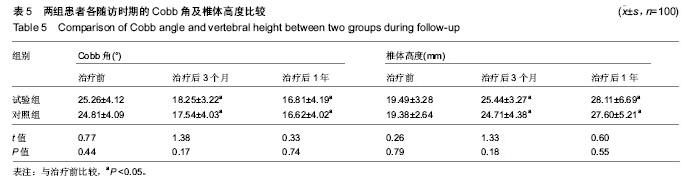
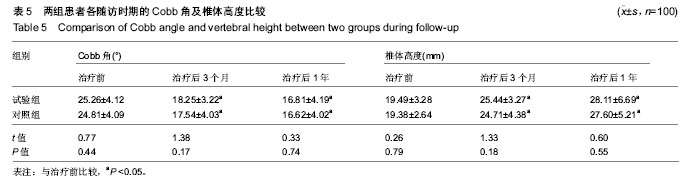
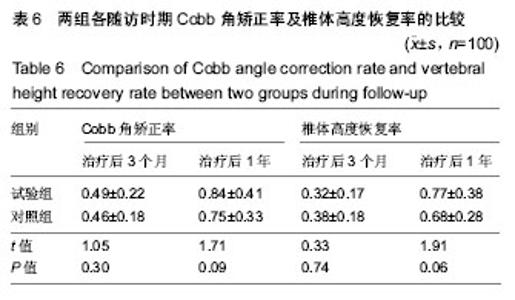
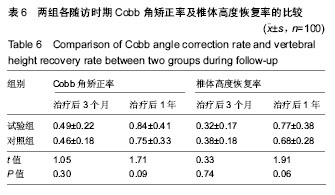
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3475-3480.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1273
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical efficacy of high viscosity bone cement vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
- 1Department of Osteopathy, 2Department of Endocrinology, Hengshui City People’s Hospital (Harrison International Peace Hospital), Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2019-03-09 -
About author:Fang Genqiang, Master, Attending physician, Department of Osteopathy, Hengshui City People’s Hospital (Harrison International Peace Hospital), Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Medical Science Research Program of Hebei Province in 2015, No. 20150427 (to FGQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Genqiang, Zhao Zhengli, Jin Xianhui, Zhang Qingsheng, Cui Shengjie, Wei Wei, Yan Guanghui, Wu Jiaqi, Zhao Lei. Clinical efficacy of high viscosity bone cement vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3475-3480.
share this article
| [1]中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2017,33(10):890. [2]杨惠林,刘昊,殷国勇,等.我国经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折现状与创新[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2017, 10(1):12-19. [3]印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.[4]Yang S,Chen C,Wang H,et al.A systematic review of unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty/percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc.2017;51(4):S1017995X17303309. [5]Yu W,Liang D,Yao Z,et al.Risk factors for recollapse of the augmented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures with intravertebral vacuum cleft.Medicine (Abingdon).2017;96(2):e5675. [6]Wang B,Zhao CP,Song LX,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):264. [7]Kan SL,Yuan ZF,Chen LX,et al.Which is best for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: balloon kyphoplasty, percutaneous vertebroplasty or non-surgical treatment? A study protocol for a Bayesian network meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2017;7(1):e012937. [8]Sun ZY,Li XF, Zhao H,et al. Percutaneous Balloon Kyphoplasty in Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Occult Vertebral Fracture: A Retrospective Study of 89 Cases.Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:1682-1690. [9]Foo LS,Yeo W,Fook S,et al.Results, experience and technical points learnt with use of the SKy Bone Expander kyphoplasty system for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective study of 40 patients with a minimum of 12 months of follow-up.Eur Spine J.2007;16(11):1944-1950. [10]刘仲宇,戎利民.骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的微创治疗进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,11(4):522-526.[11]高志祥,李淳,李磊,等.PVP、PKP、骨填充网袋治疗胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的疗效分析[J].实用骨科杂志, 2017, 23(8):680-683. [12]Macías-Hernández SI,Chávez-Arias DD,Miranda-Duarte A,et al.Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Conservative Treatment and Rehabilitation in Women with Vertebral Fractures due to Osteoporosis: A Prospective Comparative Study. Rev Invest Clin.2015;67(2):98-103.[13]Balkarli H,Kilic M,Balkarli A,et al.An evaluation of the functional and radiological results of percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment for acute symptomatic osteoporotic spinal fractures.Injury. 2016;47(4): 865-871. [14]Zuo XH,Zhu XP,Bao HG,et al. Network meta-analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty, nerve block, and conservative treatment for nonsurgery options of acute/subacute and chronic osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) in short-term and long-term effects. Medicine(Abingdon).2018;97(29):e11544-11544. [15]Yi X,Lu H,Fei T,et al.Recompression in new levels after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty compared with conservative treatment.