Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (10): 1599-1604.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0722
Previous Articles Next Articles
Current advances in the drug-loading preparation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres
- Department of Orthopaedics, Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Region, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2017-11-03Online:2018-04-08Published:2018-04-08 -
Contact:Zhen Ping, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopaedics, Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Region, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Qiu Xiao-ming, Master candidate, Department of Orthopaedics, Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Region, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81371983; the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, No. 1308RJZA146; the Medical and Health Research Foundation of PLA, No. CLZ14JB03
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qiu Xiao-ming, Zhen Ping, Li Song-kai. Current advances in the drug-loading preparation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(10): 1599-1604.
share this article
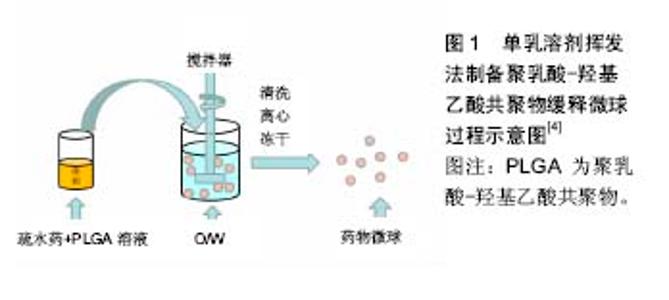
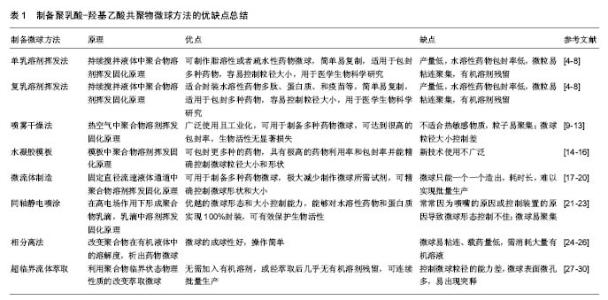
2.1 溶剂挥发法 2.1.1 单乳溶剂挥发法 单乳溶剂挥发法(图1)的代表方法是经典的水包油方法[4]。首先,将聚合物PLGA溶解在具有挥发特性的有机溶剂(二氯甲烷等)中,加入疏水性药物,将溶解有PLGA、药物的溶液乳化后,形成第一个油相也就是初乳相,加入含有乳化剂(聚乙烯醇等)的大量水中,在适当温度下经过一段时间(一般为4-6 h或者过夜)的搅拌,使搅拌形成乳滴中的有机溶剂挥发,PLGA硬化并将药物包裹于其中,形成微球,离心清洗负压冻干收集得到药物微球。 邵文尧等[5]通过改变内外水相体积比、搅拌转速剪切力,以明胶和吐温作为外水相乳化剂,制作出了形态光滑、分散性好、粒径为1.3 μm、包封率为52.42%的维A酸聚乳酸微球,并发现微球的平均粒径随着聚乳酸浓度的降低、剪切力增大呈减小趋势。而有机溶剂的挥发时间对粒径有直接影响,挥发速度快时,微球粒径增大且包封率提高,如果挥发时间长,内部药物会转移至外水相,包封率减低。"

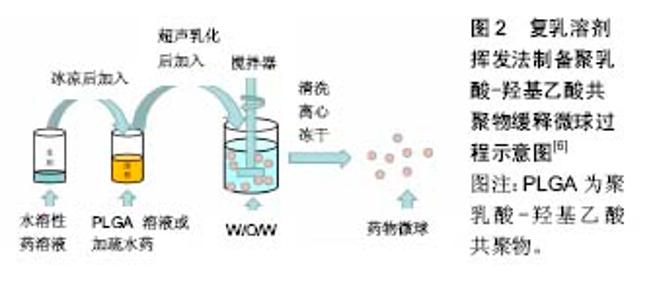
