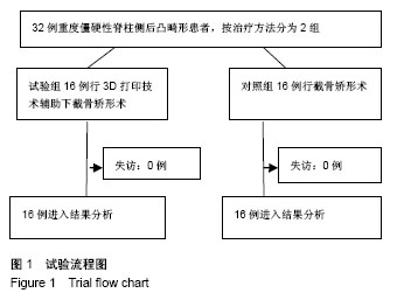
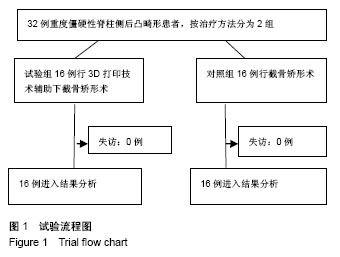
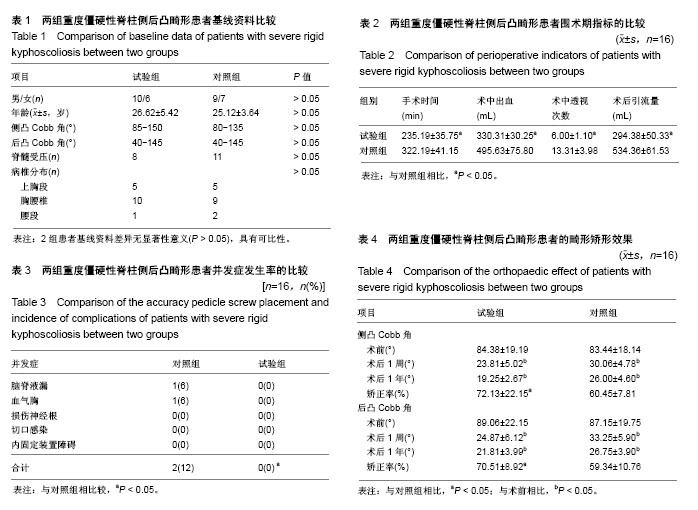
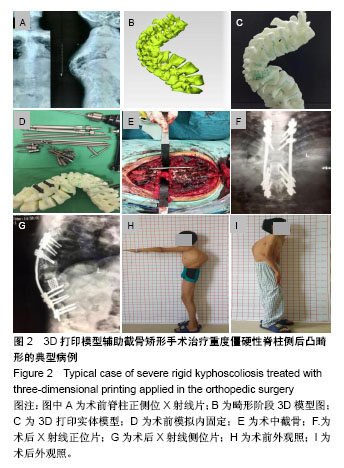
| [1] De Giorgi G, Stella G, Becchetti S, et al. Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation for the treatment of severe scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(1):8-15.[2] Tokunaga M, Minami S, Kitahara H, et al. Vertebral decancellation for severe scoliosis. Spine.2000;25(4): 469-474.[3] O’Brien MF, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Preoperative spinal canal investigation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis curves > or =70 degrees. Spine.1994;19(14): 1606-1610.[4] Rinella A, Lenke L, Whitaker C, et al. Perioperative halo-gravity traction in the treatment of severe scoliosis and kyphosis. Spine.2005;30(4):475-482.[5] Azmi H, Cagatay O, Mehmet A, et al. Posterior only pedicle screw in strumentation with intraoperative halo-femoral traction in the surgical treatment of severe scoliosis(> 100°). Spine. 2008;33(9):979-983.[6] Li M, Ni J, Fang X, et al. Single-staged anterior and posterior spinal fusion: a safe and effective alternative for severe and rigid adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in China. J Paediatr Child Health. 2009;45(5):246-253.[7] Luhmann SJ, Lenke LG, Kim YJ, et al. Thoracic adolescent idiopathicscoliosis curves between 70 degrees and 100 degrees: Is anterior release necessary? Spine. 2005; 30(18): 2061-2067.[8] 师继红,陆声,张元智,等.数字化脊柱椎弓根导航模板在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2):138-141.[9] 马立敏,张余,周烨,等.3D打印技术在股骨远端骨肿瘤的应用[J].中国数字医学2013,8(8):70-72. [10] 高方友,王曲,刘窗溪,等.个体化3D打印模型辅助后路螺钉内固定治疗颅颈交界区畸[J].中华神经外科杂志, 2013,29(9): 896-901.[11] Wasinpongwanich K, Paholpak P, Tuamsuk P, et al. Morphological study of subaxial cervical pedicles by using three-dimensional computed tomography reconstruction image. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(9):736-745.[12] Lee JY, Lee JW, Pang KM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of magnesium-based resorbable metallic screw system in a bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy model using three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(2):402.e1-13.[13] Yang M, Zeng C, Guo S, et al. Digitalized design of extraforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a computer-based simulation and cadaveric study. PLoS One. 2014;9(8): e105646.[14] Dankowski R, Baszko A, Sutherland M, et al. 3D heart model printing for preparation of percutaneous structural interventions: description of the technology and case report. Kardiol Pol. 2014;72(6):546-551. [15] 刘欣伟,于海龙,韩天宇,等.3D 打印技术在胫骨畸形矫形手术中的应用[J].解放军医药杂志,2015,27(11):26-28.[16] Wu AM, Lin JL, Kwan KYH, et al.3D-printing techniques in spine surgery: the future prospects and current challenges. Expert Rev Med Devices.2018;15(6):399-401.[17] Wu AM, Shao ZX, Wang JS, et al. The accuracy of a method for printing three-dimensional spinal models. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0124291..[18] Chen H, Wu D, Yang H, et al. Clinical use of 3D printing guide plate in posterior lumbar pedicle screw fixation. