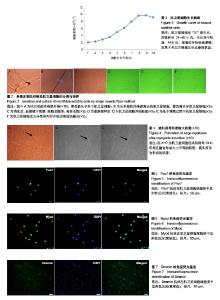
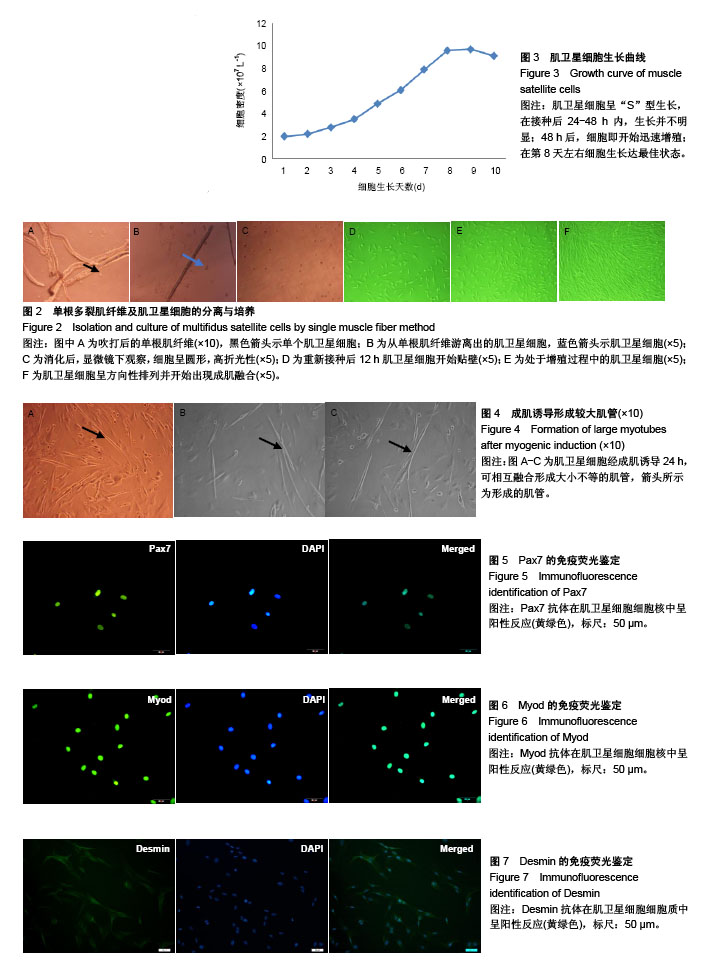
| [1] Shahidi B, Hubbard JC, Gibbons MC, et al. Lumbar multifidus muscle degenerates in individuals with chronic degenerative lumbar spine pathology. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(12): 2700-2706. [2] Hildebrandt M, Fankhauser G, Meichtry A, et al. Correlation between lumbar dysfunction and fat infiltration in lumbar multifidus muscles in patients with low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2017; 18(1):e92-92.[3] Ogon I, Takebayashi T, Takashima H, et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopic analysis of multifidus muscles lipid content and association with spino-pelvic malalignment in chronic low back pain. Br J Radiol. 2017;90(1073):20160753.[4] Wangprice S, Zafereo J, Brizzolara K, et al. Effects of different verbal instructions on change of lumbar multifidus muscle thickness in asymptomatic adults and in patients with low back pain. J Man Manip Ther. 2016; 25(1):22-29.[5] Hu ZJ, Zhang JF, Xu WB, et al. Effect of pure muscle retraction on multifidus injury and atrophy after posterior lumbar spine surgery with 24 weeks observation in a rabbit model. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(1):210-220. [6] Pourtaheri S, Issa K, Lord E, et al. Orthopedics. 2016;39(2): e209-214.[7] Mauro A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol.1961; 9(2):493-495.[8] Morgan J, Luisa B. Satellite cells and skeletal muscle regeneration. Compr Physiol.2015;5(3):1027.[9] Bekoff A, Betz W. Properties of isolated adult rat muscle fibres maintained in tissue culture. J Physiol. 1977; 271(2): 537-547.[10] Di FV, Robson L. Isolation of satellite cells from single muscle fibers from young, aged, or dystrophic muscles. Methods Mol Biol.2012;916(916):3.[11] Pasut A, Jones AE, Rudnicki MA. Isolation and culture of individual myofibers and their satellite cells from adult skeletal muscle. J Vis Exp. 2013;22(73):e50074-50074.[12] Moyle LA, Zammit PS. Isolation, Culture and Immunostaining of skeletal muscle fibres to study myogenic progression in satellite cells. Stem Cells Int. 2014;6:63-78.[13] Yang J, Liu H, Wang K, et al. Isolation, culture and biological characteristics of multipotent porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells. Cell Tissue Bank.2017;18(4):1-13.[14] Brun C E, Wang Y X, Rudnicki M A. Single EDL Myofiber Isolation for Analyses of Quiescent and Activated Muscle Stem Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1686:149-159.[15] 徐义明,白跃宏,俞红.腰痛患者肌卫星细胞生物学特性及其鉴定[J].中国康复医学杂志,2009, 24(8):734-736.[16] 刘志坚,方翊,王云龙,等.原代咬肌肌卫星细胞的提取及鉴定[J].口腔医学研究,2014,30(1):30-33.[17] 黄郁凯,李晓红,潘宇,等.成年大鼠骨骼肌干细胞的制备与新型培养方法[J].中国病理生理杂志,2013, 29(1):183-187.[18] 任宇,俞兰,赵兴胜.不同鼠龄大鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞生物学特性的探讨[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2017(5):566-574.[19] Ding S, Wang F, Liu Y, et al. Characterization and isolation of highly purified porcine satellite cells. Cell Death Discov. 2017; 3:17003.[20] 代阳,王轶敏,刘新峰,等.小鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞的分离培养和鉴定[J].天津农学院学报,2014(1):1-4.[21] 贺亚南,陈晓丽,任晓霞,等.免疫磁珠纯化小鼠精原干细胞的研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2014,34(7):38-43.[22] Fukada S, Ma Y, Ohtani T, et al. Isolation, characterization, and molecular regulation of muscle stem cells. Front Physiol. 2013;4:317.[23] Von MJ, Jones AE, Parks RJ, et al. Pax7 is critical for the normal function of satellite cells in adult skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110(41):16474-16479.[24] Kodama H, Kumai Y, Nishimoto K, et al. Modulation of satellite cells activity and MyoD in rat thyroarytenoid muscle after reinnervation. Laryngoscope.2015;125(7):e245-251.[25] Zhang F, Deng B, Wen J, et al. PPARγ and MyoD are differentially regulated by myostatin in adipose-derived stem cells and muscle satellite cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;458(2):375-380.[26] Jonuschies J, Antoniou M, Waddington S, et al. The human desmin promoter drives robust gene expression for skeletal muscle stem cell-mediated gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2014;14(4): 276-288.[27] 刘月光,史新娥,沈清武,等.利用单根肌纤维法分离和培养猪骨骼肌卫星细胞及其成肌诱导分化[J].农业生物技术学报, 2011, 19(05): 856-63.[28] Retamales A, Zuloaga R, Valenzuela CA, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 suppresses the Myostatin signaling pathway during myogenic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2015; 464(2):596-602.[29] 兴孝友,佟慧丽,李树峰.牛骨骼肌卫星细胞的分离培养及诱导分化方法的建立[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2012,6(11):27-29. |