Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (10): 1580-1585.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0719
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances in the construction of a scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering containing homogeneous and stable carbon nanotubes
- Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Drug Target Research and Pharmacodynamics Evaluation, Institute of Brain Research, Department of Physiology, Basic Medicine School of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2017-11-06Online:2018-04-08Published:2018-04-08 -
Contact:Xi Jiao-ya, Associate professor, Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Drug Target Research and Pharmacodynamics Evaluation, Institute of Brain Research, Department of Physiology, Basic Medicine School of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Chen Dian, Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Drug Target Research and Pharmacodynamics Evaluation, Institute of Brain Research, Department of Physiology, Basic Medicine School of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31100828; Independent Innovation Project of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, No. 2013TS145, 2017KFYXJJ058; the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, No. 2016A165; the National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduates, No. HUST:201710487086
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Dian, Hu Qing-lin, Zhou Mei-ling, Hong Xian, Sun Xiao-xi, Xi Jiao-ya. Advances in the construction of a scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering containing homogeneous and stable carbon nanotubes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(10): 1580-1585.
share this article
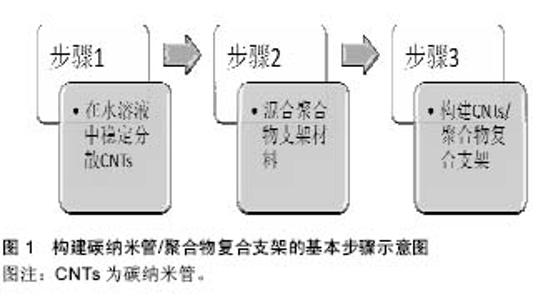
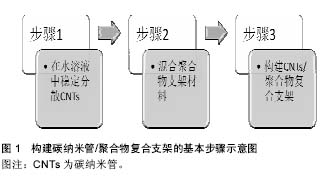
2.1 碳纳米管的一般理化特性 碳纳米管最初由日本科学家Iijima于1991年在使用高分辨透射电镜检验石墨电弧设备中产生的球状碳分子时意外发现的。碳纳米管为石墨片层卷曲形成的无缝圆柱管,是一种质量轻,六边形结构连接完美,径向尺寸为纳米量级,轴向尺寸为微米量级,管子两端基本上都封口的具有特殊结构的一维量子材料,其纵横比可超过1 000。碳纳米管是由呈六边形排列碳原子构成的数层到数十层同轴圆管,每石墨烯单层的C原子均为sp2杂化,相互之间以σ键相连,而层与层之间的C原子在垂直轴方向上则以π键相连,这赋予了碳纳米管独特的电学性质。碳纳米管的尾端有一个半富勒烯的帽状结构,该半富勒烯结构由于其更高的曲率而比碳纳米管本身具有更强的活性。碳纳米管管与管之间强大的范德华力会阻碍碳纳米管的均匀分散,因此,碳纳米管在聚合物支架中常聚合成束。另外,聚合物支架的性质,如湿度、极性、结晶度、溶解黏性等,也会影响碳纳米管在聚合物支架中形成网状结构,从而影响碳纳米管的功能[9-10]。 碳纳米管分为单壁碳纳米管和多壁碳纳米管。单壁碳纳米管,即由单片层的石墨烯卷曲形成的一个无缝圆柱状结构。单壁碳纳米管由科学家Iijima、Ichihashi和Bethune及其研究小组于1993年发现,其直径大小范围为0.4-3 nm。当单壁碳纳米管直径小于0.4 nm时,则会由于c-c键形成的曲率所产生的张力而具有热力学不稳定性。多壁碳纳米管,是由一系列同心嵌套的石墨烯片层组成,相毗邻的石墨烯片层之间存在有范德华力。多壁碳纳米管的径向尺寸可达10-20 nm,轴向尺寸则可达10-50 μm[9-10]。 2.2 构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的基本步骤 在心肌组织工程中,构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的基本步骤如图1所示,包括在水溶液中稳定分散碳纳米管、混合聚合物支架材料、构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架等3个步骤。"
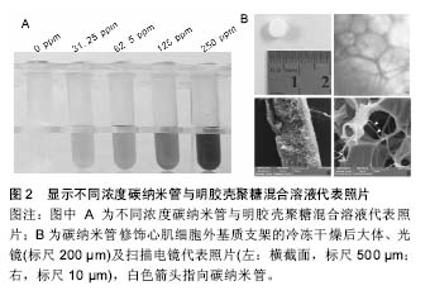
