Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (26): 4156-4161.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0859
Previous Articles Next Articles
Suturing and bonding for repair of annulus fibrosus defects in goats
Wang Yu-peng, Yin He-ping, Wu Yi-min, Li Shu-wen, Du Zhi-cai, Bai Ming, Meng Ge-dong
- Department of Spine Microsurgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2018-04-16 -
Contact:Yin He-ping, Master, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Spine Microsurgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Yu-peng, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spine Microsurgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81260287; the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 2014MS0855
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yu-peng, Yin He-ping, Wu Yi-min, Li Shu-wen, Du Zhi-cai, Bai Ming, Meng Ge-dong. Suturing and bonding for repair of annulus fibrosus defects in goats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(26): 4156-4161.
share this article
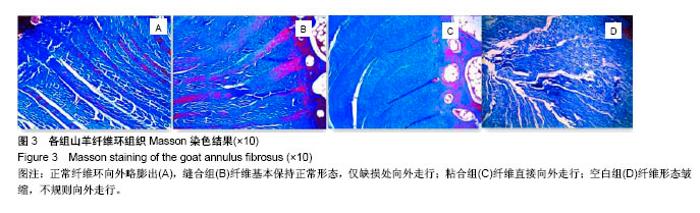
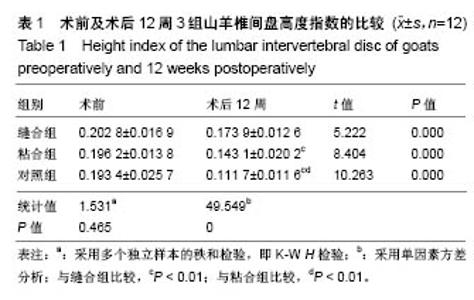
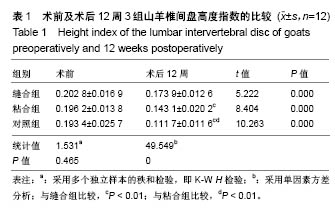
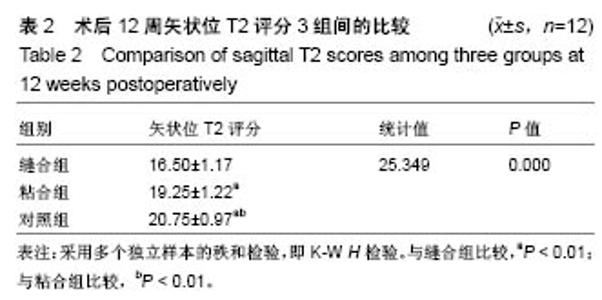
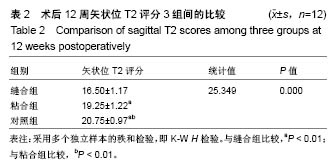
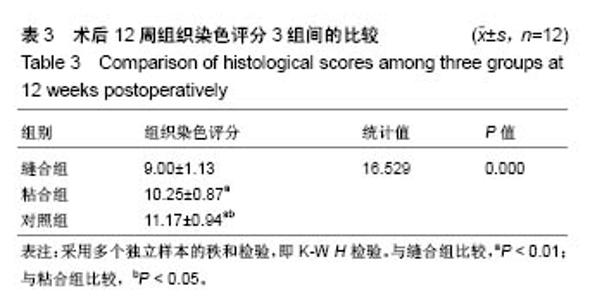
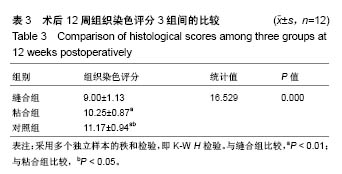
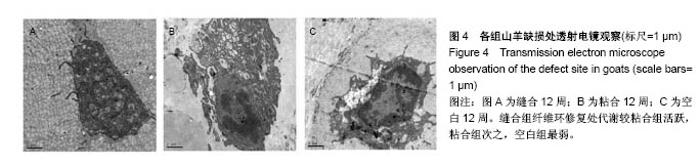
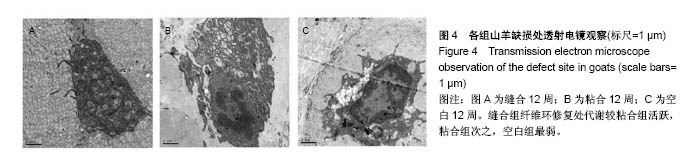
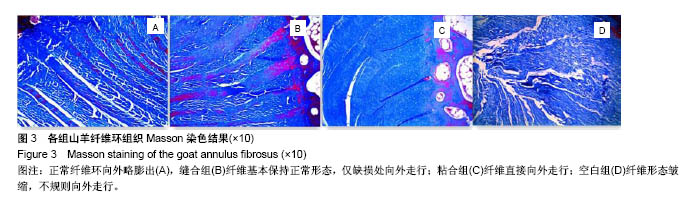
2.3 山羊组织学检查 缝合组终板处纤维粗大、形态规则。修复处纤维末端变细、逐渐小弧度向外倾斜、集中,外1/3处纤维聚集(图3)。缝合外层可见瘢痕组织及血管。内侧纤维与髓核界限可分辨。粘合组修复处可见较大间隙,纤维形态尚规则,大弧度向外倾斜,并向缺损处集中,粘合处纤维末端纤细,扭曲形态不规则,粘合缺损处纤维环表面可见瘢痕组织,内见血管。内层纤维环皱缩、形态迂曲,髓核可见裂隙,杂乱。对照组见纤维形态皱缩、杂乱、不规则、断裂,缺损处纤维逐渐靠拢但无明显集中趋势,内外层纤维环分界不清,杂乱无章。对3组组织学评分行多个独立样本的秩和检验,3组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),两两比较对资料秩转换,进行LSD-t 法检验,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3。"
| [1] Pattappa G,Li Z,Peroglio M,et al.Diversity of intervertebral disc cells: phenotype and function. J Anat. 2012;221(6): 480-496.[2] Jill PG Urban,Sally Roberts.Degeneration of the intervertebral disc.Arthritis Res Ther.2003;5(3):120-130.[3] Jacobs WC, Rubinstein SM, Willems PC,et al.The evidence on surgical interventions for low back disorders, an overview of systematic reviews.Eur Spine J.2013;22(9): 1936–1949.[4] Sedighi M,Haghnegahdar A.Lumbar Disk Herniation Surgery: Outcome and Predictors. Global Spine J. 2014;4(4): 233-244.[5] Dasenbrock HH, Juraschek SP, Schultz LR, et al.The efficacy of minimally invasive discectomy compared with open discectomy: a meta-analysis of prospective randomized controlled trials. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(5):452-462.[6] Soliman HM.Irrigation endoscopic discectomy: a novel percutaneous approach for lumbar disc prolapse. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(5):1037-1044.[7] Matsumoto M,Watanabe K,Hosogane N,et al.Recurrence of lumbar disc herniation after microendoscopic discectomy. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg.2013;74(4):222-227.[8] Cheng J, Wang H, Zheng W, et al.Reoperation after lumbar disc surgery in two hundred and seven patients. Int Orthop. 2013;37(8):1511-1517.