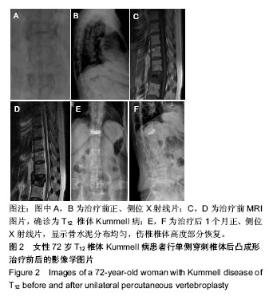
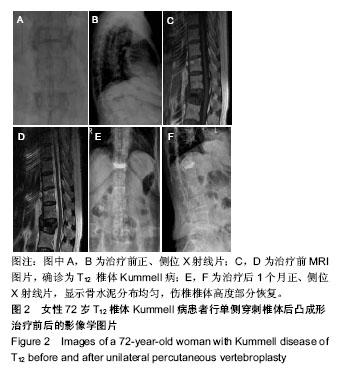
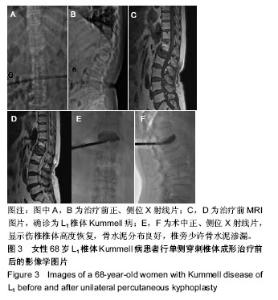
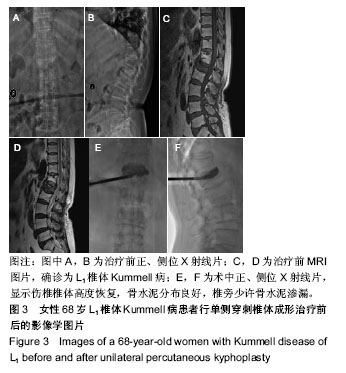
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3481-3487.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1274
Previous Articles Next Articles
Unipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty versus percutaneous kyphoplasty bone cement for treating Kummell disease
- Department of Spine Surgery, the Central Hospital of Yongzhou, Yongzhou 425000, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2019-03-04 -
About author:Jiang Jie, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spine Surgery, the Central Hospital of Yongzhou, Yongzhou 425000, Hunan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Jie, Zhang Yong. Unipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty versus percutaneous kyphoplasty bone cement for treating Kummell disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3481-3487.
share this article
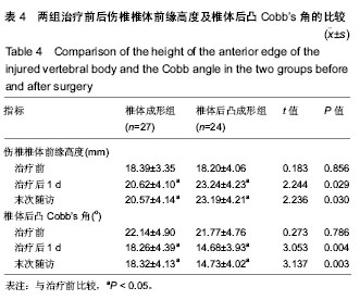
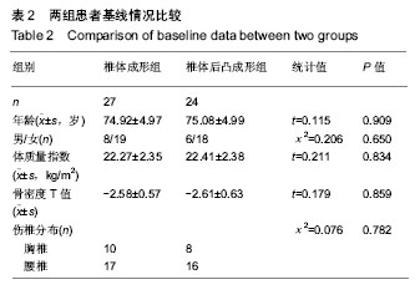
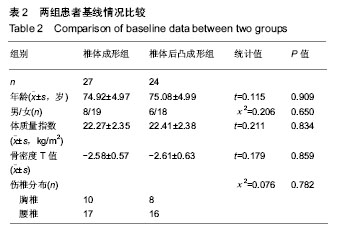
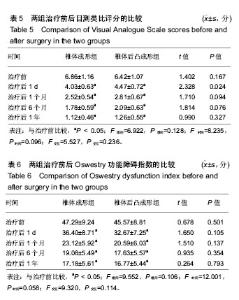
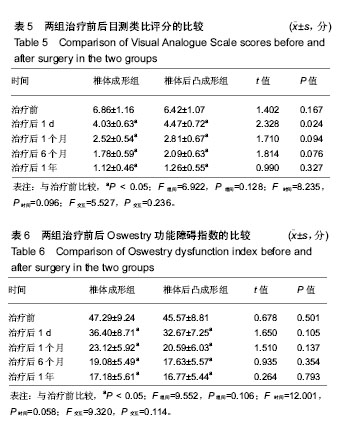
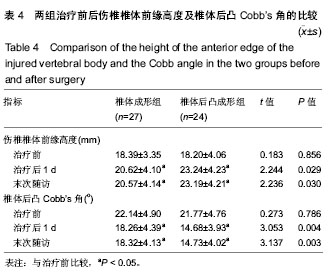
2.5 术后影像学评估 51例患者术后均获得完整随访,随访时间为11-26个月,平均14.6个月。 治疗前,两组伤椎椎体前缘高度相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);治疗后1 d及末次随访时,椎体后凸成形组椎伤椎体前缘高度均明显高于椎体成形组(P < 0.05)。治疗后1 d,椎体成形组和椎体后凸成形组伤椎椎体前缘高度均较治疗前明显增加(P < 0.05),分别增加了2.23 mm和 5.04 mm。末次随访时,两组伤椎椎体前缘高度较治疗后 1 d均无明显丢失(P > 0.05),见表4。 治疗前,两组椎体后凸Cobb’s角比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);治疗后1 d及末次随访时,椎体后凸成形组椎体后凸Cobb’s角均明显低于椎体成形组(P < 0.05)。治疗后1 d,椎体成形组和椎体后凸成形组椎体后凸Cobb’s角均较治疗前明显减少(P < 0.05),分别为减少了3.88°和7.09°。末次随访时,两组椎体后凸Cobb’s角较治疗后1 d无明显变化(P > 0.05),见表4。"
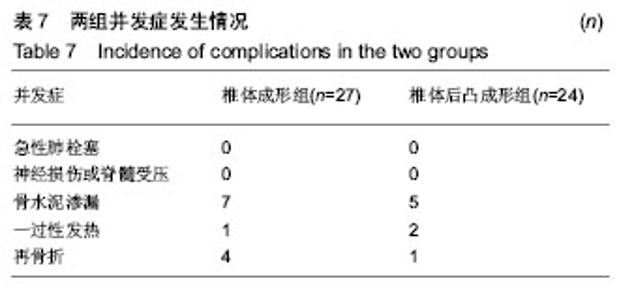
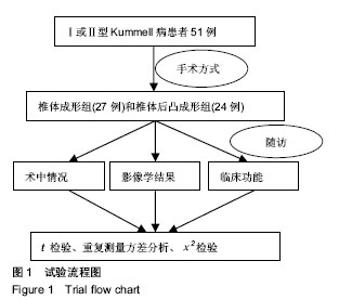
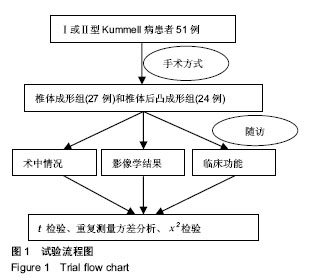
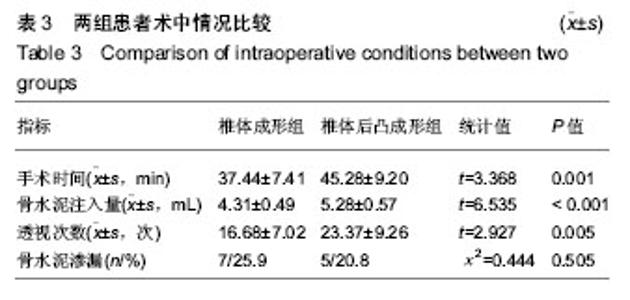
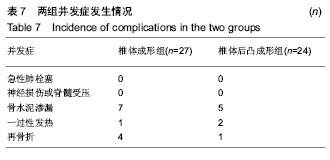
2.7 并发症比较 术中共12例(23.5%)患者出现骨水泥渗漏情况,多数为沿骨折线进行渗漏,其中椎体成形组骨水泥渗漏7例(25.9%),位置分布为椎间盘3例、椎体前2例、椎体旁1例,椎旁节段血管内1例;椎体后凸成形组(20.8%)骨水泥渗漏5例,位置分布为椎间盘4例、椎体旁1例,未出现血管性渗漏情况。其余病例穿刺针到达理想位点后,骨水泥均较好弥散在椎体内中部或偏前位置。 术后住院康复过程中,椎体成形组1例(3.7%)和椎体后凸成形组2例(8.3%)患者出现一过性发热情况,经对症支持治疗后发热好转。术后随访过程中,椎体成形组4例(14.8%)患者出现再骨折情况,椎体后凸成形组1例(4.2%)患者出现再骨折。两组术后出现骨水泥渗漏、一过性发热及再骨折等并发症比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表7。"