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134(1):21-30. [16]铁镔,何仕诚,滕皋军,等.经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥渗漏的CT评价[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(5):299-302. [17]彭志刚,崔建岭,孙英彩,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术骨水泥渗漏的CT评价[J].临床放射学杂志,2012,31(2):269-272. [18]Anselmetti GC,Zoarski G,Manca A,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and bone cement leakage: clinical experience with a new high-viscosity bone cement and delivery system for vertebral augmentation in benign and malignant compression fractures.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008; 31(5):937. [19]Liu T,Li Z,Su Q,et al.Cement leakage in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with cortical defect using high-viscosity bone cement during unilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty surgery. Medicine(Abingdon).2017;96(25):e7216. [20]Li B,Wang Q,Yu Y,et al.Confidence high viscosity bone cement system and postural reduction in treating acute severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(3): 307-310. [21]蔺福辉,易小波,任志宏,等.高粘度骨水泥在椎体成形术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(1):66-67. [22]熊文华,杨云海,林卓锋.高粘度骨水泥在治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中的临床应用[J].河北医学,2015,21(5):774-777. [23]Xie L,Zhao ZG,Zhang SJ,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: An updated meta-analysis of prospective randomized controlled trials.Int J Surg.2017;47: 25-32. [24]Choi JH,Kang HD,Park JH,et al.The Efficacy of Fentanyl Transdermal Patch as the First-Line Medicine for the Conservative Treatment of Osteoporotic Compression Fracture. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017;13(2):130-136. [25]Han S,Jang IT.Analysis of Adjacent Fractures after Two-Level Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Is the Intervening Vertebral Body Prone to Re-fracture? Asian Spine J.2018;12(3): 524-532.[26]Duan L,Yang GC,Tang WZ,et al.[Observation of clinical effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures complicated with intravertebral clefts]. Zhongguo Gu Shang.2018;31(4):328. [27]Wang H,Zhang Z,Liu Y,et al.Percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of very severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with spinal canal compromise.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018; 13(1):13. [28]Huang YS,Hao DJ,Feng H,et al.Comparison of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty and Bone Cement-Augmented Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Management of Kümmell Disease. Med Sci Monit.2018;24:1072. [29]徐耀宁,郑秋坚,尹东,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗陈旧性骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的疗效研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014, 16(9): 770-775. [30]丁小方,王元利.新鲜与陈旧性骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折行经皮椎体后凸成形术的疗效观察[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2015, 23(8):29-32. [31]Bai M,Yin H,Zhao J,et al.Application of PMMA bone cement composited with bone-mineralized collagen in percutaneous kyphoplasty. Regen Biomater.2017;4(4):251-255. [32]程兴东,孙强,刘忠厚,等.充填材料对经皮椎体后凸成形术疗效影响的观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(2):157-161. [33]滕海军,周跃,初同伟,等.注射型磷酸钙骨水泥和PMMA在椎体成形术中的生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2004,12(1): 70-73. [34]Gamal B,Meghan C,Marc B.High-viscosity cement significantly enhances uniformity of cement filling in vertebroplasty: an experimental model and study on cement leakage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(22):2562-2568. [35]李春海,刘尚礼.应用Confidennce高黏度骨水泥及其椎体成形系统治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[C].中华医学会第八届骨科学术会议暨第一届国际COA学术大会论文摘要集,2006. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||