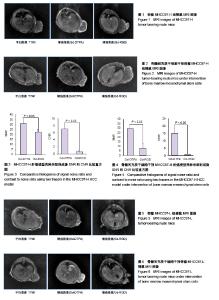
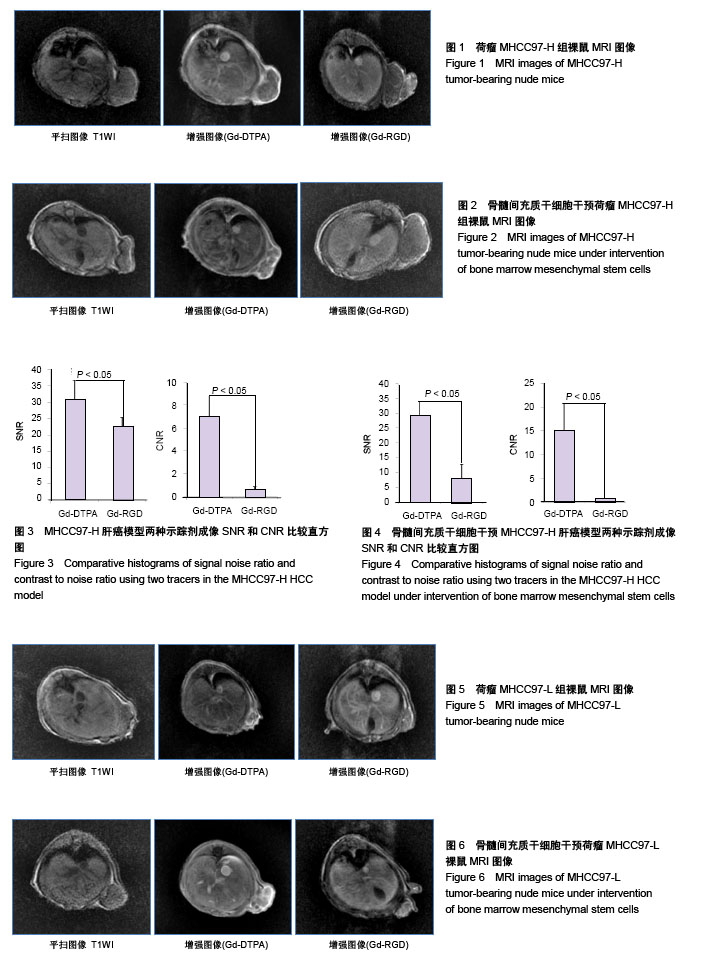
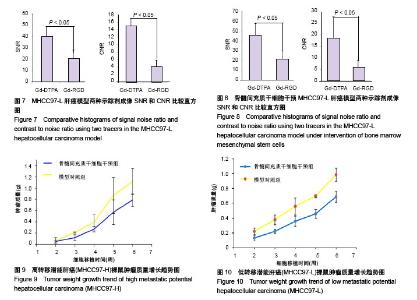
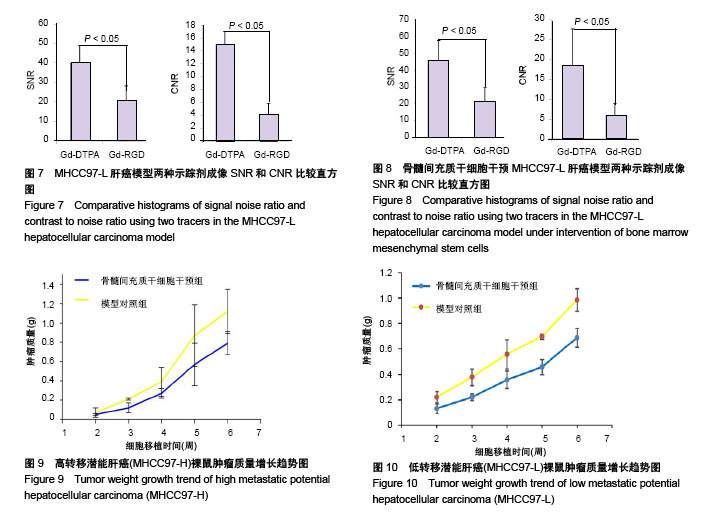
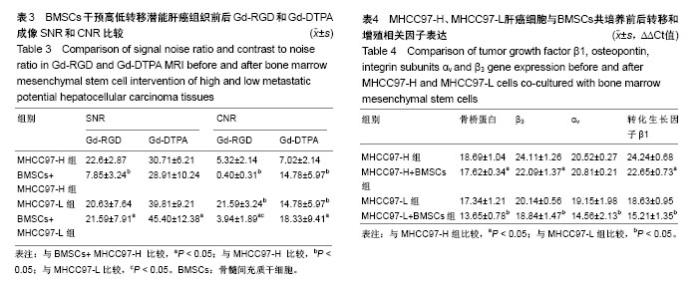
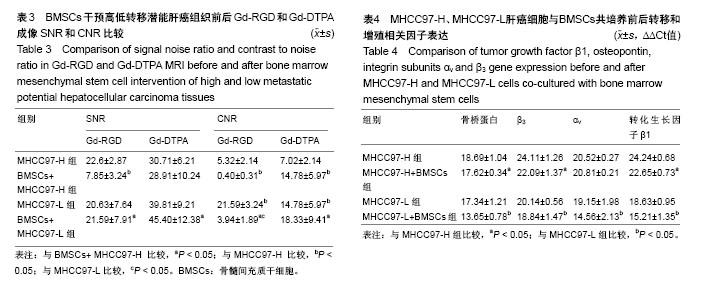
| [1] Niess H, Bao Q, Conrad C, et al. Selective targeting of genetically engineered mesenchymal stem cells to tumor stroma microenvironments using tissue-specific suicide gene expression suppresses growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2011; 254(5):767-774.[2] Liu C, Liu Y, Xu XX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance the metastasis of 3D-cultured hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:566.[3] Li T, Zhao S, Song B, et al. Effects of transforming growth factor β-1 infected human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on high- and low-metastatic potential hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20:56.[4] Li T, Song B, Du X, et al. Effect of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on high-potential hepatocellular carcinoma in mouse models: an intervention study. Eur J Med Res. 2013;18:34.[5] Leng L, Wang Y, He N, et al. Molecular imaging for assessment of mesenchymal stem cells mediated breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(19):5162-5170.[6] Supokawej A, Nimsanor N, Sanvoranart T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell in vitro labeling by hybrid fluorescent magnetic polymeric particles for application in cell tracking. Med Mol Morphol. 2015;48(4):204-213.[7] Haris M, Yadav SK, Rizwan A, et al. Molecular magnetic resonance imaging in cancer. J Transl Med. 2015;13:313. [8] Weber MR, Zuka M, Lorger M, et al. Activated tumor cell integrin αvβ3 cooperates with platelets to promote extravasation and metastasis from the blood stream. Thromb Res. 2016;140 Suppl 1:S27-36.[9] Chen L, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. Effect of integrin receptor-targeted liposomal paclitaxel for hepatocellular carcinoma targeting and therapy. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(1):77-84.[10] 张春丽,杨铭,王荣福. RGD肽与整合素αvβ3受体结合的构效关系及放射性标记配体的设计[J].肿瘤学杂志, 2009,15(1):76-81.[11] Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, et al. Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999;284(5417):1168-1170.