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:3948-3954.[19] 李明,刘洋,朱晓东,等.一期前路松解后路三维矫形治疗重度僵硬性脊柱侧凸[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(5): 271-275.[20] 黄紫房,杨军林,李佛保,等.后路全椎体截骨治疗重度脊柱畸形的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(11):967-971.[21] 董小通,解勇,蔡明,等.脊柱截骨矫形技术治疗成人复杂脊柱侧后凸畸形的安全性探讨[J].中国卫生标准管理,2016,7(14):5-12.[22] 司泽兵,吴继功,马华松,等.成人重度僵硬性脊柱侧后凸合并脊髓畸形的截骨手术治疗[J].颈腰痛杂志,2015,36(6):453-458.[23] Staff T, Eken T, Wik L, et al. Physiologic,demographic and mecha?nistic factors predicting New Injury Severity Score(NISS) in motor vehicle accident victims. Injury Inter J Care Injured.2014;45(1):9-15.[24] Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Pulmonary function in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis relative to the surgical procedure. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7): 1534 -1541.[25] Koumbourlis AC. Scoliosis and the respiratory system. Paediatric Resp. 2006;7(2): 152-160.[26] Vedantam R, Crawford AH. The role of preoperative pulmonary function tests in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis undergoing posterior spinal fusion. Spine, 1997, 22(23): 2731-2734.[27] Xie J, Lenke LG, Li T, et al. Preliminary investigation of high-dose Tranexamic Acid for controlling intraoperative blood loss in patients undergoing spine correction surgery. Spine J. 2015;15(4):647-654.[28] 曹云,羊东,彭五四,等.后路截骨联合椎弓根内固定矫形治疗僵硬性脊柱侧后凸畸形[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2016,19(4):391-394.[29] 宋林章,陈令斌,Song LZ,等.脊柱后路截骨术治疗局部严重后凸畸形的研究进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(2):123-124.[30] Auerbach JD, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Major complications and comparison between 3-column osteotomy techniques in 105 consecutive spinal deformity procedures. Spine.2012;37(14):1198-1210.[31] Carreon LY, Puno RM, Lenke LG, et al. Non-neurologic complications following surgery for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007;89 (11): 2427-2432.[32] Sansur CA, Smith JS, Coe JD, et al. Scoliosis research society morbidity and mortality of adult scoliosis surgery. Spine.2011;36(9):593-597.[33] Xie JM, Zhang Y, Wang YS, et al. The risk factors of neurologic deficits of one -stage posterior vertebral column resection for patients with severe and rigid spinal deformities. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(1):149-156.[34] Jeszenszky D, Haschtmann D, Kleinstück FS, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection in early onset spinal deformities. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(1):198-208.[35] Coe JD, Arlet V, Donaldson W, et al. Complications in spinal fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in the new millennium: a report of the Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality Committee. Spine. 2006;31(3): 345-349.[36] Adogwa O, Martin JR, Huang K, et al. Preoperative serum albumin level as a predictor of postoperative complication after spine fusion. Spine.2014;39(18): 1513-1519.[37] 于斌,仉建国,邱贵兴,等.后路顶点经椎弓根截骨术治疗重度僵硬性脊柱侧后凸畸形[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(35):2495-2499.[38] 马兆龙,邱勇,王斌,等.先天性脊柱侧凸患者中的脊髓畸形和脊椎畸形[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(8):588-592. |