Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (26): 4222-4228.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0936
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tissue-engineering scaffolds: characteristics and applications in tissue engineering
Ge Zhen1, 2, Zou Gang1, 2, Liu Yi1, 2, Zhang Jun1, 2, Li Yu-wan1, 2, Dong Li-ming1, 2
- 1Joint Orthopaedic Research Center of Zunyi Medical University & University of Rochester Medical Center (JCMR-ZMU & URMC), Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2018-06-25 -
Contact:Dong Li-ming, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Joint Orthopaedic Research Center of Zunyi Medical University & University of Rochester Medical Center (JCMR-ZMU & URMC), Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Ge Zhen, Master candidate, Joint Orthopaedic Research Center of Zunyi Medical University & University of Rochester Medical Center (JCMR-ZMU & URMC), Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; -
Supported by:the Science & Technology Program of Guizhou Province, No. LH[2017]7105
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ge Zhen, Zou Gang, Liu Yi, Zhang Jun, Li Yu-wan, Dong Li-ming. Tissue-engineering scaffolds: characteristics and applications in tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(26): 4222-4228.
share this article
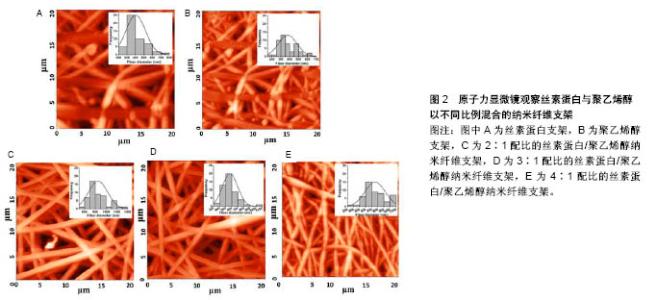
2.1 天然材料 最初记载的现代组织工程材料文献中,大部分使用的是自然来源的生物材料[11]。这些天然材料来源广泛,并且它们的可降解生物聚合物,如蛋白质(例如胶原、丝、纤维蛋白原、弹性蛋白)和多糖(例如几丁质、纤维素、糖胺聚糖)等,与细胞外基质具有显著的相似性,具有良好的生物学特征,并且无毒、具有低免疫排斥反应。此外,具有良好骨传导性的磷酸钙(CaP)等生物吸收性填充剂(如β-磷酸三钙、羟基磷灰石)又具有良好的生物相容性、可吸收性,这些材料常被用于组织工程多种类型的支架[12]。 在任何给定的组织工程应用中,支架材料均要满足应用的条件,必须具有良好的机械性能、大小适宜的孔隙结构、合适的降解时间,以及能够产生理想的组织修复效果。天然材料大多数无毒,生物相容性、细胞亲和性及亲水性都较好,并且其分解产物可被完全吸收,但其缺点是机械强度较差,单一使用很难满足组织工程的需要,并且天然支架材料的降解时间不确定性和质量重复性差等特点限制了其广泛的应用。尽管天然材料的应用范围受其固有结构的限制,但在天然材料基础上进行相应的加工修饰,或者利用某些天然材料独特的优势已取得了许多不错的进展。下面主要介绍胶原蛋白、蚕丝蛋白、壳聚糖及其衍生物。 2.1.1 胶原蛋白 胶原蛋白家族占人体蛋白总量的25.33%,是人体中最丰富的蛋白质[13-15],由大量细胞外基质蛋白构成,其中哺乳动物体内含量较多。目前胶原蛋白在韧带重建中已得到了广泛应用,因为在韧带重建手术中,不论移植物选择是自体移植还是同种异体移植,胶原蛋白均是移植物的主要成分。自体移植面临着供体来源有限、供区容易发生感染等缺点,同种异体移植也面临着免疫排斥风险,基于以上各种原因,寻求一种替代性的修复材料成为一种趋势,包括使用人工韧带,而这种合成韧带主要由胶原蛋白构成[16]。胶原蛋白具有良好的特性,所以应用较为广泛[17]。目前已有28种不同类型的胶原蛋白分子[18],其中Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ和Ⅳ型研究最多[19]。由于小牛ⅠⅡ型胶原蛋白来源丰富,且临床应用较为成功,已被广泛用于制作组织工程支架[20-21]。Nehrer等[22]从猪软骨提取Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白,然后制成多孔支架,分别在两种类型支架上接种犬软骨细胞并培养3 d、1周和2周,组织学结果显示,在各时间点具有球形形态细胞的百分比显著高于软骨细胞形态,说明胶原蛋白可为细胞的黏附和生长提供良好环境。