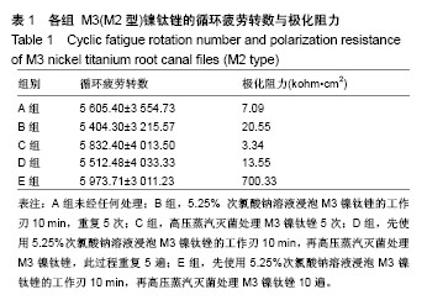
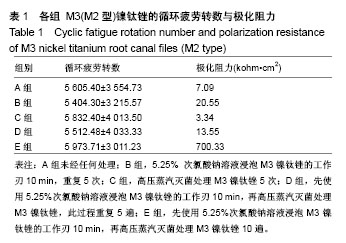
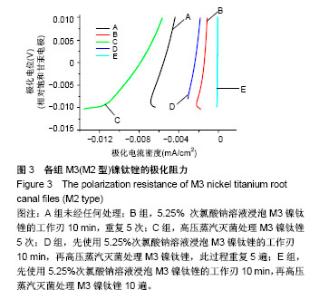
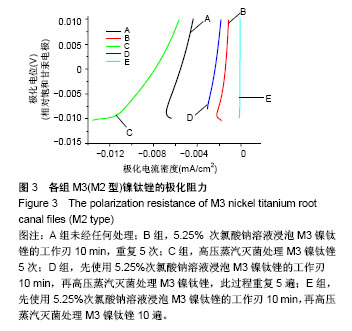
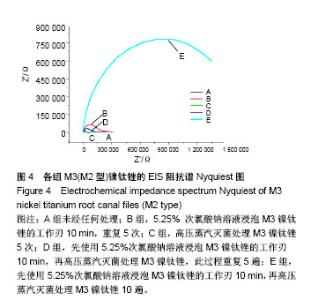
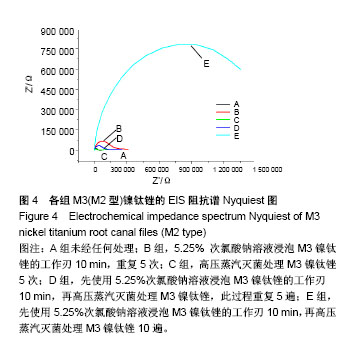
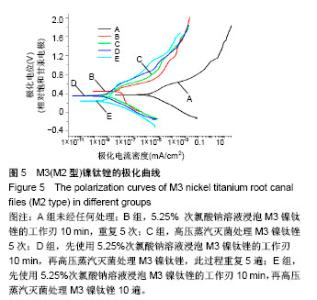
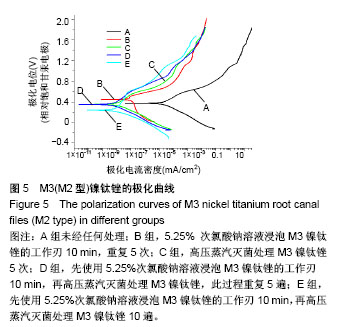
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (18): 2866-2871.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0765
Previous Articles Next Articles
The corrosion resistance of rotary nickel titanium root canal files
Hu Xin1, Wu Hui2, Wang Lei3, Zhang Qian1, Ning Jia1, Wu Wen-meng1
- 1Department of General Dentistry, Stomatological Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Tianjin Nankai Hospital, Tianjin 300100, China; 3Department of Stomatology, Tongzhou Xinhua Hospital, Beijing 101100, China
-
Received:2017-12-09Online:2018-06-28Published:2018-06-28 -
About author:Hu Xin, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of General Dentistry, Stomatological Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Foundation of the Stomatological Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, No. 2013yky02
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Xin, Wu Hui, Wang Lei, Zhang Qian, Ning Jia, Wu Wen-meng. The corrosion resistance of rotary nickel titanium root canal files[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2866-2871.
