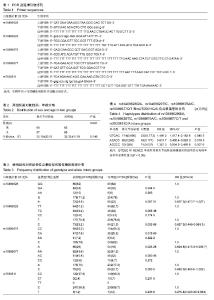
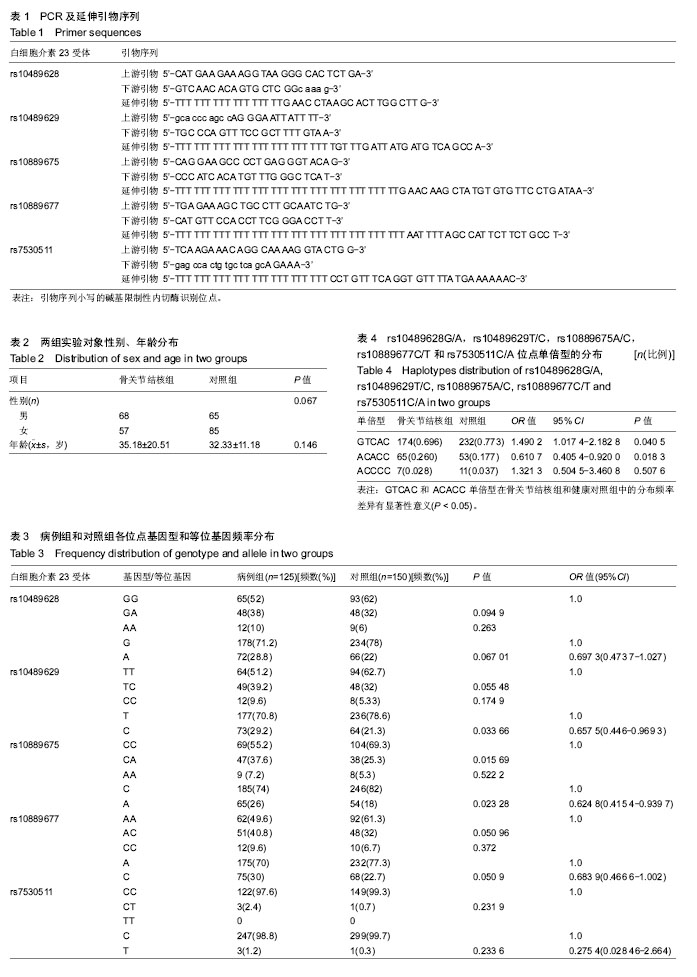
| [1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2014.[2] World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2016[OL]. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/zh/. 2016-10-13. [3] 陈伟,夏愔愔,李涛,等.2015年全球及中国结核病疫情形势分析[J].结核病与肺部健康杂志,2016,5(1):32-36.[4] Zhao Y1 Xu S, Wang L, et al. National survey of drug-resistant tuberculosis in China. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366(23):2161-2170. [5] 蒲新明,赛依旦•吐尔逊,阿尔泰,等.耐药结核病现状及研究进展[J].职业与健康,2016,32(5):717-720.[6] Charles JF, Aliprantis AO. Osteoclasts: more than 'bone eaters'. Trends Mol Med. 2014;20(8):449-459. [7] Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13(5):715-725.[8] Sun L, He C, Nair L, et al. Interleukin 12 (IL-12) family cytokines: Role in immune pathogenesis and treatment of CNS autoimmune disease. Cytokine. 2015;75(2):249-255. [9] Verreck FA, de Boer T, Langenberg DM, et al. Human IL-23-producing type 1 macrophages promote but IL-10-producing type 2 macrophages subvert immunity to (myco)bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(13): 4560-4565. [10] Zhang M, Wang Z, Graner MW, et al. B cell infiltration is associated with the increased IL-17 and IL-22 expression in the lungs of patients with tuberculosis. Cell Immunol. 2011; 270(2):217-223. [11] Peng LL, Wang Y, Zhu FL, et al. IL-23R mutation is associated with ulcerative colitis: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(3):4849-4863. [12] Bogunia-Kubik K, ?wierkot J, Malak A, et al. IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-23R Gene Polymorphisms in Polish Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2015;63(3):215-221. [13] Liu XH, Dai ZM, Kang HF, et al. Association of IL-23R Polymorphisms (rs6682925, rs10889677, rs1884444) With Cancer Risk: A PRISMA-Compliant Meta-Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(52):e2361. [14] Chen J, Lu Y, Zhang H, et al. A nonsynonymous polymorphism in IL23R gene is associated with risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Mol Carcinog. 2010;49(10): 862-868. [15] Ni B, Chen S, Xie H, et al. Functional polymorphisms in interleukin-23 receptor and susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese population. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e89111.[16] Chu H, Cao W, Chen W, et al. Potentially functional polymorphisms in IL-23 receptor and risk of esophageal cancer in a Chinese population. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(5): 1093-1097.[17] Xu Y, Liu Y, Pan S, et al. IL-23R polymorphisms, HBV infection, and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a high-risk Chinese population. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48(1):125-131.[18] Yao J, Liu L, Yang M. Interleukin-23 receptor genetic variants contribute to susceptibility of multiple cancers. Gene. 2014; 533(1):21-25. [19] 周莹,高琪乐,黄华艺,等.宿主基因多态性与结核易感性研究进展[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2016,26(2):477-480.[20] 乔宁宁,唐毓金,陈文成,等.红细胞补体受体1单核苷酸多态性与骨关节结核易感性的关联研究[J].免疫学杂志, 2016,32(7): 601-606.[21] 陆潞,韦贵将,谢克恭,等.白细胞介素12基因多态性与广西壮族人群骨关节结核易感性的关系[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(29):4290-4296.[22] 吴昭元,唐毓金,卓航宇,等.广西地区骨与关节结核患者外周血中白细胞介素-23的水平及临床意义[J].右江医学, 2017,45(2): 142-145.[23] Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J, et al. A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J Immunol. 2002; 168(11):5699-5708.[24] Watford WT, Hissong BD, Bream JH, et al. Signaling by IL-12 and IL-23 and the immunoregulatory roles of STAT4. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:139-156.[25] Lankford CS, Frucht DM. A unique role for IL-23 in promoting cellular immunity. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73(1):49-56.[26] Frucht DM. IL-23: a cytokine that acts on memory T cells. Sci STKE. 2002;2002(114):pe1.[27] Hao JS, Shan BE. Immune enhancement and anti-tumour activity of IL-23. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006;55(11): 1426-1431. [28] Gran B, Zhang GX, Rostami A. Role of the IL-12/IL-23 system in the regulation of T-cell responses in central nervous system inflammatory demyelination. Crit Rev Immunol. 2004;24(2): 111-128.[29] Ben-Selma W, Boukadida J. IL23R(Arg381Gln) functional polymorphism is associated with active pulmonary tuberculosis severity. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012;19(8): 1188-1192. [30] 阿不都吉力力•居来提.新疆维吾尔族人群IL-23R基因多态性与肺结核相关性研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2016. |