同时将其植入体内后不仅不会引起炎症或毒性反应,而且该支架还可被机体吸收,其降解速度与组织再生速度相一致,说明胶原蛋白支架应用于组织修复中具有一定的可行性。胶原蛋白也存在着一些不足之处,由于胶原材料大多来源于动物组织,移植入体内后会引起免疫反应,而且可能存在免疫排斥、外源性病毒感染的风险[23]。因此研究者在胶原蛋白的基础上,通过基因工程技术研发出了重组胶原蛋白。重组胶原蛋白是利用基因工程技术开发重组系统来生产的人类序列胶原,通过使用各种宿主细胞比如转基因蚕、烟草、小鼠和酵母等生产重组胶原蛋白。相对于动物胶原蛋白而言,重组胶原蛋白具有安全性高、亲水性好、免疫排斥较低等优点,因此存在较为广泛的应用[24]。 2.1.2 蚕丝蛋白 蚕丝蛋白是从蚕丝中提取的天然高分子纤维蛋白,主要由丝素蛋白和丝胶蛋白组成,其来源决定了蚕丝蛋白的结构和性质。由于家蚕易于培育和生产,故家蚕是生物材料应用中最常见的蚕丝蛋白来 源[25]。但蚕丝并不是唯一的天然蚕丝来源,除了桑蚕以外,还有其他几种昆虫和动物产生丝绸,包括蜜蜂、黄蜂、蚂蚁[26]、贻贝[27]、蜘蛛等。丝素主要由3种氨基酸(如甘氨酸、丙氨酸和丝氨酸)组成;丝胶是一种易溶于水的物质。在韧带重建中,因为蚕丝蛋白具有超微物理构造和特殊的多孔结构,同时具有很好的细胞和组织相容性,种子细胞在具有这些特性的支架结构中增殖良好[28],因此在韧带重建中应用得比较多。有研究发现将成骨细胞接种于丝素蛋白支架内之后,丝素蛋白膜在体外可诱导骨组织生长[29]。蚕丝蛋白为基质支架设计提供了多种多样的组织工程需求[30]。组织工程学的出现,增加了对多种生物材料组合的需求,以在体内植入之前支持体外组织的发展[31]。由于丝素在提纯过程中常会发生丝胶残余,因而存在生物相容性问题。随着技术的改进,目前丝胶残存发生概率降低。丝胶蛋白的存在是丝素生物材料使用过程中的关键问题,因为丝胶蛋白与超敏反应和生物相容性差有关;丝胶被去除后,免疫应答反应也有显著降低。丝素在体内几个月的时间内可降解,主要通过异物反应介导的蛋白水解活性增加来达到降解。然而,降解过程取决于许多因素,包括植入部位、该部位的机械性能、丝的加工条件及丝支架的物理特性(即孔隙率、孔径大小、表面积)[32]。Pillai等[33]用静电纺丝技术制备了不同配比(2∶1,3∶1和4∶1)的丝素蛋白和聚乙烯醇混合电纺纳米纤维支架,使用原子力显微镜表征支架的形态学(图2),将混合纳米纤维垫用体积分数25%戊二醛蒸气交联,交联的纳米纤维在模拟体液中培养35 d后,显示缓慢降解20%的质量;在纳米纤维中,3∶1的丝素蛋白与聚乙烯醇共混物显示出均匀的形态和纤维直径,将人原代半月板细胞传代培养并接种到混合纳米纤维支架上,发现3∶1的丝素蛋白与聚乙烯醇纳米纤维支架可更好地支持细胞附着和生长,显著增加DNA和胶原含量,结果表明丝素蛋白与聚乙烯醇比例为3∶1的纳米纤维支架适合于半月板细胞增殖。"
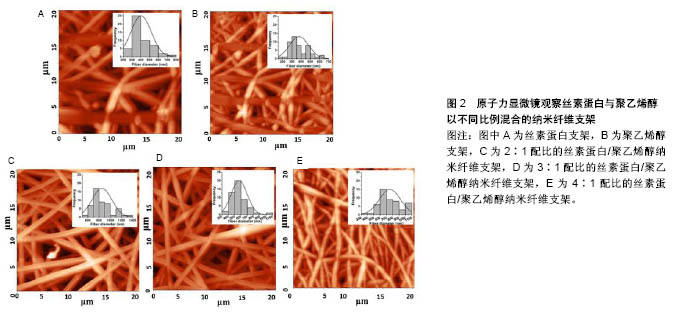
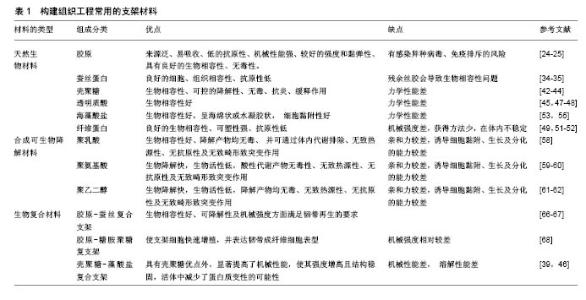
2.1.3 壳聚糖及其衍生物 壳聚糖是由甲壳素通过脱乙酰化后形成的天然高分子聚合物,在自然界中广泛存在,其含量仅次于纤维素。壳聚糖的具体形成过程是:由N-乙酰葡萄胺和葡萄胺通过脱乙酰化的β-1,4糖苷键而形成,是一种具有线性结构的多糖,与软骨基质糖氨多糖结构相似。由于壳聚糖是一种带正电荷的聚合物,因此能够很好地吸附细胞和其他物质,与之结合。例如:带负电荷的生物分子或DNA可与壳聚糖的阳离子链复合,提高壳聚糖支架的生物活性,或保护DNA等分子规避热失活和核酸酶降解的机会[34];阴离子葡萄糖胺聚糖如肝素与壳聚糖形成离子复合物,赋予壳聚糖材料特定的生物学功能[34],其在许多组织的生长中发挥积极作用。壳聚糖的降解产物是氨基葡萄糖单体,对人体无毒无害,因此其具有良好的生物相容性。此外,壳聚糖还具有甲壳素的优良特征:良好的吸水性、亲水性,无免疫排斥反应等。但壳聚糖分子内和分子间含有大量的氢键,因此其结晶度高,此弱点限制了其广泛的应用和发展。通过一些改性的方法可适度改善壳聚糖的性能[35-36],国内外常用的改性方法有:聚合物接枝壳聚糖、小分子接枝壳聚糖、交联壳聚糖等。 基于壳聚糖良好的生物相容性、低免疫原性、可降解性等优良特性,作为能够替代细胞外基质的支架材料,具有其自身的优越性,在医学领域的应用越来越多,也取得了很多不错的成绩。另外壳聚糖本身可促进血管内皮细胞生长,成骨分化及其角质细胞的增生,此外壳聚糖的阳离子结构可能是壳聚糖具有一定抗菌性能的原因之一,由于阳离子氨基与阴离子微生物壁的相互作用,可抑制细菌的生物合成或破坏穿过细胞壁的蛋白物质转运,干扰细菌微生物的正常代谢[37-38]。在骨、软骨及韧带等组织工程中,壳聚糖已被用作生长因子载体和支架材料[39-41]。Boukari等[42]发现天然衍生壳聚糖制成的多孔支架具有生物可降解性,其机械和生物学性能良好,间充质干细胞容易附着到含有壳聚糖的支架上,与间充质干细胞搭载后可显著促进细胞的成骨分化,并且在体内研究显示该支架具有良好的组织相容性。壳聚糖支架是从生理pH值溶液中制备的,这样能提供有利的环境,降低掺入具有变性风险的蛋白质,具有适合快速进入临床试验的机械性能和生物学特性。 2.1.4 海藻酸盐 海藻酸盐是在海藻中发现的一种生物聚合物,形态较易改变,制成的产品有水凝胶、微球、微胶囊、海绵、泡沫和纤维等[43]。可通过化学和物理方法修饰海藻酸盐,以调节其生物降解能力、机械强度、凝胶性质和细胞亲和力等功能。