2.1.2 复乳溶剂挥发法 复乳溶剂挥发法(图2)的代表方法是经典水包油包水方法[6]。首先,将适量药物溶解在水相(去离子水),然后这种药物添加到溶解有PLGA的有机溶剂(二氯甲烷等)中,乳化后形成初乳。将这种油包水乳液添加聚乙烯醇水溶液再次乳化,搅拌挥发有机溶剂,最终产生微球。笔者在课题研究中发现用此法成功造出微球的关键是必须构建出稳定的初乳液,而要构成稳定乳液的条件是:油水相比例要大(9∶1),油相中聚合物的浓度要高(≥5%)。王飞[7]采用复乳溶剂挥发法,通过正交试验优化制备微球方案,最终制备出了粒径约 60 μm,包封率70%的盐酸万古霉素/PLGA载药微球,检测其体外释放时间超过30 d,兔椎间盘局部此载药微球较静脉注射药物更能有效治疗感染性椎间盘炎。何胤等[8]甚至用此方法制备出了三联抗结核菌药物PLGA微球,得出微球圆整均匀无粘连,粒径为10 μm大小,缓释微球中3种药物的包封率均超过了50%。前10 d药物缓释度达50%,3种药物的累计缓释度均超过了50%,且于缓释 50 d时释放药物各自浓度均大于最低抑菌浓度。 采用溶剂挥发法制备微球的过程中,聚合物浓度、溶剂选择和搅拌速度是影响微球包封率和粒径大小的主要因素。单乳溶剂挥发法经常用于制作脂溶性或者疏水性药物微球,而复乳溶剂挥发法则适合封装水溶性药物多肽、蛋白质和疫苗等。此法简单易复制,适用于包封多种药物,容易控制粒径大小,被大量用于医学生物科学研究,但也有很多不足之处,如产量低、水溶性药物包封率低、微粒易粘连聚集、有机溶剂残留等。 "

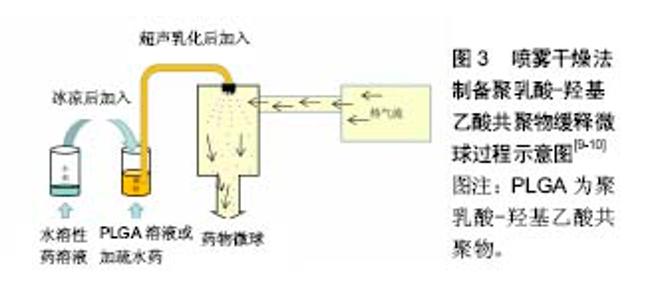
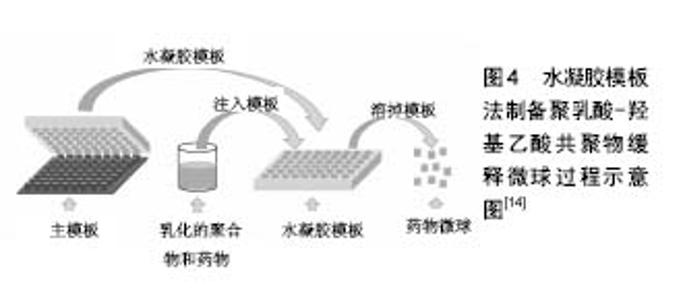
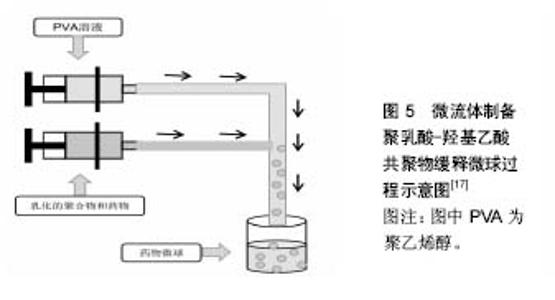
2.2 喷雾干燥法 喷雾干燥法(图3)是把药物溶液加入到聚合物PLGA溶液中并乳化,通过喷头将乳液喷入热空气流,乳滴在热空气的作用下溶剂蒸发,PLGA硬化成膜包裹形成微球[9-10]。 张丽梅[11]采用油包固体喷雾干燥法制备了异烟肼/聚乳酸微球,微球表面光滑,粒径为5.62 μm,包封率达89%,体外23 d药物累计释放70%,无明显突释;体内药物释放缓释效果良好,28 d肺内药物浓度为仍高于的最低抑菌浓度。施敏[12]用此法制备了聚乳酸-乙基纤维素为聚合物的罗红霉素中空微球,结果微球药物包封率均在90%以上,药物与聚合物的比例明显影响微球的药物释放机制,药物释放速率及释药率随着药物与聚合物的比例的增大而增多、加快。Zhu等[13]用喷雾干燥法和磁盘旋转的方法分别制作了粒径5 μm、33 μm,包封率85%、90%的艾塞那肽缓释微球,磁盘旋转相比较喷雾干燥法制作的微球圆整光滑,体外为期60 d的药物释放对比中,喷雾干燥法制作的微球20 d释放70%,45 d全部释放;磁盘旋转原理微球释放较平缓,20 d释放60%,60 d时释放完全。 喷雾干燥方法被广泛使用且可工业化,可用于制备多种药物微球,制备过程中无外水相的药物损失,可达到很高的包封率,生物活性无显著损失,但这种技术在制作微球时,微球易黏附在喷雾干燥器的内部墙壁且不适合对热敏感的药物。干燥温度在制备过程中的重要影响因素之一,高干燥温度易至微球变形、粒子易聚集;干燥温度过低时溶剂残余量大、微球粒径大小控制差。 2.3 水凝胶模板法 水凝胶模版法(图4)是利用凝胶的溶胶-凝胶可转换的物理特性,用事先制作好的硅模板为母模板制作出不溶于有机溶剂的水凝胶模板,在模板中加入乳化的聚合物药物溶液,待聚合物PLGA药物溶液中溶剂挥发后,溶解水凝胶模板,得到药物微球[14]。 齐献利[15]采用溶剂挥发法和水凝胶模板法制作出不同形状的PLGA微球,并对制作工艺进行改进,制作出了粒径2 μm、包封率最高可达95%的药物缓释微球,体外药物释放结果表明,溶剂挥发法制作的球形微球 24 h释放率显著高于水凝胶模板制作的圆柱体微球,水凝胶模板制作的圆柱体微球突释效应不明显。Lu等[16]通过孔径10 μm的水凝胶模板母板制作出粒径10 μm(测量偏离不超过10%)的利培酮/PLGA微球,与传统溶剂挥发法制作的利培酮/ PLGA微球进行了21 d的体外释放比较,21 d时两种微球释放率均为60%,但水凝胶模板法制作的微球释放更平稳。 水凝胶模板方法可包封更多种药物,具有极高的药物利用率和包封率并能精确控制微球粒径大小和形状,生产出各种理想粒径的微球,制作微球过程简单快速,但由于是新技术使用不广泛。 