share this article
| [1] Nakagawa RK,Alves JL,Buono VT,et al.Flexibility and torsional behaviour of rotary nickel-titanium PathFile, RaCe ISO 10, Scout RaCe and stainless steel K-File hand instruments. Int Eendod J. 2014;47(3):290-297.[2] Walia HM,Brantley WA,Gerstein H.An initial investigation of the bending and torsional properties of Nitinol root canal files. J Endod.1988;14(7):346-351.[3] Miyara K,Yahata Y,Hayashi Y,et al.The influence of heat treatment on the mechanical properties of Ni-Ti file materials. Dent Mater J.2014;33(1):27-31.[4] Elnaghy AM.Cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Nex t nickel-titanium rotary files.Int Eendod J. 2014;47:1034-1039.[5] 顾永春,倪龙兴.2061支临床废弃手用ProTaper锉的损伤分析[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(5):528-532.[6] 韦宁.机用镍钛锉预备根管的效果观察[J].现代实用医学, 2013, 25(3):305-307.[7] Dagna A.Nickel-Titanium Single-file System in Endodontics.J Contemp Dent Pract.2015;16(10):834-839. [8] Yürüker S,Görduysus M,Küçükkaya S,et al.Efficacy of Combined Use of Different Nickel-Titanium Files on Removing Root Canal Filling Materials.J Endod. 2016;42(3): 487-493. [9] Duke 1,Shen Y,Zhou H,et al.Cyclic Fatigue of ProFile Vortex and Vortex Blue Nickel-Titanium Files in Single and Double Curvatures.J Endod.2015;41(10):1686-1690. [10] Aminsobhani M,Meraji N,Sadri E.Comparison of Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Five Nickel Titanium Rotary File Systems with Different Manufacturing Techniques.J Dent (Tehran).2015;12(9):636-646.[11] Agrawal V,Kapoor S,Patel M.Ultrasonic Technique to Retrieve a Rotary Nickel-Titanium File Broken Beyond the Apex and a Stainless Steel File from the Root Canal of a Mandibular Molar: A Case Report. J Dent (Tehran). 2015; 12(7):532-536.[12] Ha JH,Cheung GS,Versluis A,et al.'Screw-in' tendency of rotary nickel-titanium files due to design geometry.Int Endod J.2015;48(7):666-672. [13] Can Sa?lam B,Görgül G.Evaluation of Surface Alterations in Different Retreatment Nickel-Titanium Files: AFM and SEM Study.Microsc Res Tech.2015;78(5):356-362. [14] Nair AS,Tilakchand M,Naik BD.The effect of multiple autoclave cycles on the surface of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files: An in vitro atomic force microscopy investigation. J Conserv Dent. 2015;18(3):218-222. [15] Seago ST,Bergeron BE,Kirkpatrick TC,et al.Effect of repeated simulated clinical use and sterilization on the cutting efficiency and flexibility of Hyflex CM nickel-titanium rotary files.J Endod. 2015;41(5):725-728.[16] Kwak SW,Lee JY,Goo HJ,et al.Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section.Restor Dent Endod.2017;42(3):216-223.[17] Özyürek T,Y?lmaz K,Uslu G.The effects of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium instruments.Restor Dent Endod.2017;42(4):301-308.[18] Kesim B,Sagsen B,Aslan T.Evaluation of dentinal defects during root canal preparation using thermomechanically processed nickel-titanium files.Eur J Dent. 2017;11(2): 157-161.[19] Bennett J,Chung KH,Fong H,et al.Analysis of Surface Characteristics of ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next Instruments by Scanning Electron Microscopy.J Clin Exp Dent. 2017;9(7):879-885.[20] Özyürek T,Keskin NB,Furuncuo?lu F,et al.Comparison of cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium files: an examination using high-speed camera.Restor Dent Endod.2017;42(3):224-231.