关于海藻酸盐作为骨组织工程材料的应用已进行了大量研究[44-45]。Almeida等[46]开发了一种多孔仿生形状记忆藻酸盐支架,使用碳二亚胺化学共价交联藻酸盐,引入形状记忆特性,使用定向冷冻技术改变支架的结构。这种排列的孔隙结构改善了支架的机械性能,并且促进了更高水平的硫酸化糖胺聚糖和胶原沉积,同时胶原蛋白的复合促进了干细胞与支架的黏附,促进了整个构建体中软骨组织更均匀的沉积。将Ⅱ型胶原蛋白并入支架,促进更大的细胞增殖,更高的硫酸化糖胺聚糖和胶原积累,并且与用Ⅰ型胶原功能化的支架相比组织强度更高。这项研究结果表明,支架结构和组成可在形状记忆海藻酸盐支架中制定,以指导干细胞分化并支持软骨组织的发育。此外还有研究发现藻酸盐对细胞没有毒性,具有良好的生物相容性,因此适用于多种生物医学应用。 2.2 合成可生物降解材料 合成生物可降解的聚合物材料较天然材料有更多的优势,其材料质地均一,与机体发生免疫排斥反应性较低,是一种可靠的组织工程支架材料来源[47]。另外由于高分子材料具有基本的结构单元,具有简单而清楚的结构和特性。目前合成的可生物降解支架材料主要包括聚乙二醇、聚酯、聚 β羟基丁酯、聚氨基酸、聚γ羟基丁酯等,研究最多的还是脂肪族聚酯,如聚乳酸[48]、聚乙醇酸及其共聚物[49-52]。生物可降解材料具有良好的可降解性、组织相容性、生物相容性,无细胞毒性,可塑性好,无致热源性,无致畸形致突变,这类材料都能体内代谢并最终被完全吸收。部分高分子材料还可作为植入型药物释放体系的载体材料、神经导管、临时血管移植物及人工皮肤支架。但是这些合成的高分子支架材料疏水性强、细胞黏附能力差,不具备组织工程化韧带要求的生物力学特性[52]。此外,与天然生物材料相比,其亲和力较差。因此,合成的生物可降解材料仍需要通过表面修饰法、化学改性法及杂化改性法等对其表面进行改造,以增加其对于细胞的黏附能力和促进细胞生长分化。有研究将合成生物降解材料与天然生物材料结合做成混合支架,不仅改善了天然生物材料的力学性能,而且提高了合成生物降解材料的促进细胞黏附和增殖能力[52]。Bach等[53]采用温冷冻干燥方法将聚乙烯醇与胶原制成复合支架,将前交叉韧带细胞种植到该复合支架上培养,24 h后通过扫描电镜观察到细胞贴附支架生长,表明这种复合支架具有良好的生物相容性和组织相容性,能够成为体外培养前交叉韧带细胞的理想支架。但其力学性能还远远达不到人韧带的力学标准,有待进一步改善。 2.3 生物复合材料 目前的研究表明任何一种单一材料的生化特性无法满足组织工程韧带的要求,因此,将不同材料通过一定的手段复合在一起,使其优缺点相互互补,进一步提高各自的优良特性,已成为目前支架研究的一种趋势。目前新兴的复合材料结合了单一材料的特点,并且将各自的特点整合,使其功能更加全面。复合支架材料的发展具有吸引力,因为两种或多种材料的优点可结合在一起,更好地满足宿主组织的机械和生理需求,因而复合支架材料成为当前组织工程研究的重点。 生物复合材料是由2种或2种以上不同物理化学性质的材料复合而成的新材料,一般由基体材料和增强材料组成[54]。生物复合材料不仅能保持原有组分的部分优点,而且可产生原组分所不具备的更优特性。可降解高分子材料聚乳酸、聚羟基乙酸等的降解产物会使局部pH降低,引发炎症,同时力学性质也较差。因此,有学者将聚乳酸与羟基磷灰石、胶原等混合制成复合材料,能够在一定程度上改善聚乳酸的一些不足之处,有望获得性能更好的组织工程的支架材料[55]。胶原-蚕丝复合支架的机械承受强度与正常前交叉韧带数值接近[54]。疏水性的聚乙内酯和亲水性的聚羟基乙酸共聚物组成的混合支架,可调节支架的亲水性、机械强度和降解速率。将超细聚乳酸纤维和脱胶后编织好的微纤维蚕丝支架制成支架,可促进祖细胞的黏附、增殖、分化等功能,提高韧带中胶原及基质蛋白表达量,增强支架材料的机械强度[55]。胶原-糖胺聚糖复支架使支架细胞快速增殖,并表达韧带成纤维细胞表型[56-57]。相比于单纯壳聚糖支架而言,壳聚糖-藻酸盐复合支架不仅力学性能明显提高了,而且力学强度显著增高,并且这种结构也相对稳定,活体中减少了蛋白质变性的可能性[58-59]。文章重点介绍石墨烯与不同物质复合制备的复合支架材料,在组织工程中的应用和最新研究进展。 石墨烯作为目前世界上最薄的新型纳米材料[60],在组织工程中已得到了广泛应用,并且也取得了突破性的进展。石墨烯是以sp2杂化轨道而形成的单层二维平面晶体,其厚度只有0.335 nm[60-62],最早是由Konstantin和Andre分离并发现的,因其良好的稳定性、导电性、导热性、机械强度,所以近几年在组织工程学、生物医学等领域应用广泛[63-66]。单纯的石墨烯质地较薄,很难塑形,并且其生物相容性和水溶性并不是特别理想,所以很多研究者通过对石墨烯进行改性和修饰来提高它的性能。常用的方法通常是将石墨烯与其他物质复合,进一步完善它的特性。Wang等[67]的研究发现,MC3T3-E1细胞在涂有石墨烯的聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯表面增殖速度明显提高,并且该复合材料有助于加速细胞的成骨分化,对腱-骨愈合有一定的促进作用。通过进一步的实验发现:用石墨烯和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯复合制成的人工韧带性能较单纯的石墨烯或者聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯人工韧带更好,表现出较高的骨平均矿物沉积速率和更好的生物力学性能。尽管很多研究者通过复合技术制备了纳米羟基磷灰石-聚酰胺支架,但其性能、对细胞的黏附能力、促进细胞增殖能力还需要进一步提高。Zhang等[68]将石墨烯材料进一步与纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺支架复合,进而使原有的支架性能得到进一步改善。并且将鼠骨髓间充质干细胞种植在改支架上,发现骨髓间充质干细胞在经过石墨烯修饰后复合支架上的黏附能力和增殖速度均较单纯纳米羟基磷灰石-聚酰胺支架好,并且与成骨相关的基因和蛋白表达水平也明显提高,提示石墨烯有促进间充质干细胞成骨分化的能力。组织工程化韧带支架材料见表1。 "