2.4 微流体制造 微流体制造是将乳化好的聚合物药物乳液经过微通道(图5),进入流动中的外水相,在微通道内形成微球,通过调整微通道直径的大小和改变外水相的流速,控制微球粒径大小,待微球中溶剂挥发后得到微球[17]。 Liu等[18]利用T型微通道装置,通过调节微通道中油相和水相的流速,制备出粒径150 μm、包封率为60%的Fe3O4/聚乳酸磁性微球,有癌症治疗和靶向药物输送的潜在用途。Leno等[19]利用溶剂挥发微流体方法经过改进微球药物配方,制备出了粒径145 μm、3 d释放率20%的地塞米松/PLGA缓释微球,可作为一种很有前途的局部眼部药物,减少滴眼药水频率,显著促进患者的依从性和严格的激素药物使用剂量。Xu等[20]用此方法制作出了粒径均一(28 μm)的布比卡因/PLGA缓释微球,并与传统溶剂挥发法制作出的11,41 μm布比卡因/PLGA缓释微球进行了比较,结果单纯溶剂挥发法制作的微球粒径大小不一,体外药物突释效应较微流体微球明显,且粒径越小这种突释越明显。 微流体制作方法可极大减少制作微球所需的试剂,可精确控制微球壳厚度、微球形状和大小、药物包封率,良好缓控药物释放速率。不足之处是微球只能一个一个造出,耗时长,难以实现批量生产。"

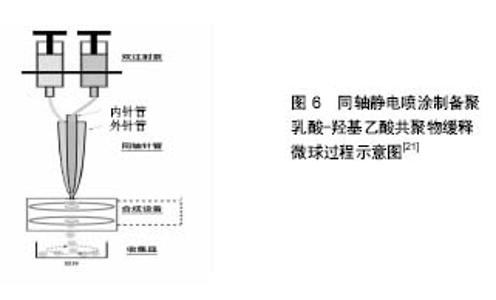
2.5 同轴静电喷涂 同轴静电喷涂(图6)方法:内针管内为PLGA丙酮药物溶液,外针管作为聚合物PLGA乙酸乙酯溶液,于喷嘴尖端在电极高电场的作用下形成乳滴,滴入聚乙烯醇水溶液中并磁力搅拌挥发溶剂,微球硬化,最后清洗冻干收集[21]。 Yuan等[21]研究发现,在同轴静电喷涂过程中改变正电压会导致不同流动模式,最终优化制备方案,制备出了2 μm左右、包封率最高达95.4%的姜黄素PLGA微球,体外第一个12 h药物释放10%,之后药物持续缓慢释放,30 d时累计释放60%,认为应用电电压和液体流速是影响微球的大小最重要因素。Zhang等[22]用改进同轴静电喷涂法制造出了针对年龄相关性黄斑变性的血管生长因子/PLGA微球,粒径为5 μm,包封率达70%,采用Rhodamine-6G模型作了25 d药物体外释放实验, 21 d药物释放为70%;体内实验以小鸡为模型,注射微球后评估炎症和视网膜细胞死亡,结果表明这种微球内包封的药物能够持续释放超过1个月,没有明显小胶质细胞反应或细胞死亡。Wang等[23]以牛血清白蛋白作为模型蛋白,用此法制作出了粒径23 µm的PLGA缓释微球,体外第1天药物释放超过30%,之后释放速度减慢,40 d时累计释放60%,结果认为同轴电喷射法是一个很好的制作缓释药物微球方法。 理论上来说,此方法能够对水溶性药物和蛋白质实现100%的封装,可有效保护生物活性,可控制微球形态和大小,但这些很大程度上都依赖于喷嘴的设计和制作过程中电场控制装置,常常因为喷嘴的原因或控制装置的原因导致微球形态控制不佳;常用的收集方法也易致微球发生聚集,且不能很好地促进壳硬化,致使乳滴中药物损失,包封率降低。 2.6 相分离法 相分离法是将亲水性药物溶于水,分散于聚合物溶液中;或将疏水性药物溶解、分散与有机聚合物溶液中,在持续搅拌中加入有机媒介,使聚合物溶解度降低形成载药乳滴,通过改变搅拌速率、温度、聚合物浓度可调节乳滴大小,再将此液体倒入萃取液中,最终洗涤、筛选、过滤、离心分离、冷冻干燥收集微 球[24]。 Awwad等[25]用此法制备了地塞米松/PLGA微球,粒径250-425 μm,球体圆整光滑,表面遍布0.2-1.0 μm大小孔隙,在体外眼睛房水流出模型实验显示,相分离法制作出的这种地塞米松/PLGA微球明显延长了药物释放。郁晓等[26]用此方法以丙酮为聚乳酸-聚乙二醇的溶剂,制备出了包封率50%、粒径122 nm的两性霉素B缓释微球,在不同溶剂、不同表面活性剂量、不同聚合物共聚比等方面研究了对微球成型及包封率的影响,结果显示微球粒径和包封率随聚合物分子量和聚乳酸与聚乙二醇比值的增大而增大。 相分离制备微球的过程较其他方法而言比较复杂,聚合物浓度、搅拌方式、搅拌速率、萃取液加入时机及加入量等均对微球形态和载药率、包封率产生影响,进而影响药物的释放特性。该法的优点是微球的成球性好,操作简单,缺点是微球易发生粘连、载药量低,需消耗大量的有机溶液,微球中有机溶剂残留。 