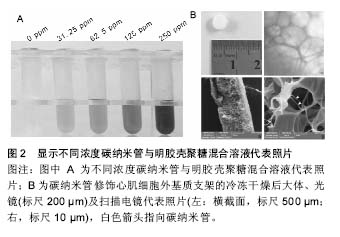
为构建碳纳米管/聚合物心肌组织工程复合支架,首先需要制备均匀分散有碳纳米管的水溶液。碳纳米管通过表面修饰的方式可一定程度稳定均一地溶解于水溶液中,所得到的碳纳米管溶液往往需要进一步的超声处理[4-5,8,11-15]。当高频的超声声波穿过溶液介质时,震荡的声波会将溶液中聚集成束的碳纳米管从表面开始进行一层层地剥离,以得到单个分散的碳纳米管。碳纳米管在经过表面修饰与超声处理后,通过进一步的离心,除去聚集在一起的碳纳米管(未能良好分散的碳纳米管)后,即可获得均质的碳纳米管水溶液。 混合聚合物支架材料,即将均一稳定分散有碳纳米管的水溶液与常见的具有一定生物活性的聚合物支架材料相混合,如聚DL-乳酸-聚乙二醇共聚物[4]、聚癸二酸丙三醇酯-明胶复合物[13]、明胶[5, 8]、Ⅰ型胶原[11]、聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺[16-17]、甲基丙烯酰明胶[12-13,15]、聚己内酯等[14]。研究者在这一步骤中,可根据实验要求,通过加入定量的聚合物支架材料来制备含不同碳纳米管浓度的复合支架。图2显示不同浓度碳纳米管与明胶壳聚糖混合溶液代表照片。"
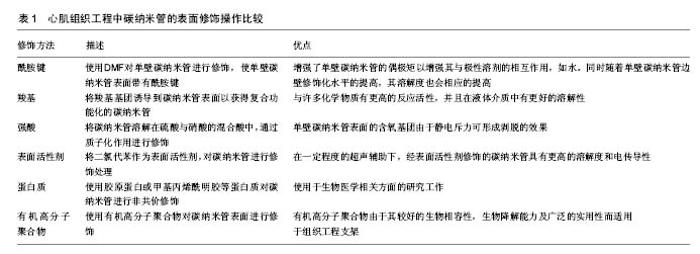
最后,使用不同的支架构建方法,将碳纳米管与聚合物支架材料构建为复合支架。常见的构建方法有冻干法与静电纺丝技术[4, 8,13-14,16]。有些研究者还通过使用物理(紫外线[12,15])或化学(戊二醛[5])交联来构建支架。 2.3 制备均一、稳定分散有碳纳米管水溶液的方法 如前所述,碳纳米管的高比表面积、高深宽比和表面的高低不平会导致碳纳米管聚集成束。近年来越来越多的数据表明,能否将碳纳米管在聚合物支架中均匀稳定的分散开来是构建理想的碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的关键之一。心肌组织工程中,对碳纳米管表面进行化学操作(共价修饰)或物理操作(非共价修饰)能够有效实现这个目标。心肌组织工程中碳纳米管的表面修饰操作比较见表1。 2.3.1 共价修饰 研究人员发现化学基团与碳纳米管表面进行共价结合时,会改变氢键的结构,从而修饰碳纳米管的堆叠性质,并且化学基团插入碳纳米管束之间,可促进碳纳米管束的解聚。这种化学共价修饰的方法极大程度地提高了碳纳米管在水溶液中的溶解度,并促进了碳纳米管在高分子聚合物支架中的均匀分散。碳纳米管含有富勒烯尾端一样的帽状结构,这一帽状结构易于氧化,因此碳纳米管容易被氧化成氧化型的碳纳米管。氧化型的碳纳米管可以进一步地与许多不同的功能基团相结合,包括酰胺键[4, 14, 16, 18-19]、酯类[20]、氨基[21]、羧基[13,15,18,22-24]、羟基[23],甚至可与有机金属化合物相结合等[25-26]。强酸也可以将碳纳米管直接质子化以克服管-管之间强大的的范德华力[12,27-30]。心肌组织工程中,目前文献报道中较为常用的共价修饰手段包括酰胺键[4,16]、羧基及强酸对碳纳米管的修饰[12-13,15,24,29]。 Liu等[4]使用二甲基甲酰胺对碳纳米管进行分散后,与聚DL-乳酸-聚乙二醇共聚物进行混合,采用静电纺丝技术构建碳纳米管/聚DL-乳酸-聚乙二醇共聚物复合支架。他们使用透射电镜与扫描电镜对复合支架进行观察,发现支架中的碳纳米管呈大量密集的有序分布,提示酰胺键的引入使碳纳米管得以有效的分散。这种复合支架可以维持新生大鼠心室肌细胞的活性,促进肌节形成以及心肌细胞的同步自主收缩活动。 Li等[16]同样使用二甲基甲酰胺对碳纳米管进行分散,并将碳纳米管与聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺混合构建复合支架。他们在使用透射电镜对碳纳米管水溶液进行观察时发现,碳纳米管均一稳定地相互分散开来,同时有串珠样结构形成。这种复合支架作为载体,极大地增强了梗死心肌处棕色脂肪组织来源的间充质干细胞的黏附与存活能力,有望增加心肌梗死的治疗效果。 Mooney[24]与Kharaziha等[13]均使用羧基修饰过的碳纳米管。Kharaziha等将碳纳米管与聚癸二酸丙三醇酯-明胶复合物混合,使用静电纺丝技术构建复合支架。他们通过透射电镜观察到平行排列的单个碳纳米管,说明使用羧基基团对碳纳米管进行修饰可以有效分散碳纳米管。同时,碳纳米管极大地提升了复合支架的导电性能与机械性能。这与Mooney等的研究结果相一致。Shin等[15]使用羧基基团修饰碳纳米管,并与甲基丙烯酰明胶一起构建复合支架,极大地改善了复合支架的电生理特性和机械性能。 Ahadian等[12]则将硝酸与硫酸以1∶3的比例混合后对碳纳米管进行质子化修饰,然后使用双向电泳技术将碳纳米管有序分散在GelMA中,并使用扫描电镜观察到有序排列的碳纳米管。这种复合支架可促进胚体向心肌细胞方向分化。 对碳纳米管进行共价修饰,极大地扩展了纳米材料的实用性。碳纳米管在经过共价修饰后,表面附着的基团能够与聚合物基质中的功能基团反应性地结合,从而提高碳纳米管的溶解性和分散程度。然而,碳纳米管的共价修饰方法也存在一定的局限性,如引起碳纳米管导电性能的损失。共价修饰会极大程度地影响碳纳米管的固有特性,从而进一步地影响整个碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的功能效果[31-32]。 2.3.2 非共价修饰 非共价修饰是另一种有效分散碳纳米管的方法。非共价修饰在改变碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架表面属性的同时,还保留着碳纳米管功能的完整性。这种修饰方式可在改变碳纳米管表面结构的基础上,不损害碳纳米管之间化学键的形成,因此广受人们的关注。近些年来,人们采用各式各样的方法来达到非共价修饰碳纳米管表面结构的目的,包括将表面活性剂作为碳纳米管的表面涂层[14,33-34],使用高分子聚合物[5,8,17,35]、脱氧核糖核苷酸[36]、多肽[37]、蛋白质[11,38-39]、卟啉化合物或离子液体等来修饰碳纳米管[40-43]。其中,心肌组织工程常使用表面活性剂[14,34]、蛋白质[11,39]、高分子聚合物等来分散碳纳米管[5,8,17]。 Namgung等[34]与Crowder等[14]均使用二氯代苯作为表面活性剂,来增加碳纳米管在水溶液中的溶解度与分散程度。有研究将碳纳米管与聚己内酯混合,使用静电纺丝技术构建复合支架。