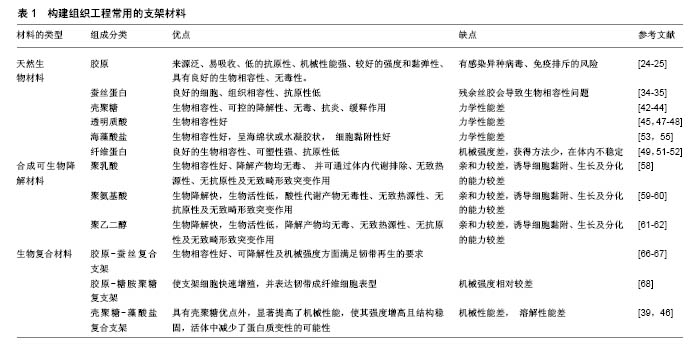
| [1] Langer R.Tissue engineering.Science. 2000;260(5110):920-926.[2] World Health Organization.Men, ageing and health: Achieving health across the life span.2001.[3] Santos ML,Rodrigues MT,Domingues RMA,et al.Biomaterials as Tendon and Ligament Substitutes: Current Developments// Regenerative Strategies for the Treatment of Knee Joint Disabilities. Springer International Publishing, 2017:349-371.[4] Makris EA,Gomoll AH,Malizos KN,et al.Repair and tissue engineering techniques for articular cartilage.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):21-34.[5] Tatara AM,Mikos AG.Tissue engineering in orthopaedics. JBJS. 2016;98(13):1132-1139.[6] Graber LW,Vanarsdall RL,Vig KW,et al.Orthodontics-E-Book: Current Principles and Techniques. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2016.[7] Schreiber SL.Chemical Biology Towards Precision Medicine. Israel J Chem.2017; 57(3-4):174-178.[8] Nuelle CW,Cook JL,Gallizzi MA,et al.Posterior single-incision semitendinosus harvest for a quadrupled anterior cruciate ligament graft construct: determination of graft length and diameter based on patient sex, height, weight, and body mass index.Arthroscopy.2015;31(4):684-690.[9] Sena M,Chen J,Dellamaggioria R,et al. Dynamic evaluation of pivot-shift kinematics in physeal-sparing pediatric anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction techniques.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(4): 826-834.[10] Cain EL Jr,Fleisig GS,Ponce BA,et al.Variables Associated with Chondral and Meniscal Injuries in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery.J Knee Surg.2016;30(7):659-667.[11] Vacanti CA.History of tissue engineering and a glimpse into its future.Tissue Eng Part A.2006; 12(5):1137-1142. [12] Pina S,Oliveira JM,Reis RL.Natural-based nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: a review.Adv Mater.2015;27(7):1143-1169.[13] Yuan T,Zhang L,Li K,et al. Collagen hydrogel as an immunomodulatory scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2014;102(2):337-344.[14] Shrivats AR,McDermott MC,Hollinger JO.Bone tissue engineering: state of the union.Drug Discov Today. 