2.7 超临界流体萃取 CO2在一定压力和温度下,由气体状态转变为液体状态,而这个气液相互转变的条件就叫做临界点。PLGA正常的玻璃化温度为40-60 ℃,但其在CO2超临界的环境下,塑化温度显著降低,无需溶剂就可溶解于CO2超流体中,再经喷头喷入到低于CO2临界点的气体环境中,聚合物溶解度迅速降低析出成微球[27]。 Falco等[28]使用超临界乳剂萃取法制备出了粒径为 1 μm和5 μm、包封率75%-80%之间的的醋酸氢化可的松/PLGA微球,可持续释放药物6-15 d,一种可注射的长期抗炎药物,且可根据治疗要求制备出不同载药率的微球。Della等[29]用超临界乳剂萃取法制作出了粒径 2 μm加载3 mg/g胰岛素和粒径3 μm加载6 mg/g胰岛素的PLGA微球,包封率均在60%以上,进行体外药物释放提示这种微球释放胰岛素平稳,对细胞的存活与增殖无影响。Della等[30]研究发现,临界乳剂萃取法可有效无污染的制作出包封率90%、粒径1.4 μm和 2.2 μm的特立帕肽、硫酸庆大霉素/PLGA微球,将不同微球在体外PBS中15 d检测其药物释放,结果证实微球壳聚糖涂层可明显降低药物微球的突释现象,可用于复杂骨折局部、骨感染治疗或老年患者的治疗。 超临界CO2流体萃取方法在制备微球的过程中无需加入有机溶剂,或经萃取后几乎无有机溶剂残留,可连续批量生产,但此法控制微球粒径的能力差,且微球表面微孔多,易出现突释现象。"

| [1]谭深,宋媛媛,张建安,等.聚乳酸载药微球的制备及改性的应用进展[J].化工新型材料,2015,43(9):231-233.[2]Sherwood JK,Riley SL,Palazzolo R,et al.A three-dimensional osteochondral composite scaffold for articular cartilage repair. Biomaterials.2002;23(24):4739-4751.[3]Park TG.Degradation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: effect of copolymer composition. Biomaterials.1995;16(15): 1123-1130.[4]李秀娟.乳化—减压溶剂挥发法制备聚合物微球的研究[D].天津大学, 2012.[5]邵文尧,何彩云,冯艳玲,等.乳化-溶剂挥发法制备聚乳酸载药微球[J].功能材料,2015,46(3):3121-3126.[6]李静涵.复乳溶剂挥发法制备利多卡因-PLGA缓释微球工艺改进[D].天津大学,2015.[7]王飞.万古霉素局部微球注射治疗耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染性椎间盘炎的实验研究[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2013,6(6):519-525.[8]何胤,杨宗强,王骞,等.复合三联抗结核药聚乳酸-羟基乙酸缓释微球的制备及体外释药特性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2015,25(5):456-461.[9]Wan F,Yang M.Design of PLGA-based depot delivery systems for biopharmaceuticals prepared by spray drying.Int J Pharm. 2015; 498(1-2):82-95.[10]Sosnik A,Seremeta KP.Advantages and challenges of the spray-drying technology for the production of pure drug particles and drug-loaded polymeric carriers.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2015;223:40-54.[11]张丽梅.异烟肼缓释微球的制备与评价研究[D].北京协和医学院中国医学科学院;北京协和医学院,中国医学科学院,清华大学医学部, 2013.