[9] Grunert P,Borde BH,Hudson KD,et al.Annular repair using high-density collagen gel: a rat-tail in vivo model.Spine. 2014; 39(3):198-206.[10] Bailey A,Araghi A,Blumenthal S,et al.Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study of Anular Repair in Lumbar Discectomy: Two-Year Follow-up.Spine. 2013;38(14): 1161-1169.[11] Nerurkar NL,Elliott DM,Mauck RL.Mechanics of oriented electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for annulus fibrosus tissue engineering.J Orthop Res.2007;25(8):1018-1028. [12] DePalma MJ,Ketchum JM,Saullo TR,et al.Is the history of a surgical discectomy related to the source of chronic low back pain?.Pain Physician.2012;15(1):E53-58.[13] Grunert P,Borde BH,Hudson KD,et al.Annular repair using high-density collagen gel: a rat-tail in vivo model.Spine. 2014; 39(3):198-206.[14] Wang W,Wang Y,Deng G,et al.Transplantation of Hypoxic-Preconditioned Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Retards Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Enhancing Implanted Cell Survival and Migration in Rats.Stem Cells Int. 2018;2(14);7564159.[15] Pennicooke B,Hussain I,Berlin C,et al.Annulus Fibrosus Repair Using High-Density Collagen Gel: An In Vivo Ovine Model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2018;15;43(4):E208-E215. [16] Wang Y,Wang X,Shang J,et al.Repairing the ruptured annular fibrosus by using type I collagen combined with citric acid, EDC and NHS: an in vivo study.Eur Spine J. 2017;26(3):884-893.[17] Kazezian Z,Li Z,Alini M,et al.Injectable hyaluronic acid down-regulates interferon signaling molecules, IGFBP3 and IFIT3 in the bovine intervertebral disc.Acta Biomater. 2017;1; 52:118-129. [18] Li X,Zhang Y,Song B,et al.Experimental Application of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Repair of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus.Med Sci Monit. 2016;18; 22:4426-4430.[19] Xu X,Hu J,Lu H.Histological observation of a gelatin sponge transplant loaded with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with platelet-rich plasma in repairing an annulus defect.PLoS One.2017;8;12(2):e0171500.[20] Li Z, Lezuo P, Pattappa G,et al.Development of an ex vivo cavity model to study repair strategies in loaded intervertebral discs.Eur Spine J.2016;25(9):2898-2908.[21] Bateman AH,Balkovec C,Akens MK,et al.Closure of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc using a novel suture application device-in vivo porcine and ex vivo biomechanical evaluation.Spine J.2016;16(7):889-895.[22] Freeman B J,Kuliwaba J S,Jones CF,et al.Allogeneic Mesenchymal Precursor Cells Promote Healing in Postero-lateral Annular Lesions and Improve Indices of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in an Ovine Model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2016;41(17):1331-1339. [23] Borde B,Grunert P,Härtl R,et al.Injectable, high-density collagen gels for annulus fibrosus repair: An in vitro rat tail model.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(8):2571-2581.[24] Kang R,Li H,Lysdahl H,et al.Cyanoacrylate medical glue application in intervertebral disc annulus defect repair: Mechanical and biocompatible evaluation.