2014;19(6):781-786. [15] Chen FM,Liu X.Advancing biomaterials of human origin for tissue engineering. Prog Polym Sci.2016;53:86-168.[16] Hirukawa M,Katayama S,Sato T,et al.Development of Tissue-Engineered Ligaments: Elastin Promotes Regeneration of the Rabbit Medial Collateral Ligament. Artif Organs.2017 Dec 21. doi: 10.1111/aor.13066. [Epub ahead of print][17] Yu L,Huang J,Wang J,et al.Antler collagen/chitosan scaffolds improve critical calvarial defect healing in rats.J Biomater Tissue Eng.2015;5(10):774-779.[18] Zhang D,Wu X,Chen J,et al.The development of collagen based composite scaffolds for bone regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2018; 3(1):129-138.[19] Aravamudhan A,Ramos DM,Nip J,et al.Micro-Nanostructures of Cellulose-Collagen for Critical Sized Bone Defect Healing. Macromol Biosci. 2018;18(2).doi:10.1002/mabi.201700263. Epub 2017 Nov 27.[20] Kämmerer PW,Scholz M,Baudisch M,et al.Guided Bone Regeneration Using Collagen Scaffolds, Growth Factors, and Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells for Treatment of Peri-Implant Bone Defects In Vivo.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3548435..[21] Mti M,Kitamura N,Nonoyama T,et al.Anisotropic tough double network hydrogel from fish collagen and its spontaneous in vivo bonding to bone.Biomaterials.2017;132:85.[22] Nehrer S,Breinan HA,Ramappa A,et al.Canine chondrocytes seeded in type I and type II collagen implants investigated in vitro.J Biomed Mater Res A.1997;38(2):95-104. [23] Clark RAF,Ghosh K,Tonnesen MG.Tissue engineering for cutaneous wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127(5):1018-1029.[24] Attia E,Bohnert K,Brown H,et al. Characterization of total and active matrix metalloproteinases-1, -3, and -13 synthesized and secreted by anterior cruciate ligament fibroblasts in three- dimensional collagen gels.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014; 20(1-2): 171.[25] Shen W,Chen X,Hu Y,et al.Long-term effects of knitted silk–collagen sponge scaffold on anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and osteoarthritis prevention.Biomaterials. 2014; 35(28):8154-8163.[26] Khamhaengpol A,Siri S.Composite Electrospun Scaffold Derived from Recombinant Fibroin of Weaver Ant(Oecophylla smaragdina) as Cell-Substratum.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2017;183(1):1-16.