他们通过扫描电镜发现,经过二氯代苯处理过的碳纳米管直径更细,并有串珠样结构生成。相较于单纯的聚己内酯支架,这种复合支架杨氏模量与电传导性能均有所改善,并且能诱导人间充质干细胞的早期分化。 Sun等[11]使用Ⅰ型胶原蛋白来分散单壁碳纳米管,同时与Ⅰ型胶原蛋白一起构建复合支架。他们使用透射电镜观察发现,单壁碳纳米管在复合支架中均匀分散开来,并且以条束状结构出现。扫描电镜的结果则显示单壁碳纳米管在复合支架中形成了连续的网状结构。他们通过向聚合物支架中加入了具有优良电传导性能的单壁碳纳米管,促进了心肌细胞之间闰盘结构的形成。 Shin等[39]则是使用甲基丙烯酰明胶对碳纳米管进行表面修饰。他们将一薄层甲基丙烯酰明胶包裹在碳纳米管的表面,并同时与甲基丙烯酰明胶混合构建复合支架。同时使用了原子力显微镜对分散效果做出评估,即经过修饰的碳纳米管直径增加,比表面积减小,提示修饰后的碳纳米管吉布斯自由能降低,碳纳米管更稳定,更不容易发生团聚。碳纳米管在加入甲基丙烯酰明胶支架后,极大地增强了复合支架的机械性能,且这种复合支架有利于人间充质干细胞的生长,并可观察到细胞在生长过程中发生了形态的改变。 许多研究者还使用高分子聚合物来增加碳纳米管在水中的溶解度。如Pok等[8]选用壳聚糖来作为碳纳米管的稳定分散剂。他们在获得均一稳定分散有碳纳米管的水溶液后,对其进行紫外可见吸收光谱测量,发现经过壳聚糖修饰的碳纳米管比未经修饰的碳纳米管吸光度值更高,提示经过修饰的碳纳米管水溶液浓度更大,即碳纳米管在水溶液中分散效果更好。他们将碳纳米管与明胶混合,使用冻干法来构建复合支架,并将新生大鼠的心室肌细胞植入该复合支架。他们发现向明胶支架中引入分散良好的、高质量的单壁碳纳米管,可极大地提高支架的电传导性能,并且心室肌细胞的跳动频率近似于人在体心脏的跳动频率。 Zeng等[17]则构建了一个碳纳米管/聚丙烯酸复合支架,他们使用聚丙烯酸作为分散的试剂。而Zhou等[5]则使用聚氧乙烯-聚丙乙烯共聚物来分散单壁碳纳米管,并使用扫描电镜观察发现,单壁碳纳米管在支架中形成了均匀连续分布的网状结构,并且高度多孔化。他们将新生大鼠的心肌细胞与心肌成纤维细胞植入该复合支架,同时使用新生大鼠构建了心肌梗死模型。他们将支架移植到在体模型的梗死心肌处时,发现该支架有利于提高在体心功能,并且能与梗死心肌产生有效融合,从而有利于心肌组织的重塑。 "
| [1]Lozano R,Naghavi M,Foreman K,et al.Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (vol 380, pg 2095, 2012). Lancet.2013;381(9867): 628-628.[2]Amezcua R,Shirolkar A,Fraze C,et al.Nanomaterials for Cardiac Myocyte Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials.2016;6(7):133.[3]Chan V,Raman R,Cvetkovic C,et al.Enabling Microscale and Nanoscale Approaches for Bioengineered Cardiac Tissue.Acs Nano.2013;7(3):1830-1837.[4]Liu Y,Lu J,Xu G,et al.Tuning the conductivity and inner structure of electrospun fibers to promote cardiomyocyte elongation and synchronous beating.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69: 865-874.[5]Zhou J,Chen J,Sun H,et al.Engineering the heart: evaluation of conductive nanomaterials for improving implant integration and cardiac function.Sci Rep.2014;4:3733.[6]Chen YS,Tsou PC,Lo JM,et al.Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with interpenetrating multiwalled carbon nanotubes for cell sheet engineering.Biomaterials.2013;34(30):7328-7334.[7]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon nanotubes promote growth and spontaneous electrical activity in cultured cardiac myocytes.Nano Lett.2012;12(4):1831-1838.[8]Pok S,Vitale F,Eichmann SL,et al.Biocompatible Carbon Nanotube-Chitosan Scaffold Matching the Electrical Conductivity of the Heart.Acs Nano.2014;8(10):9822-9832.[9]Hopley EL,Salmasi S,Kalaskar DM,et al.Carbon nanotubes leading the way forward in new generation 3D tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv.2014;32(5):1000-1014.[10]Atif R, Inam F.Reasons and remedies for the agglomeration of multilayered graphene and carbon nanotubes in polymers. Beilstein J Nanotechnol.2016;7:1174-1196.[11]Sun H,Lü S,Jiang XX,et al.Carbon nanotubes enhance intercalated disc assembly in cardiac myocytes via the beta1-integrin-mediated signaling pathway.Biomaterials.2015;55:84-95.