[12] Sato Y, Araki H, Kato J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells xenografted directly to rat liver are differentiated into human hepatocytes without fusion. Blood. 2005;106(2):756-763.[13] Choi D, Kim JH, Lim M, et al. Hepatocyte-like cells from human mesenchymal stem cells engrafted in regenerating rat liver tracked with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008;14(1):15-23.[14] Snykers S, Vanhaecke T, Papeleu P, et al. Sequential exposure to cytokines reflecting embryogenesis: the key for in vitro differentiation of adult bone marrow stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells. Toxicol Sci. 2006;94(2):330-341.[15] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[16] Liu G, Fan X, Tang M, et al. Osteopontin induces autophagy to promote chemo-resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;383(2):171-182.[17] Chen WT, Shih TT, Chen RC, et al. Integrin αvβ3-targeted dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using a gadolinium- loaded polyethylene gycol-dendrimer-cyclic RGD conjugate to evaluate tumor angiogenesis and to assess early antiangiogenic treatment response in a mouse xenograft tumor model. Mol Imaging. 2012;11(4):286-300.[18] Durand DJ, Carrino JA, Fayad LM, et al. MRI pyschophysics: an experimental framework relating image quality to diagnostic performance metrics. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37(6):1402-1408.[19] Zhang L, Li HY, Yin XL, et al. Relative analysis of OPN and its related signal molecules in hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2011;19(1):48-51.[20] Zhang R, Pan X, Huang Z, et al. Osteopontin enhances the expression and activity of MMP-2 via the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23831.[21] Liu C, Liu DB, Long GX, et al. Specific targeting of angiogenesis in lung cancer with RGD-conjugated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles using a 4.7T magnetic resonance scanner. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(12):2242-2247. [22] Jarzyna PA, Deddens LH, Kann BH, et al. Tumor angiogenesis phenotyping by nanoparticle-facilitated magnetic resonance and near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging. Neoplasia. 2012;14(10): 964-973. |