[21] Özyürek T,Tek V,Y?lmaz K,et al.Incidence of apical crack formation and propagation during removal of root canal filling materials with different engine driven nickel-titanium instruments.Restor Dent Endod.2017;42(4):332-341.[22] Adl A,Shahravan A,Farshad M,et al.Success Rate and Time for Bypassing the Fractured Segments of Four NiTi Rotary Instruments.Iran Endod J.2017;12(3):349-353.[23] Khabiri M,Ebrahimi M,Saei MR.The Effect of Autoclave Sterilization on Resistance to Cyclic Fatigue of Hero Endodontic File #642 (6%) at Two Artificial Curvature.J Dent (Shiraz).2017;18(4):277-281.[24] Iussif Mamede-Neto I,Borges AH,Guedes QA,et al.Root Canal Transportation and Centering Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Mandibular Premolars Assessed Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography.Open Dent J. 2017;11: 71-78.[25] Y?lmaz K,Özyürek T.Cyclic fatigue life of Tango-Endo, WaveOne GOLD,and Reciproc NiTi instruments.Restor Dent Endod.2017;42(2):134-139.[26] Forghani M,Hezarjaribi M,Teimouri H.Comparison of the shaping characteristics of Neolix and Protaper Universal systems in preparation of severely-curved simulated canals.J Clin Exp Dent.2017;9(4):556-559.[27] Aracena D,Borie E,Betancourt P,et al.Wear of the Primary WaveOne single file when shaping vestibular root canals of first maxillary molar.J Clin Exp Dent.2017;9(3):368-371.[28] Özyürek T,Y?lmaz K,Uslu G.Effect of adaptive motion on cyclic fatigue resistance of a nickel titanium instrument designed for retreatment.Restor Dent Endod.2017;42(1):34-38.[29] Maniglia-Ferreira C,de Almeida Gomes F,Ximenes T,et al.Influence of reuse and cervical preflaring on the fracture strength of reciprocating instruments.Eur J Dent. 2017;11(1): 41-47.[30] Çitak M,Özyürek T.Effect of different nickel-titanium rotary files on dentinal crack formation during retreatment procedure.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2017;11(2): 90-95.[31] Sa?lam BC,Kocak S,Kocak MM,et al.Effects of irrigation solutions on the surface of ProTaper instruments: a microscopy study.Microsc Res Tech.2012;75(11):1534-1538.[32] Pedullà E,Grande NM,Plotino G,et al.Cyclic fatigue resistance of two reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.Int Endod J. 2013;46(2): 155-159.[33] 胡坤娥,李昀生,谭荣,等.两种压力蒸汽灭菌器多次高压灭菌对镍钛锉表面形貌影响的AFM研究[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2011, 27(6):346-348.[34] 赵渤锐,胡欣,吴卉,等.高温高压蒸汽灭菌对不锈钢根管器械循环疲劳性能的影响[J].天津医药,2014,42(10):1037-1039.[35] Hilfer PB,Bergeron BE,Mayerchak MJ,et al.Multiple autoclave cycle effects on cyclic fatigue of nickel-titanium rotary files produced by new manufacturing methods.J Endod. 2011; 37(1):72-74.[36] Plotino G,Costanzo A,Grande NM,et al.Experimental evaluation on the influence of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue of new nickel-titanium rotary instruments.J Endod.2012;38(2):222-225.[37] Viana AC,Gonzalez BM,Buono VT,et al.Influence of sterilization on mechanical properties and fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments.Int Endod J. 2006;39(9):709-715.[38] Casper RB,Roberts HW,Roberts MD,et al.Comparison of autoclaving effects on torsional deformation and fracture resistance of three innovative endodontic file systems.J Endod.2011;37(11):1572-1575.[39] Braga LC,Faria SA,Buono VT,et al.Impact of heat treatments on the fatigue resistance of different rotary nickel-titanium instruments.J Endod.2014;40(9):1494-1497.[40] 陈建治,张富强.钛表面氧化物膜的形成与活化[J].国外医学:口腔医学分册,2006,33(1):48-50. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||