[12]Ahadian S,Yamada S,Ramón-Azcón J,et al.Hybrid hydrogel-aligned carbon nanotube scaffolds to enhance cardiac differentiation of embryoid bodies.Acta Biomater.2016;31:134-143.[13]Kharaziha M,Shin SR,Nikkhah M,et al.Tough and flexible CNT-polymeric hybrid scaffolds for engineering cardiac constructs. Biomaterials.2014;35(26):7346-7354.[14]Crowder SW,Liang Y,Rath R,et al. Poly(epsilon-caprolactone)- carbon nanotube composite scaffolds for enhanced cardiac differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanomedicine. 2013;8(11):1763-1776.[15]Shin SR,Jung SM,Zalabany M,et al.Carbon-nanotube-embedded hydrogel sheets for engineering cardiac constructs and bioactuators. Acs Nano.2013;7(3):2369-2380.[16]Li X,Zhou J,Liu Z,et al.A PNIPAAm-based thermosensitive hydrogel containing SWCNTs for stem cell transplantation in myocardial repair.Biomaterials.2014;35(22):5679-5688.[17]Zeng YZ,Lu JQ.Optothermally Responsive Nanocomposite Generating Mechanical Forces for Cells Enabled by Few-Walled Carbon Nanotubes.Acs Nano.2014;8(11):11695-11706.[18]Mananghaya M.Modeling of single-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with carboxylic and amide groups towards its solubilization in water.J Mol Liq.2015;212:592-596.[19]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon Nanotubes Instruct Physiological Growth and Functionally Mature Syncytia: Nongenetic Engineering of Cardiac Myocytes.Acs Nano. 2013; 7(7):5746-5756.[20]Bayazit MK,Coleman KS.Ester-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes via addition of haloformates.J Mater Sci. 2014;49(14):5190-5198.[21]Basiuk EV,Ramírez-Calera TJ,Meza-Laguna V,et al.Solvent-free functionalization of carbon nanotube buckypaper with amines. Appl Surf Sci.2015;357:1355-1368.[22]Wu, B,Li Y,Wang C,et al.High aqueous solubility of carboxylated-carbon nanotubes as support for PtRu nanoparticles: Enhanced dispersion and electrocatalytic performance.Int J Hydrogen Energy.2014;39(14):7318-7325.[23]Liang S,Li G,Tian R.Multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with a ultrahigh fraction of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups by ultrasound-assisted oxidation.JMater Sci.2015;51(7):3513-3524.[24]Mooney E,Mackle JN,Blond DJ,et al.The electrical stimulation of carbon nanotubes to provide a cardiomimetic cue to MSCs. Biomaterials.2012;33(26):6132-6139.[25]Kalinina I,Al-Hadeethi YF,Bekyarova E,et al.Solution-phase synthesis of chromium-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.Mater Lett.2015;142:312-316.[26]Gu SY,Gao XF,Zhang YH.Synthesis and characterization of solvent-free ionic molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) nanofluids. Mater Chem Phys.2015;149-150:587-593.