[12]施敏.喷雾干燥法制备P(MMA-BA)、PLA/EC中空微球及其性能研究[D].湖南大学,2012.[13]Zhu C,Huang Y,Zhang X,et al.Comparative studies on exenatide-loaded poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microparticles prepared by a novel ultra-fine particle processing system and spray drying. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2015;132:103-110.[14]Malavia N,Reddy L,Szinai I,et al.Biodegradable sustained-release drug delivery systems fabricated using a dissolvable hydrogel template technology for the treatment of ocular indications.Inv Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(7):1296-1296.[15]齐献利.伊立替康微球突释效应的影响因素及控制方法[D].河北科技大学, 2015.[16]Lu Y,Sturek M,Park K.Microparticles produced by the hydrogel template method for sustained drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2013; 461(1-2):258-269.[17]魏文浩.单分散微球制备装置的构建及载COL海藻酸钙—壳聚糖复合微球制备的研究[D].中国海洋大学,2015.[18]Liu P,Zhong Y,Luo Y.Preparation of monodisperse biodegradable magnetic microspheres using a novel T-shaped microchannel reactor.Mater Lett.2014;(117):37-40.[19]Leon RAL,Somasundar A,Badruddoza AZM,et al.Microfluidic Fabrication of Multi‐Drug‐Loaded Polymeric Microparticles for Topical Glaucoma Therapy.Part Part Syst Char. 2015;32(5): 567-572.[20]Xu Q,Hashimoto M,Dang TT,et al.Preparation of Monodisperse Biodegradable Polymer Microparticles Using a Microfluidic Flow-focusing Device for Controlled Drug Delivery.Small. 2009; 5(13):1575.[21]Yuan S,Lei F,Liu Z,et al.Coaxial Electrospray of Curcumin-Loaded Microparticles for Sustained Drug Release.PLoS One. 2014;10(7): e0132609.[22]Zhang L,Si T,Fischer AJ,et al.Coaxial Electrospray of Ranibizumab-Loaded Microparticles for Sustained Release of Anti-VEGF Therapies.PloS One.2015;10(8):e0135608.[23]Wang Y,Yang X,Liu W,et al.Controlled release behaviour of protein-loaded microparticles prepared via coaxial or emulsion electrospray.J Microencapsul.2013;30(5):490.