| [1]Lim J,Choi SW,Youm JY,et al.Posttraumatic Delayed Vertebral Collapse : Kummell's Disease. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2018;61(1):1-9.[2]He D,Yu W,Chen Z,et al.Pathogenesis of the intravertebral vacuum of Kummell's disease. Exp Ther Med.2016;12(2): 879-882.[3]谢胜荣,卢小刚,伍成东,等.Kummell病的发病机制研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2014,8(20):3675-3678. [4]张磊磊,李健.Kummell病的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(9):816-819.[5]Li KC,Li AF, Hsieh CH,et al.Another option to treat Kummell's disease with cord compression. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(9): 1479-1487.[6]Zhang C,Wang G,Liu X,et al.Failed percutaneous kyphoplasty in treatment of stage 3 Kummell disease: A case report and literature review.Medicine(Baltimore). 2017;96(47):e8895.[7]李业成,张巍,张成亮,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定结合椎体后凸成形术治疗Ⅲ型Kummell病[J].实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(6): 496-499.[8]Kim P,Kim SW.Balloon Kyphoplasty: An Effective Treatment for Kummell Disease? Korean J Spine.2016;13(3):102-106. [9]Chen GD,Lu Q,Wang GL,et al.Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Kummell Disease with Severe Spinal Canal Stenosis.Pain Physician.2015;18(6):E1021-E1028.[10]Matzaroglou C,Georgiou CS,Panagopoulos A,et al.Kummell's Disease: Clarifying the Mechanisms and Patients' Inclusion Criteria.Open Orthop J.2014;8:288-297. [11]李良辰,何登伟,黄文君,等.Kummell病椎体裂隙征发生机制的研究进展[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2015,8(4):363-366.[12]俞海明,李毅中,姚学东,等.经皮椎体成形或经皮椎体后凸成形治疗伴椎体后壁塌陷Kummell病:如何个体化选择?[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(26):3856-3862.[13]Lee K,Adsul N,Kim HS,et al.Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation with Bone Cement Augmentation Under Epidural Anesthesia for Treatment of Kummell Disease in Extremely Old Age.World Neurosurg.2018;119:506-510.[14]Fabbriciani G,Pirro M,Floridi P,et al. Osteoanabolic therapy: a non-surgical option of treatment for Kummell's disease? Rheumatol Int.2012;32(5):1371-1374.[15]Cho Y.Corpectomy and circumferential fusion for advanced thoracolumbar Kummell's disease. Musculoskelet Surg.2017; 101(3):269-274.[16]Zhang GQ,Gao YZ,Zheng J,et al.Posterior decompression and short segmental pedicle screw fixation combined with vertebroplasty for Kummell's disease with neurological deficits.Exp Ther Med.2013;5(2):517-522.[17]Chen L,Dong R,Gu Y,et al.Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kummell's Disease. Pain Physician.2015;18(4):373-381.[18]Park JW,Park JH,Jeon HJ,et al.Kummell's Disease Treated with Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Minimum 1 Year Follow-Up.Korean J Neurotrauma.2017;13(2):119-123.[19]梁德,江晓兵,姚珍松,等.过伸体位下椎体成形术治疗Kümmell病的近期疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(3):260-261.[20]Xia YH,Chen F,Zhang L,et al.Percutaneous kyphoplasty treatment evaluation for patients with Kummell disease based on a two-year follow-up.Exp Ther Med.2018;16(4):3617-3622.[21]Zhang J,Fan Y,He X,et al.Is percutaneous kyphoplasty the better choice for minimally invasive treatment of neurologically intact osteoporotic Kummell's disease? A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures.Int Orthop. 