[27]Parra-Vasquez AN,Behabtu N,Green MJ,et al.Spontaneous Dissolution of Ultralong Single- and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Acs Nano.2010;4(7):3969-3978.[28]Davis VA,Parra-Vasquez AN,Green MJ,et al.True solutions of single-walled carbon nanotubes for assembly into macroscopic materials.Nat Nanotechnol.2009;4(12):830-834.[29]Wese?ucha-Birczyńska A,Stodolak-Zych E,Turrell S,et al. Vibrational spectroscopic analysis of a metal/carbon nanotube coating interface and the effect of its interaction with albumin.Vib Spectrosc.2016;85:185-195.[30]Ramesh S,Ericson L,Davis VA,et al.Dissolution of pristine single walled carbon nanotubes in superacids by direct protonation.J Phys Chem B.2004;108(26):8794-8798.[31]Dyke CA,Tour JM.Covalent functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes for materials applications.J Phys Chem A. 2004;108(51):11151-11159.[32]Zhu WH,MinamiN,KazaouiS,et al.π-Chromophore-functionalized SWNTs by covalent bonding: substantial change in the optical spectra proving strong electronic interaction.J Mater Chem. 2004; 14(13):1924-1926.[33]Omastová M,Mi?ušík M,Fedorko P,et al.The synergy of ultrasonic treatment and organic modifiers for tuning the surface chemistry and conductivity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes.Surf Interface Anal.2014;46(10-11):940-944.[34]Namgung S,Baik KY,Park J,et al.Controlling the growth and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by the arrangement of individual carbon nanotubes.Acs Nano. 2011; 5(9):7383-7390.[35]Chen Z,Zhang J,Guo Y,et al.Effects of various factors on the modification of carbon nanotubes with polyvinyl alcohol in supercritical CO2 and their application in electrospun fibers.Chem Res Chin U.2014;30(4):690-697.[36]Umemura K.Hybrids of Nucleic Acids and Carbon Nanotubes for Nanobiotechnology. Nanomaterials.2015; 5(1):321-350.[37]Huang CW,Mohamed MG,Zhu CY,et al.Functional Supramolecular Polypeptides Involving pi-pi Stacking and Strong Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions: A Conformation Study toward Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Dispersion. Macromolecules. 2016; 49(15):5374-5385.[38]Nepal D,Geckeler KE.Proteins and carbon nanotubes: close encounter in water.Small.2007;3(7):1259-1265.[39]Shin SR,Bae H,Cha JM,et al.Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Hybrid Microgels as Scaffold Materials for Cell Encapsulation.Acs Nano. 2012;6(1):362-372.[40]Eguílaz M,Gutiérrez A,Rivas G.Non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with cytochrome c: Enhanced direct electron transfer and analytical applications.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2016;225:74-80.[41]Wei D,Kvarnström C,Lindfors T,et al.Electrochemical functionalization of single walled carbon nanotubes with polyaniline in ionic liquids. Electrochem commun.2007;9(2):206-210.