[27] Burke KA,Roberts DC,Kaplan DL.Silk Fibroin Aqueous-Based Adhesives Inspired by Mussel Adhesive Proteins. Biomacromolecules.2015;17(1):237.[28] Ma D,Wang Y,Dai W.Silk fibroin-based biomaterials for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2018; 89:456-469.[29] Sahu N,Baligar P,Midha S,et al.Nonmulberry Silk Fibroin Scaffold Shows Superior Osteoconductivity Than Mulberry Silk Fibroin in Calvarial Bone Regeneration.Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(11): 1709-1721.[30] Bhawal UK,Uchida R,Kuboyama N,et al.Effect of the surface morphology of silk fibroin scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomed Mater Eng.2016;27(4):413.[31] Bhattacharjee P,Kundu B,Naskar D,et al.Silk scaffolds in bone tissue engineering: An overview. Acta Biomaterialia. 2017;63:1-17.[32] Aigner TB,Desimone E,Scheibel T.Biomedical Applications of Recombinant Silk-Based Materials. AdvMater.2018:1704636.[33] Pillai MM,Gopinathan J,Indumathi B,et al.Silk-PVA Hybrid Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Enhanced Primary Human Meniscal Cell Proliferation.J Membr Biol.2016;249(6):1-10.[34] Jiang T,Kumbar SG,Nair LS,et al.Biologically active chitosan systems for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Curr Top Med Chem.2008;8(4):354-364.[35] d'Ayala GG,Malinconico M,Laurienzo P. Marine derived polysaccharides for biomedical applications: chemical modification approaches.Molecules.2008;13(9):2069-2106.[36] Venkatesan J,Bhatnagar I,Kim SK.Chitosan-alginate biocomposite containing fucoidan for bone tissue engineering. Marine Drugs.2014;12(1):300-316.[37] Kim IY,Seo SJ,Moon HS,et al.Chitosan and its derivatives for applications.Biotechnol Adv.2008;26:1-21.[38] Liu Y,Wang S,Zhang R.Composite poly(lactic acid)/chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol.2017;103:1130-1137.[39] Silva JM,Rodrigues LC,Silva SS,et al.Engineered tubular structures based on chitosan for tissue engineering applications.J Biomater Appl.2018;32(7):841-852.[40] Chameettachal S,Murab S,Vaid R,et al.Effect of visco-elastic silk-chitosan microcomposite scaffolds on matrix deposition and biomechanical functionality for cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2017;11(4):1212-29.[41] Gholizadeh S,Moztarzadeh F,Haghighipour N,et al.Preparation and characterization of novel functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes/chitosan/ beta-Glycerophosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol.2017;97:365-372.