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2017;105(1):14-20. [25] 王言,孙超,黄博,等.柠檬酸-EDC/NHS胶原凝胶修复破损纤维环[J].第三军医大学学报,2016,38(10):1078-1084.[26] Smith JW,Walmsley R.Experimental incision of the intervertebral disc.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1951;33(4):612-25.[27] Guo S,DiPietro LA.Factors Affecting Wound Healing.J Dent Res.2010;89(3): 219–229.[28] Guterl CC, Torre OM, Purmessur D, et al.Characterization of Mechanics and Cytocompatibility of Fibrin-Genipin Annulus Fibrosus Sealant with the Addition of Cell Adhesion Molecules.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(17-18):2536-2545.[29] Moreno-Arotzena O, Meier JG, Del Amo C,et al. Characterization of Fibrin and Collagen Gels for Engineering Wound Healing Models. Materials (Basel). 2015 ;8(4): 1636-1651. [30] Canonico S.The use of human fibrin glue in the surgical operations. Acta Biomed.2003;74(Suppl 2):21-5.[31] Amrani DL,Diorio JP,Delmotte Y.Wound healing.Role of commercial fibrine sealants.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936: 566-579.[32] Urquhart DM,Kurniadi I,Triangto K,et al.Obesity is associated with reduced disc height in the lumbar spine but not at the lumbosacral junction.Spine.2014;39(16):E962-966.[33] Siepe CJ,Heider F,Haas E,et al. Influence of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration on the outcome of total lumbar disc replacement: a prospective clinical, histological, X-ray and MRI investigation. Eur Spine J.2012; 21(11): 2287-2299.[34] Chen C,Huang M,Han Z,et al.Quantitative T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compared to Morphological Grading of the Early Cervical Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: An Evaluation Approach in Asymptomatic Young Adults.PLoS One.2014;9(2): e87856.[35] Yu LP, Qian WW, Yin GY, et al.MRI Assessment of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration with Lumbar Degenerative Disease Using the Pfirrmann Grading Systems.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e48074.[36] Chiang CJ,Cheng CK,Sun JS,et al.The effect of a new anular repair after discectomy in intervertebral disc degeneration: an experimental study using a porcine spine model.Spine. 2011; 36(10):761-769.[37] Bailey A,Araghi A,Blumenthal S,et al.Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study of Anular Repair in Lumbar Discectomy: Two-Year Follow-up.Spine. 2013;38(14): 1161-1169.[38] Sakai D,Mochida J,Yamamoto Y,et al.Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells embedded in Atelocollagen gel to the intervertebral disc: a potential therapeutic model for disc degeneration.Biomaterials.2003;24(20):3531-3541.[39] Sha'ban M,Yoon SJ,Ko YK,et al.Fibrin promotes proliferation and matrix production of intervertebral disc cells cultured in three-dimensional poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold.J Biomater Sci Polym.2008;19(9):1219-1237.[40] Hunter CJ,Matyas JR,Duncan NA.The three-dimensional architecture of the notochordal nucleus pulposus: novel observations on cell structures in the canine intervertebral disc.J Anat.2003;202(3): 279-291. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||