxygen for Cytotoxicity Test.Biochip J.2018;12(2):1-10.[9]Honarmandi P,Lee H,Lang MJ,et al. A microfluidic system with optical laser tweezers to study mechanotransduction and focal adhesion recruitment.Lab Chip.2011;11(4):684-694.[10]Thompson TJ, Han B.Analysis of adhesion kinetics of cancer cells on inflamed endothelium using a microfluidic platform.Biomicrofluidics.2018;12(4):042215.[11]Tu L,Li X,Bian S,et al.Label-free and real-time monitoring of single cell attachment on template-stripped plasmonic nano-holes.Sci Rep.2017;7(1):1-11.[12]Hoffmann M,Tserpes K,Moutsompegka E,et al.Determination of adhesion strength of pre-bond contaminated composite-to- metal bonded joints by centrifuge tests.Compos B Eng.2018; 147: 114-121.[13]Kim H, Yamagishi A,Imaizumi M, et al. Quantitative measurements of intercellular adhesion between a macrophage and cancer cells using a cup-attached AFM chip. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017; 155:366-372.[14]Hogan B,Babataheri A,Hwang Y,et al.Characterizing Cell Adhesion by Using Micropipette Aspiration.Biophys J. 2015;109(2):209-219.[15]Jing P,Liu Y,Keeler EG,et al.Optical tweezers system for live stem cell organization at the single-cell level.Biomed Opt Express.2018;9(2):771-779.[16]Fuhrmann A,Engler AJ.The cytoskeleton regulates cell attachment strength.Biophys J. 2015;109(1):57-65.[17]Kim HW, Han S,Kim W,et al.Modulating wall shear stress gradient via equilateral triangular channel for in situ cellular adhesion assay.Biomicrofluidics.2016;10(5):11-25.[18]Li Y,Gao A,Yu L.Monitoring of TGF-β 1-Induced Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation Process by Measuring Cell Adhesion Force with a Microfluidic Device.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016; 178(1):114-125.[19]Lu L, Zheng GX, Yang YS, et al. Measurement of Giardia lamblia, adhesion force using an integrated microfluidic assay.Anal Bioanal Chem.2017;409(5):1-9.[20]Christ KV,Williamson KB,Masters KS,et al.Measurement of single-cell adhesion strength using a microfluidic assay. Biomed Microdevices.2010;12(3):443-455.[21]Mao S,Zhang W,Huang Q,et al.In Situ Scatheless Cell Detachment Reveals Correlation between Adhesion Strength and Viability at Single-Cell Resolution.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017;57(1):236-240.[22]Mao S,Zhang Q,Li H,et al.Adhesion analysis of single circulating tumor cells on a base layer of endothelial cells using open microfluidics.Chem Sci.2018;9:7694-7699.[23]Cheng Z,Wu X,Cheng J,et al. Microfluidic fluorescence- activated cell sorting (μFACS) chip with integrated piezoelectric actuators for low-cost mammalian cell enrichment.Microfluid Nanofluidics.2017;21(1):9-19.[24]Kwak B, Lee J, Lee D, et al. Selective isolation of magnetic nanoparticle-mediated heterogeneity subpopulation of circulating tumor cells using magnetic gradient based microfluidic system. Biosens Bioelectron.2017;88:153-158.[25]Pang L, Shen S, Ma C, et al. Deformability and size-based cancer cell separation using an integrated microfluidic device. Analyst.2015;140(21):7335-7346.[26]Ali H,Park CW.Numerical study on the complete blood cell sorting using particle tracing and dielectrophoresis in a microfluidic device.Korea-Aust Rheol J.2016;28(4):327-339.[27]Ung L,Mutafopulos K, Spink P, et al. Enhanced Surface Acoustic Wave Cell Sorting by 3D microfluidic chip design. Lab Chip.2017;17(23):4059-4069.[28]Singh A,Singh A, Suri S, et al. Adhesion strength-based, label-free isolation of human pluripotent stem cells.Nat Methods.2013;10(5):438-444.[29]桑维维,常亚男,李娟.微流控芯片对乳腺癌细胞mda-mb-231的捕获及再培养研究[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2015,35(6):46-53. [30]Zhang Y,Wu M,Han X,et al.High-throughput, label-free isolation of cancer stem cells based on cell adhesion capacity.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2015;54(37):10838-10842.