2018;42(6):1321-1326.[22]冯方,孙育良.经皮椎体成形术与经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗Kümmell病的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2018,7(3):225-229.[23]李志君,慈元,郑玉鹏,等.聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯囊袋加压椎体后凸成形治疗Kummell病[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(34): 5433-5438.[24]路文超,王宇鹏,湛川,等.椎体后凸成形治疗Kummell病过程中发生的骨水泥渗漏[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(2):172-177.[25]Graham J,Ahn C,Hai N,et al.Effect of bone density on vertebral strength and stiffness after percutaneous vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(18): E505-E511.[26]Liebschner MA,Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(14):1547-1554.[27]任海龙,王吉兴,陈建庭,等.单侧与双侧穿刺经皮椎体成形术治疗Kummell's病的临床对比[J].南方医科大学学报, 2014,34(9): 1370-1374.[28]Zhang GQ,Gao YZ,Chen SL,et al.Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty for the management of Kummell's disease: A retrospective study.Indian J Orthop.2015;49(6):577-582.[29]Wu AM,Chi YL,Ni WF.Vertebral compression fracture with intravertebral vacuum cleft sign: pathogenesis, image, and surgical intervention.Asian Spine J.2013;7(2):148-155. |
| [1] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [4] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [5] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [6] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Zhu Zhenqi, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of sciatic scoliosis caused by lumbar disc herniation: a 2-year follow-up of coronal and sagittal balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 409-413. |
| [7] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [10] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [11] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenhua, Liu Zichen, Yu Baoqing. Status and problems of polycaprolactone and its composite materials in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3571-3577. |
| [13] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Li Zhuangyan, Xia Peige, Qiao Renqiu. Effects of intravenous tranexamic acid combined with periarticular multipoint injection of tranexamic acid cocktail on blood loss and pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2833-2839. |
| [14] | Sun Yiqiang, Xing Jianqiang, Li Xuecheng, Wang Xin, Tian Shenglan, Zhao Zihao, Geng Xiaopeng. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in the elderly: a comparison of vertebral height recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2851-2855. |
| [15] | Li Qiang, Li Jun, Luan Jian, Jin Canghai, Hao Meng, Lin Yong. Bone cement distribution of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2466-2471. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||