[42]Roohi H,Khyrkhah S.Green chemical functionalization of single-wall carbon nanotube with methylimidazolium dicyanamid ionic liquid: A first principle computational exploration.J Mol Liq. 2015. 211(1):498-505.[43]Raiah K,Djalab A,Hadj-Ziane-Zafour A,et al.Influence of the hydrocarbon chain length of imidazolium-based ionic liquid on the dispersion and stabilization of double-walled carbon nanotubes in water.Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2015;469(6): 107-116. [1]Lozano R,Naghavi M,Foreman K,et al.Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (vol 380, pg 2095, 2012). Lancet.2013;381(9867): 628-628.[2]Amezcua R,Shirolkar A,Fraze C,et al.Nanomaterials for Cardiac Myocyte Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials.2016;6(7):133.[3]Chan V,Raman R,Cvetkovic C,et al.Enabling Microscale and Nanoscale Approaches for Bioengineered Cardiac Tissue.Acs Nano.2013;7(3):1830-1837.[4]Liu Y,Lu J,Xu G,et al.Tuning the conductivity and inner structure of electrospun fibers to promote cardiomyocyte elongation and synchronous beating.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69: 865-874.[5]Zhou J,Chen J,Sun H,et al.Engineering the heart: evaluation of conductive nanomaterials for improving implant integration and cardiac function.Sci Rep.2014;4:3733.[6]Chen YS,Tsou PC,Lo JM,et al.Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with interpenetrating multiwalled carbon nanotubes for cell sheet engineering.Biomaterials.2013;34(30):7328-7334.[7]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon nanotubes promote growth and spontaneous electrical activity in cultured cardiac myocytes.Nano Lett.2012;12(4):1831-1838.[8]Pok S,Vitale F,Eichmann SL,et al.Biocompatible Carbon Nanotube-Chitosan Scaffold Matching the Electrical Conductivity of the Heart.Acs Nano.2014;8(10):9822-9832.[9]Hopley EL,Salmasi S,Kalaskar DM,et al.Carbon nanotubes leading the way forward in new generation 3D tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv.2014;32(5):1000-1014.[10]Atif R, Inam F.Reasons and remedies for the agglomeration of multilayered graphene and carbon nanotubes in polymers. Beilstein J Nanotechnol.2016;7:1174-1196.[11]Sun H,Lü S,Jiang XX,et al.Carbon nanotubes enhance intercalated disc assembly in cardiac myocytes via the beta1-integrin-mediated signaling pathway.Biomaterials.2015;55:84-95.[12]Ahadian S,Yamada S,Ramón-Azcón J,et al.Hybrid hydrogel-aligned carbon nanotube scaffolds to enhance cardiac differentiation of embryoid bodies.Acta Biomater.2016;31:134-143.[13]Kharaziha M,Shin SR,Nikkhah M,et al.Tough and flexible CNT-polymeric hybrid scaffolds for engineering cardiac constructs. Biomaterials.2014;35(26):7346-7354.[14]Crowder SW,Liang Y,Rath R,et al. Poly(epsilon-caprolactone)- carbon nanotube composite scaffolds for enhanced cardiac differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanomedicine. 