[31]Chen W,Allen SG,Reka AK,et al.Nanoroughened adhesion-based capture of circulating tumor cells with heterogeneous expression and metastatic characteristics. BMC Cancer.2016;16:614-625.[32]Dasanna AK,Schwarz US.Adhesion-based sorting of blood cells: an adhesive dynamics simulation study.Soft Matter. 2018;14(44):9061-9070.[33]Ermis M,Antmen E,Hasirci V.Micro and Nanofabrication methods to control cell-substrate interactions and cell behavior: A review from the tissue engineering perspective. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(3):355-369.[34]Francesco R,Simone B, Federica F, et al. A micron-scale surface topography design reducing cell adhesion to implanted materials.Sci Rep.2018;8(1):10887-10899.[35]Zahran R,Rosales LJI,Rodríguez Valverde MA,et al.Effect of Hydrofluoric Acid Etching Time on Titanium Topography, Chemistry, Wettability, and Cell Adhesion.PLoS One.2016; 11(11):e0165296.[36]余劭婷,秦金桥,关国平,等.丝素纤维表面改性提高细胞黏附性能[J].生物医学工程学进展,2016, 37(3):144-149.[37]Tang Z,Akiyama Y,Itoga K,et al.Shear stress-dependent cell detachment from temperature-responsive cell culture surfaces in a microfluidic device.Biomaterials. 2012; 33(30): 7405-7411.[38]Hampe A,Li Z,Sethi S,et al.A Microfluidic Platform to Study Astrocyte Adhesion on Nanoporous Gold Thin Films. Nanomaterials.2018;8(7):452-463. [39]Li P,Yu H,Liu N,et al.Visible Light Induced Electropolymerization of Suspended Hydrogel Bioscaffolds in a Microfluidic Chip.Biomater Sci.2018;6(6):1371-1378.[40]Stamp ME,Jötten AM, Kudella PW,et al.Exploring the Limits of Cell Adhesion under Shear Stress within Physiological Conditions and beyond on a Chip.Diagnostics. 2016;6(4): 38-52.[41]Gong X, Yao J, He H, et al.Combination of flow and micropattern alignment affecting flow-resistant endothelial cell adhesion.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2017;74:11-20.[42]Vanessa K,Christoph G,Ivannikov D,et al. vasQchip: A Novel Microfluidic, Artificial Blood Vessel Scaffold for Vascularized 3D Tissues.Adv MaterTechnol.2018;3(4):1700246.[43]Sharmistha N, Kumar PA, Viswanathan K, et al.Controlled shear flow directs osteogenesis on UHMWPE based hybrid nano-biocomposites in custom designed PMMA microfluidic device.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018;1(2):414−435.[44]秦建华,张敏,于浩,等.人体器官芯片[J].中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(12):18-26.[45]Ahn S,Ardoña HAM,Lind JU,et al.Mussel-inspired 3D fiber scaffolds for heart-on-a-chip toxicity studies of engineered nanomaterials. Anal Bioanal Chem.2018;410(24):6141-6154. [46]Khazali AS, Clark AM, Wells A. A Pathway to Personalizing Therapy for Metastases Using Liver-on-a-Chip Platforms. Stem Cell Rev.2017;13(3):364-380.[47]Humayun M,Chow CW,Ewk Y.Microfluidic lung airway-on-a-chip with arrayable suspended gels for studying epithelial and smooth muscle cell interactions. Lab Chip. 2018;18(9):1298-1309.[48]Wilmer MJ,Ng CP,Lanz HL,et al.Kidney-on-a-Chip Technology for Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity Screening. Trends Biotechnol.2016;34(2):156-170.[49]Jalili-Firoozinezhad S,Prantil-Baun R,Jiang A,et al.Modeling radiation injury-induced cell death and countermeasure drug responses in a human Gut-on-a-Chip. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9(2):223-236.[50]Kucukal E, Little JA,Gurkan UA. Shear dependent red blood cell adhesion in microscale flow. Integr Biol. 2018;10(4): 194-206.[51]Kim M, Alapan Y, Adhikari A, et al. Hypoxia enhanced adhesion of red blood cells in microscale flow. Microcirculation. 2017;24(5):e12374.[52]Shea DJ,Li YW,Stebe KJ,et al. E-selectin-mediated rolling facilitates pancreatic cancer cell adhesion to hyaluronic acid. FASEB J.2017;31(11):5078-5086.[53]Antoniellis Silveira AA,Dominical VM,Morelli Vital D,et al. Attenuation of TNF-induced neutrophil adhesion by simvastatin is associated with the inhibition of Rho-GTPase activity, p50 activity and morphological changes.Int Immunopharmacol.2018;58:160-165. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||