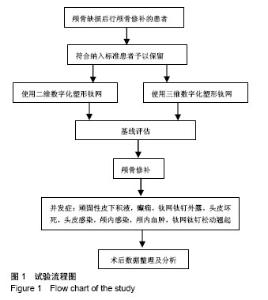
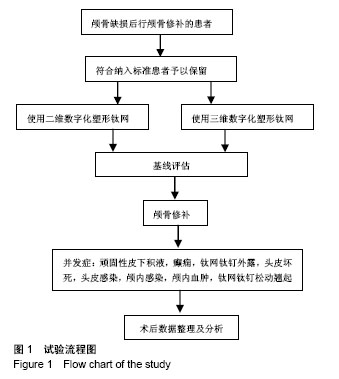
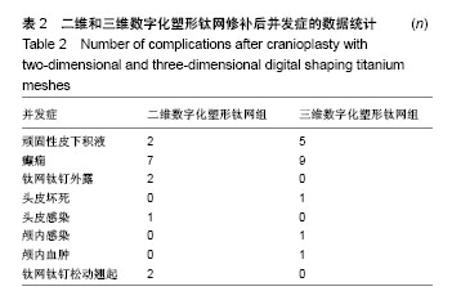
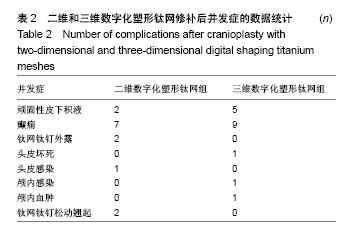
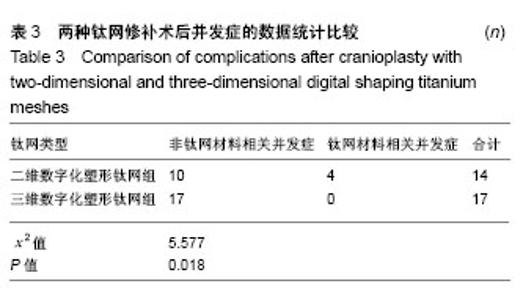
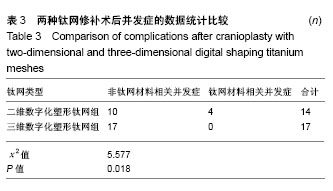
| [1] 庄亚瑟,方志成,刘伯毅,等.基于CT灌注评价早期钛网修补颅骨缺损对脑血流量及神经功能康复的影响:随机对照临床试验[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(26):4228-4233.[2] Krause-Titz UR,Warneke N,Freitab-Wolf S,et al.Factors influencing the outcome (GOS) in reconstructive cranioplasty. Neurosurg Rev. 2016; 39(1):133-139.[3] Andrew Post T,Blaine Hoshizaki Michael D,Gilchrist,et al.The influence of acceleration loading curve characteristics on traumatic brain injury.J Biomech.2014;47(5):1074-1081.[4] Coelho F,Oliveira AM,Paiva WS,et al.Comprehensive cognitive and cerebral hemodynamic evaluation after cranioplasty.Neuropsychialx Dis Treat. 2014;10:695-701.[5] Chen B,Li W,Chen D,et al.Partial titanium mesh explantation cured post-cranioplasty implant-associated scalp infection.J Clin Neurosci. 2017;44:196-202.[6] 张海防.不同材料修复颅骨缺损的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(34):5142-5148.[7] Fischer M,Joguet D,Robin G,et al.In situ elaboration of a binary Ti-26Nb alloy by selective laser melting of elemental titanium and niobium mixed powders.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;62:852-859.[8] Takematsu E,Katsumata K,Okada K,et al.Bioactive surface modification of Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr alloy through alkali solution treatments.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016; 62:662-667.[9] 胡均贤,徐春林,吴雅兰.高血压脑出血微创穿刺清除术后手术相关并发症及预后分析[J].临床外科杂志,2016,24(4):318.[10] Piedra MP,Ragel BT,Dogan A,et al.Timing of cranioplasty after decompressive craniectomy for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.J Neurosurg.2013;118(1):109-114.[11] Song J,Liu M,Mo X,et al.Beneficial impact of early cranioplasty in patients with decompressive craniectomy: evidence from transcranial Doppler ultrasonography.Acta Neurochir(Wien).2014;156(1):193-198.[12] Honeybul S,Ho KM.Decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury:The relationship between surgical complications and the prediction of an unfavourable outcome. Injury.2014;45(9):1332-1339.[13] Wang Y,Wang C,Liu Y.Chronic subdural haematoma evolving from traumatic subdural hydroma.Brain Ink. 2015;29(4): 462-465.[14] Songara A,Gupta R,Jain N,et al.Early Cranioplasty in Patients With Posttraumatic Decompressive Craniectomy and Its Correlation with Changes in Cerebral Perfusion Parameters and Neurocognitive Outcome.World Neurosurg. 2016;94: 303-308.[15] Xu H, Niu C, Fu X,et al.Early cranioplasty vs.late cranioplasty for the treatment of cranial defect:a systematic review.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;136:33-40.[16] Thavarajah D,De Lacy P,Hussien A,et al.The minimum time for eranioplasty insertion from craniectomy is six months to reduce risk of infection-a case series of 82 patients.Br J Neurosurg. 2012;26(1): 78-80.[17] Xu H,Niu C,Fu X,et al.Early cranioplasty vs.late cranioplasty for the treatment of cranial defect:a systematic review.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;136(9):33-40.[18] Williams LR,Fan KF,Bentley RP.Custom-made titanium cranioplasty: early and late complications of 151 cranioplasties and review of the literature.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2015;44(5):599-608.[19] 郑金玉,齐亮,陈中俊,等.三维钛网颅骨修补的手术技巧与并发症探讨[J].临床神经外科杂志,2014,11(6):464-466.[20] 周军格,邱勇,岑波,等.数字成型钛网颅骨修补后的皮下积液[J]中国组织工程研究,2014,18(8):1301-1306.[21] Zanaty M,Chalouhi N,Starke RM,et al.Complications following cranioplasty:incidence and predictors in 348 eases.J Neurosurg. 2015;123(1):182-188.[22] Lee L,Ker J,Quah BL,et al.A retrospective analysis and review of an institution’s experience with the complications of cranioplasty.Br J Neurosurg.2013;27(5):629-635.[23] Sobani ZA,Shamim MS,Zafar SN,et a1.Cranioplasty after decompressive craniectomy:An institutional audit and analysis of factors related to complications.Surg Neurol Int. 2011;2:123.[24] 向言召,闵怀伍.颅骨修补术后并发症分析及其防治的研究进展[J].中国综合临床,2012,28(10):1110-1112.[25] 黄学才,叶锦平.颅骨修补感染的风险因素分析[J].中华神经医学杂志, 2016,15(8):839-842.[26] 赵文校,阮玉山.三维塑形钛网颅骨修补术并发症分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2014,31(3):507-508. |