2013;8(11):1763-1776.[15]Shin SR,Jung SM,Zalabany M,et al.Carbon-nanotube-embedded hydrogel sheets for engineering cardiac constructs and bioactuators. Acs Nano.2013;7(3):2369-2380.[16]Li X,Zhou J,Liu Z,et al.A PNIPAAm-based thermosensitive hydrogel containing SWCNTs for stem cell transplantation in myocardial repair.Biomaterials.2014;35(22):5679-5688.[17]Zeng YZ,Lu JQ.Optothermally Responsive Nanocomposite Generating Mechanical Forces for Cells Enabled by Few-Walled Carbon Nanotubes.Acs Nano.2014;8(11):11695-11706.[18]Mananghaya M.Modeling of single-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with carboxylic and amide groups towards its solubilization in water.J Mol Liq.2015;212:592-596.[19]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon Nanotubes Instruct Physiological Growth and Functionally Mature Syncytia: Nongenetic Engineering of Cardiac Myocytes.Acs Nano. 2013; 7(7):5746-5756.[20]Bayazit MK,Coleman KS.Ester-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes via addition of haloformates.J Mater Sci. 2014;49(14):5190-5198.[21]Basiuk EV,Ramírez-Calera TJ,Meza-Laguna V,et al.Solvent-free functionalization of carbon nanotube buckypaper with amines. Appl Surf Sci.2015;357:1355-1368.[22]Wu, B,Li Y,Wang C,et al.High aqueous solubility of carboxylated-carbon nanotubes as support for PtRu nanoparticles: Enhanced dispersion and electrocatalytic performance.Int J Hydrogen Energy.2014;39(14):7318-7325.[23]Liang S,Li G,Tian R.Multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with a ultrahigh fraction of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups by ultrasound-assisted oxidation.JMater Sci.2015;51(7):3513-3524.[24]Mooney E,Mackle JN,Blond DJ,et al.The electrical stimulation of carbon nanotubes to provide a cardiomimetic cue to MSCs. Biomaterials.2012;33(26):6132-6139.[25]Kalinina I,Al-Hadeethi YF,Bekyarova E,et al.Solution-phase synthesis of chromium-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.Mater Lett.2015;142:312-316.[26]Gu SY,Gao XF,Zhang YH.Synthesis and characterization of solvent-free ionic molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) nanofluids. Mater Chem Phys.2015;149-150:587-593.[27]Parra-Vasquez AN,Behabtu N,Green MJ,et al.Spontaneous Dissolution of Ultralong Single- and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Acs Nano.2010;4(7):3969-3978.[28]Davis VA,Parra-Vasquez AN,Green MJ,et al.True solutions of single-walled carbon nanotubes for assembly into macroscopic materials.Nat Nanotechnol.2009;4(12):830-834.[29]Wese?ucha-Birczyńska A,Stodolak-Zych E,Turrell S,et al. Vibrational spectroscopic analysis of a metal/carbon nanotube coating interface and the effect of its interaction with albumin.Vib Spectrosc.2016;85:185-195.