[42] Boukari Y,Qutachi O,Scurr DJ,et al.A dual-application poly (dl-lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA)-chitosan composite scaffold for potential use in bone tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2017;28(16):1966-1983.[43] Venkatesan J,Bhatnagar I,Manivasagan P,et al.Alginate composites for bone tissue engineering: a review.Int J Biol Macromol.2015;72:269-281.[44] Bidarra SJ,Barrias CC,Granja PL.Injectable alginate hydrogels for cell delivery in tissue engineering.Acta Biomaterialia. 2014;10(4): 1646-1662.[45] Liu Y,Ai K,Lu L.Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields.Chem Rev. 2014;114(9):5057-5115. [46] Almeida H,Sathy BN,Dudurych I,et al.Anisotropic Shape-Memory Alginate Scaffolds Functionalized with either Type I or Type II Collagen for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;23(1-2):55-68.[47] Santoro M,Shah SR,Walker JL,et al.Poly (lactic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;107: 206-212.[48] Nakao H,Jacquet RD,Shasti M,et al.Long-Term Compari60son between Human Normal Conchal and Microtia Chondrocytes Regenerated by Tissue Engineering on Nanofiber Polyglycolic Acid Scaffolds.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(4):911e-921e.[49] Murdock MH,Badylak SF.Biomaterials-based in situ tissue engineering.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2017;1:4-7.[50] Shih YC.Effects Of Degradation On Mechanical Properties Of Tissue-Engineering Poly (glycolic Acid) Scaffolds (2015).Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library. 2011. http://elischolar.library. yale.edu/ymtdl/2011 2015.[51] Gentile P,Chiono V,Carmagnola I,et al.An overview of poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA)-based biomaterials for bone tissue engineering.Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(3):3640-3659.[52] Elsawy MA,Kim KH,Park JW,et al.Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) and its composites.Renewa Sust Energy Rev.2017;79:1346-1352.[53] Bach JS,Detrez F,Cherkaoui M,et al.Hydrogel fibers for ACL prosthesis: design and mechanical evaluation of PVA and PVA/UHMWPE fiber constructs.J Biomech. 2013;46(8): 1463-1470.[54] Naahidi S,Jafari M,Logan M,et al.Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv.2017;35(5):530-544. [55] Wang J,Yang Q,Cheng N,et al.Collagen/silk fibroin composite scaffold incorporated with PLGA microsphere for cartilage repair. Mater Sci Eng C.2016;61:705-711.