[24]Jain RA.The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide- co -glycolide)(PLGA) devices. Biomaterials. 2001;21(23):2475-2490.[25]Awwad S,Day RM,Khaw PT,et al.Sustained release ophthalmic dexamethasone: In vitro in vivo correlations derived from the PK-Eye. Int J Pharm.2017;522(1-2):119-127..[26]郁晓,任杰,任天斌,等.两性霉素B缓释微球的制备及缓释性能研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2007, 26(3):445-451.[27]忻娜.超临界CO_2抗溶剂法制备姜黄素及姜黄素-PLGA复合纳米颗粒[D].上海交通大学,2014.[28]Falco N,Reverchon E,Porta GD.Injectable PLGA/hydrocortisone formulation produced by continuous supercritical emulsion extraction. Int J Pharm. 2013;441(1-2):589-597.[29]Della PG,Falco N,Giordano E,et al.PLGA microspheres by Supercritical Emulsion Extraction: a study on insulin release in myoblast culture.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(16):1831.[30]Della PG,Campardelli R,Cricchio V,et al.Injectable PLGA/Hydroxyapatite/ Chitosan Microcapsules Produced by Supercritical Emulsion Extraction Technology: An In Vitro Study on Teriparatide/Gentamicin Controlled Release.J Pharm Sci. 2016;105(7):2164-2172.[31]安森博,汪龙,胡懿郃.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物载药微球性质及缓释行为的影响因素[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2016,36(13):1140-1144.[32]王芳,袁健,刘秀秀,等.PLGA基载药复合微球的制备及其释放性能[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,40(2):95-99.[33]程德林.骨修复聚合物微球/支架的表面形貌构建及其对干细胞影响规律研究[D].华南理工大学,2014.[34]孙爱平.喷雾干燥法制备聚乳酸载药微球及其药物释放行为研究[D].天津大学,2008.[35]缪世锋.基于超临界流体技术的银杏黄酮提取和微粒化过程研究[D].浙江大学,2011.[36]李俊起,朱爱臣,马丽霞,等.聚乳酸在3D打印医疗器械产品中的研究进展[J].生物医学工程研究,2016,35(4):309-312.[37]贺超良,汤朝晖,田华雨,等.3D打印技术制备生物医用高分子材料的研究进展[J].高分子学报,2013,57(6):722-732.[38]黄玉,孟令贤,侯一帆,等.小粒径PLGA纳米颗粒的制备[J].平顶山学院学报, 2015,30(2):44-49. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||