[30]Ramesh S,Ericson L,Davis VA,et al.Dissolution of pristine single walled carbon nanotubes in superacids by direct protonation.J Phys Chem B.2004;108(26):8794-8798.[31]Dyke CA,Tour JM.Covalent functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes for materials applications.J Phys Chem A. 2004;108(51):11151-11159.[32]Zhu WH,MinamiN,KazaouiS,et al.π-Chromophore-functionalized SWNTs by covalent bonding: substantial change in the optical spectra proving strong electronic interaction.J Mater Chem. 2004; 14(13):1924-1926.[33]Omastová M,Mi?ušík M,Fedorko P,et al.The synergy of ultrasonic treatment and organic modifiers for tuning the surface chemistry and conductivity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes.Surf Interface Anal.2014;46(10-11):940-944.[34]Namgung S,Baik KY,Park J,et al.Controlling the growth and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by the arrangement of individual carbon nanotubes.Acs Nano. 2011; 5(9):7383-7390.[35]Chen Z,Zhang J,Guo Y,et al.Effects of various factors on the modification of carbon nanotubes with polyvinyl alcohol in supercritical CO2 and their application in electrospun fibers.Chem Res Chin U.2014;30(4):690-697.[36]Umemura K.Hybrids of Nucleic Acids and Carbon Nanotubes for Nanobiotechnology. Nanomaterials.2015; 5(1):321-350.[37]Huang CW,Mohamed MG,Zhu CY,et al.Functional Supramolecular Polypeptides Involving pi-pi Stacking and Strong Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions: A Conformation Study toward Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Dispersion. Macromolecules. 2016; 49(15):5374-5385.[38]Nepal D,Geckeler KE.Proteins and carbon nanotubes: close encounter in water.Small.2007;3(7):1259-1265.[39]Shin SR,Bae H,Cha JM,et al.Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Hybrid Microgels as Scaffold Materials for Cell Encapsulation.Acs Nano. 2012;6(1):362-372.[40]Eguílaz M,Gutiérrez A,Rivas G.Non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with cytochrome c: Enhanced direct electron transfer and analytical applications.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2016;225:74-80.[41]Wei D,Kvarnström C,Lindfors T,et al.Electrochemical functionalization of single walled carbon nanotubes with polyaniline in ionic liquids. Electrochem commun.2007;9(2):206-210.[42]Roohi H,Khyrkhah S.Green chemical functionalization of single-wall carbon nanotube with methylimidazolium dicyanamid ionic liquid: A first principle computational exploration.J Mol Liq. 2015. 211(1):498-505.[43]Raiah K,Djalab A,Hadj-Ziane-Zafour A,et al.Influence of the hydrocarbon chain length of imidazolium-based ionic liquid on the dispersion and stabilization of double-walled carbon nanotubes in water.Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2015;469(6): 107-116. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||