[56] Fernandez-Yague MA,Abbah SA,McNamara L,et al.Biomimetic approaches in bone tissue engineering: Integrating biological and physicomechanical strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2015;84:1-29.[57] Hoogenkamp HR.Novel Collagen-based Scaffolds For Hollow Organ Regeneration[M].[Sl:sn],2015.[58] Wojak-Cwik IM,Hintze V,Schnabelrauch M,et al.Poly (L‐lactide‐co‐glycolide) scaffolds coated with collagen and glycosaminoglycans: Impact on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(11):3109-3122.[59] Sajesh KM,Jayakumar R,Nair SV,et al.Biocompatible conducting chitosan/polypyrrole–alginate composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;62:465-471.[60] Au H,Rubio N,Shaffer MSP.Brominated graphene as a versatile precursor for multifunctional grafting.Chem Sci. 2018;9(1):209-17.[61] Fan Z,Wang J,Wang Z,et al.One-pot synthesis of graphene/hydroxyapatite nanorod composite for tissue engineering. Carbon.2014;66(1):407-416.[62] Chen C,Zhang Q,Ma T,et al.Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene/Copper Sulphide Nanocomposite for Supercapacitor. Journal of nanoscience and nanotechnology. 2017;17(4):2811-816.[63] Zhang B,Wang Y,Zhai G,et al.Biomedical applications of the graphene -based materials.Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;61(8): 953-964.[64] Holt BD,Wright ZM,Arnold AM,et al.Graphene oxide as a scaffold for bone regeneration.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol.2017;9(3).doi:10.1002/wnan.1437. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Review.[65] Jafari M,Paknejad Z,Rad MR,et al.Polymeric scaffolds in tissue engineering: a literature review.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2015;105(2):431-459.[66] Gong T,Xie J,Liao J,et al.Nanomaterials and bone regeneration. Bone Res.2015;3(3):123-129.[67] Wang CH,Guo ZS,Pang F,et al.Effects of Graphene Modification on the Bioactivation of Polyethylene-Terephthalate-Based Artificial Ligaments.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:15263-15276.[68] Zhang S,Yang Q,Zhao W,et al.In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility and osteogenesis of graphene-reinforced nanohydroxyapatite polyamide66 ternary biocomposite as orthopedic implant material. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:3179-3189. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||