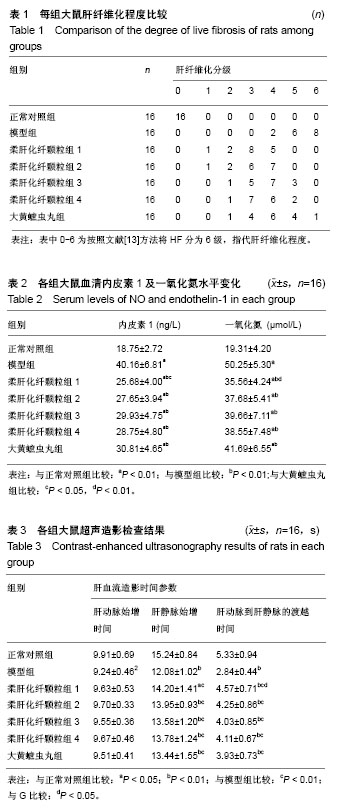
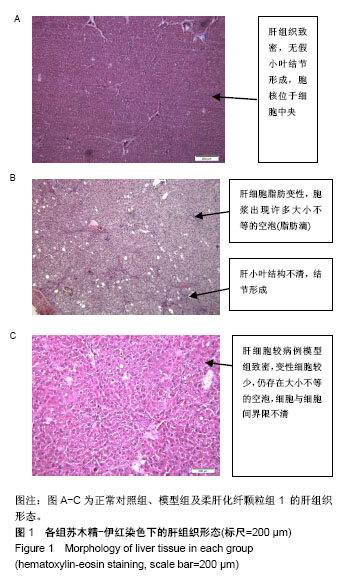
| [1] 曾民德.肝纤维化治疗对策[J].中华肝病杂志,2001,9(2):68.[2] Hao JH, Shi J, Ren WH, et al. Hepatic microcirculatory disturbances in patiens with chronic hepatitis B. Chin Med J (Engl). 2002;115:65-68. [3] 王希君,姚旌旗,彭娜.肝硬化时肝脏微循环障碍的特点及血流测定[J].咸宁学院学报(医学版),2010,24(1):362-364.[4] 王勇,丁体龙,马勇.等.肝窦病变对慢性乙型肝炎肝脏微循环障碍的影响[J].实用肝脏病学杂志,2012,15(4):309-311.[5] 覃伟华,王振常,黄晶晶.等.柔肝化纤颗粒对肝硬化失代偿期的临床疗效[J].中外医疗,2014,33(14):126.[6] 王振常,杨删,黄晶晶,等.柔肝化纤颗粒对CCL4诱导的肝纤维化大鼠肝脏MMP-2、TIMP-2的影响[J].疑难病杂志,2014,3(1):74-82.[7] 王振常,朱智德,杨删,等.柔肝化纤颗粒对肝纤维化大鼠ACT A表达的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2012,23(11):2705-2707.[8] 王振常,黄晶晶,夏兰,等.柔肝化纤颗粒联合普萘洛尔对肝硬化门脉高压患者血流动力学的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2013,24(3):726-726.[9] 林寿宁,黄贵华,王振常,等.壮肝逐瘀煎抗大鼠肝纤维化的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合脾胃病杂志,2004,12(5):267-270.[10] 林寿宁,王振常,刘强,等.壮肝逐瘀煎对肝纤维化大鼠肝转化生长因子β1及其I型和II型受体mRNA表达的影响[J].中国中西医结合消化杂志,2007, 15(4):211-213.[11] 林寿宁,王振常,何磊,等.壮肝逐瘀煎对肝纤维化大鼠TβRI/II、Smad3、Smad4和Smad7表达的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2008,16(10): 1105-1109.[12] 乔金莹,夏国园,董梁,等.实时组织弹性成像在CCl4诱导大鼠肝纤维化造模中的应用价值[J].中国超声医学杂志,2013,29(11):1031-1034.[13] 王宝恩,王惠吉.中药复方丹参不同剂型治疗肝纤维化的实验研究与临床观察[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,1993,(1):69-72.[14] 刘文娜.肝硬化门静脉高压症血流动力学变化的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(20):3431-3433.[15] 张景,张庆富.肝脏微循环的研究进展[J].中国微循环, 2007,11(4): 278-281.[16] Hsu SJ, Lin TY, Wang SS, et al. Endothelin receptor blockers reduce shunting and angiogenesis in cirrhotic rats. Eur J Clin Invest. 2016; 46(6):572-580. [17] 夏宣平,倪莉,施正超,等.肝硬化患者血一氧化氮和内皮素-1的变化及其临床意义[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(7):1063-1065.[18] 宋丽秀,陈卫刚,郑勇,等.内源性一氧化氮/一氧化氮合酶体系及一氧化碳/血红素合酶体系对大鼠肝硬化门静脉压力的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2014,22(19):2686-2691.[19] 张小华,黄玉荣,杨娟.内皮素-1在肝纤维化和肝硬化中的变化及意义[J].长江大学学报(自科版),2014,11(27):10-16.[20] 杨季红,马巍,马静,等.血清内皮素-1与肝硬化门脉高压的关系[J].河北医药,2010,32(23):3296-3297.[21] Searle J, Mendelson R, Zelesco M, et al. Non-invasive prediction of the degree of liver fibrosis in patients withhepatitis C using an ultrasound contrast agent. A pilot study. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2008;52(2):130-133. [22] Li N, Ding H, Fan P, et al. Intrahepatic transit time predicts liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: quantitative assessment with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Ultra Med Biol. 2010;36(7): 1066-1075. [23] 包中涛,叶真,古立娟,等.肝动静脉渡越时间及剪切波速评估肝纤维化程度的对比研究[J].临床超声医学杂志,2014,16(2):10-13. |